Current issue
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Current issue
Editorial
- Research ethics and emerging challenges in the era of coexistence with artificial intelligence
- Heeseung Choi, Youn Sun Hwang, Youngrye Park
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):489-491. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25138
- 982 View
- 75 Download

Invited Paper
- Lessons from the US Advanced Practice Registered Nurse system
- Eun-Ok Im, Dongmi Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):492-505. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25120
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This review compares the development of South Korea’s Advanced Practice Registered Nurse (APRN) system the well-established APRN system in the United States and provides recommendations for future improvements to the APRN system in South Korea.
Methods
To compare the APRN systems between the two countries, an integrative literature review was conducted using multiple databases and professional nursing organization documents and reports from both the United States and South Korea.
Results
Issues were identified in five major domains: (1) research evidence, (2) education and training, (3) the scope of practice, (4) financial mechanisms, and (5) public awareness and acceptance.
Conclusion
Recommendations are made in four areas: (1) building evidence to support APRN programs; (2) strengthening APRN education; (3) establishing legal support and reimbursement mechanisms; and (4) improving public awareness and acceptance of APRNs.
- 780 View
- 118 Download

Research Papers
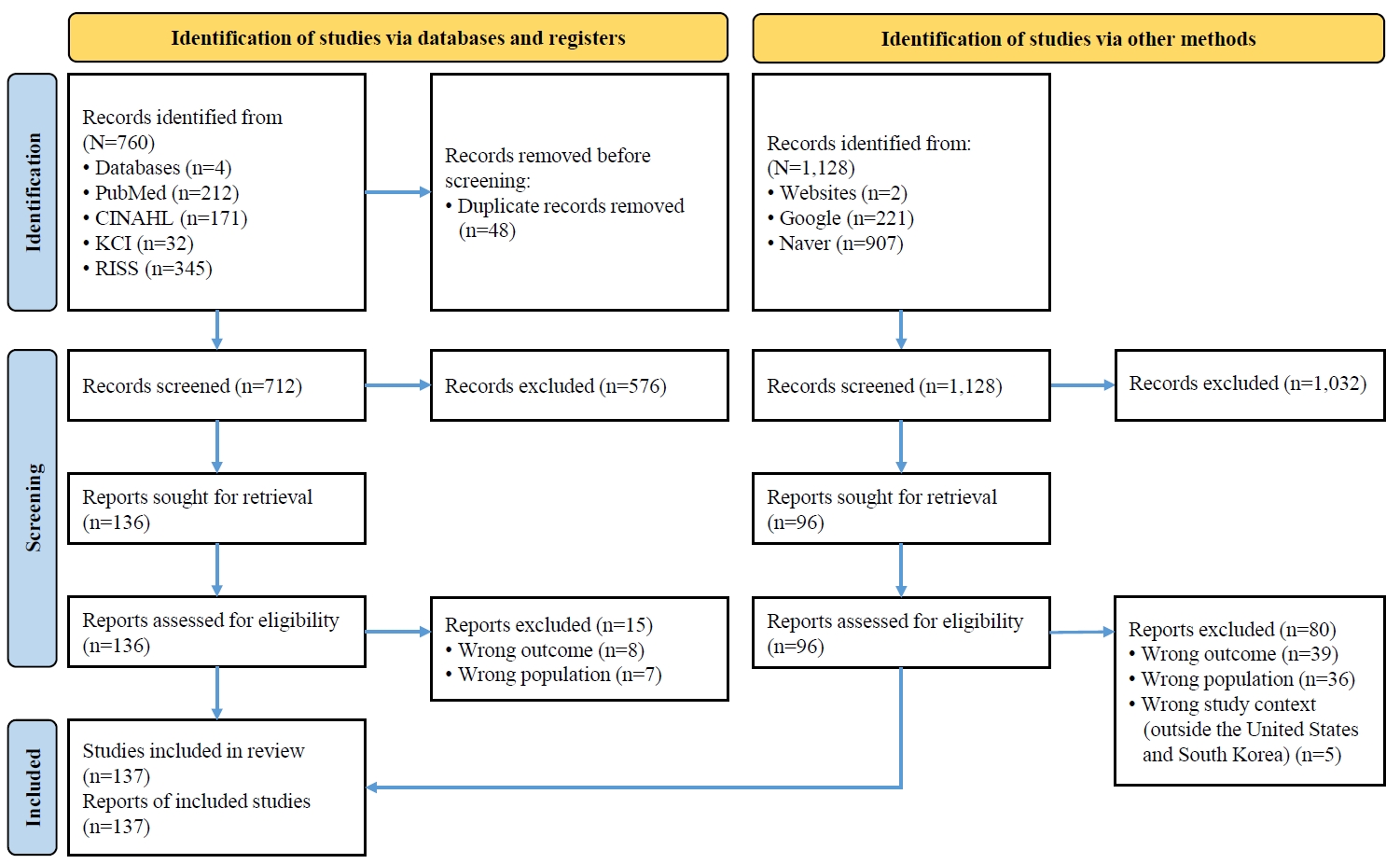
- Effects of an integrated healthcare program for postpartum women: a quasi-experimental study
- Eun Suk Hwang, Ju-Hee Nho
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):506-518. Published online November 7, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25076
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and evaluate an integrated healthcare program for postpartum mothers based on Cox’s interaction model of client health behavior.
Methods
A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used. The integrated healthcare program was administered 6 times over 2 weeks to postpartum mothers in the experimental group (n=21), while the control group (n=23) received standard care. Data were collected from June 3 to July 15, 2024, through structured questionnaires measuring postpartum fatigue, depression, marital intimacy, and mother-infant attachment. Analyses were conducted using IBM SPSS ver. 23.0.
Results
The experimental group showed significantly lower postpartum fatigue (Z=–2.00, p=.023), a significantly proportion of improvement in postpartum depression (χ2=10.32, p=.012), and a significant increase in mother-infant attachment (t=1.70, p=.048) compared to the control group. However, there was no significant difference in marital intimacy between groups (Z=–0.46, p=.326).
Conclusion
These results suggest that an integrated health management program including physical health, psychological stability, and relational support can be used as an effective nursing intervention to promote health in postpartum mothers. Therefore, additional research is warranted that expands and applies integrated programs for postpartum mothers in various environments in postpartum care centers and communities.
- 1,441 View
- 181 Download

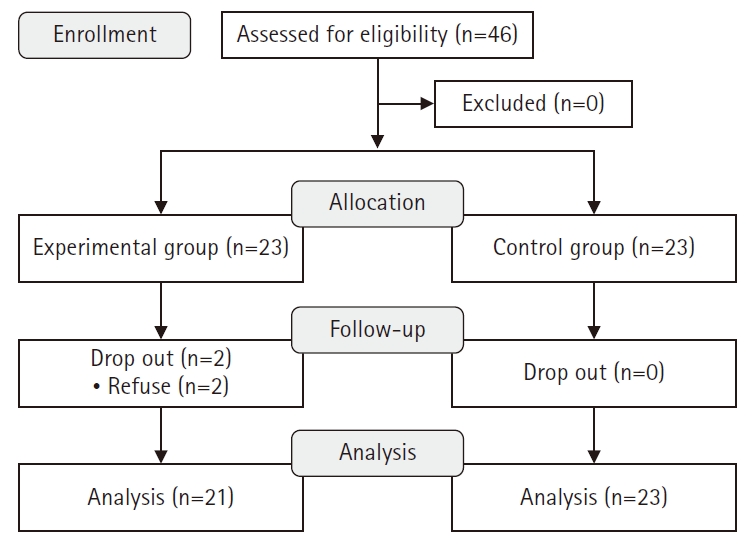
- Development of a predictive model for exclusive breastfeeding at 3 months using machine learning : a secondary analysis of a cross-sectional survey
- Hyun Kyoung Kim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):519-527. Published online October 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25086
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a machine learning model to predict exclusive breastfeeding during the first 3 months after birth and to explore factors affecting breastfeeding outcomes.
Methods
Data from 2,579 participants in the Korean Early Childhood Education & Care Panel between March 1 and June 3, 2025 were analyzed using Python version 3.12.8 and Colab. The dataset was split into training and testing sets at an 80:20 ratio, and five classifiers (random forest, logistic regression, decision tree, AdaBoost, and XGBoost) were trained and evaluated using multiple performance metrics and feature importance analysis.
Results
The confusion matrix of the random forest classifier model demonstrated strong performance, with a precision of 86.6%, accuracy of 84.8%, recall of 96.8%, F1-score of 91.9%, and an area under the curve of 86.0%. Twenty-one features were analyzed, from which feeding plan, breastfeeding at 1 month, marriage period, maternal prenatal weight, self-respect, alcohol consumption, grit, value placed on children, maternal age, and depression emerged as important predictors of exclusive breastfeeding in the first 3 months.
Discussion
A robust model was developed to predict exclusive breastfeeding that identified feeding planning and breastfeeding at 1 month as the most influential predictors. The model could be implemented in clinical and community settings to guide tailored breastfeeding support strategies, coupled with the integration of maternal self-respect, grit, and the value placed on children in counseling programs to promote exclusive breastfeeding.
- 1,516 View
- 137 Download

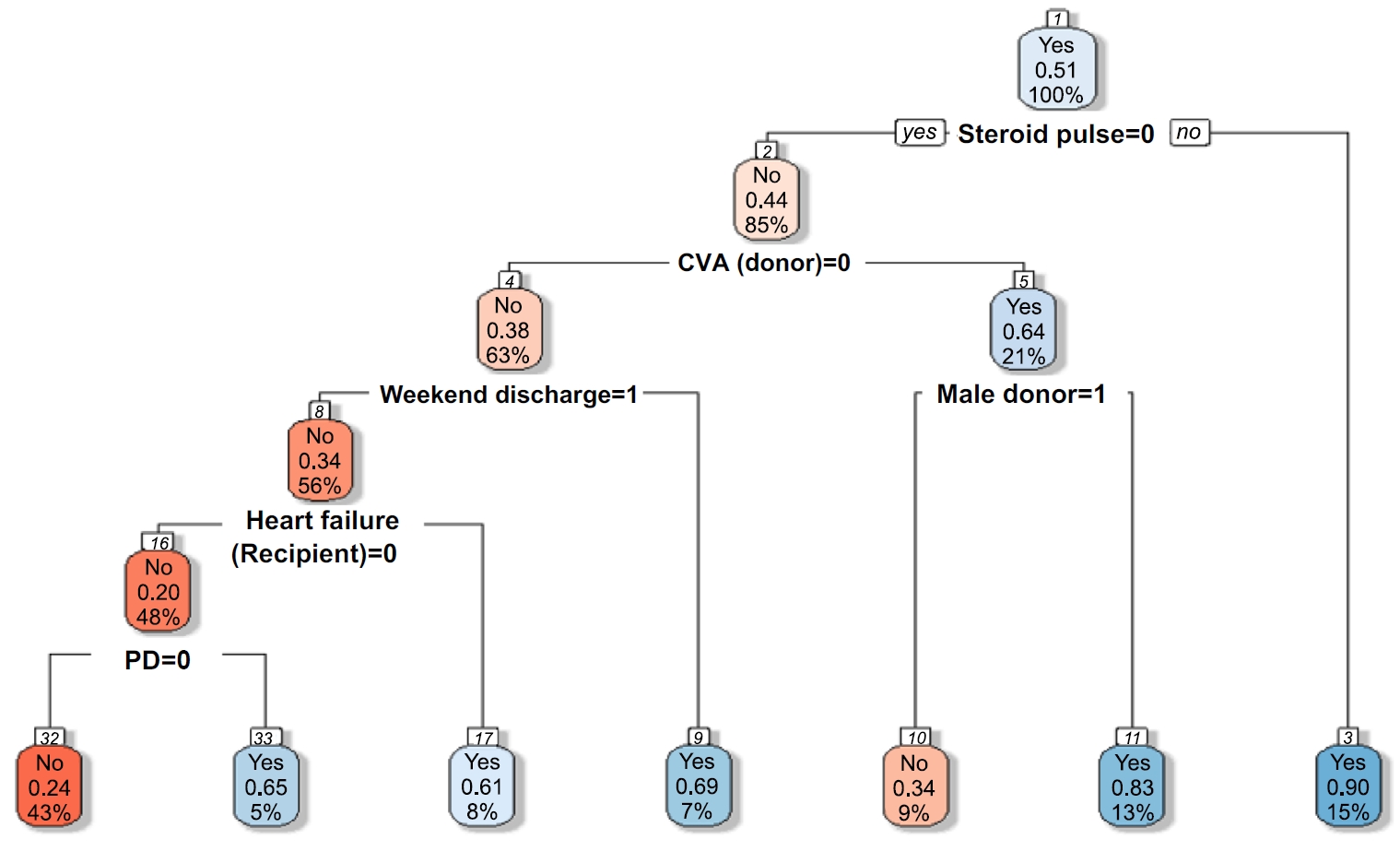
- Development of a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission after kidney transplantation: a retrospective study
- Hye Jin Chong, Ji-hyun Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):528-542. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission (EHR) post-kidney transplantation.
Methods
The study was conducted at the organ transplantation center of a university hospital, utilizing data from 470 kidney transplant recipients. We built and trained four machine learning models and tested them to identify the strongest EHR predictors. Predictive performance was evaluated using confusion matrices and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC).
Results
Among the 470 kidney transplant recipients with a mean age of 46.1 ± 12.02 years, 322 (68.5%) were males, and 74 (15.7%) were readmitted within 30 days after kidney transplantation. In total, 241 (51.2%) recipients were found to have experienced EHR after applying the random over-sampling examples method. The random forest model achieved the best performance, with an ROC AUC of .87 (validation set) and .82 (test set). The 15 most important features were steroid pulse therapy (recipient), cerebrovascular accident (recipient), heart failure (recipient), male sex (donor), cardiovascular disease (recipient), weekend discharge (recipient), peritoneal dialysis (recipient) cerebrovascular accident as the cause of brain death (donor), current smoker (recipient), cardiac arrest (donor), previous kidney transplantation (recipient), age (donor), hypertension (donor), male sex (recipient), and dialysis duration (recipient).
Conclusion
Our framework demonstrated strong predictive interpretability. It can support appropriate and effective clinical decision-making by assisting transplant professionals in stratifying recipients based on their risk of EHR. prioritizing post-discharge care and follow-up for high-risk individuals, and allocating targeted interventions such as closer monitoring or education.
- 973 View
- 124 Download

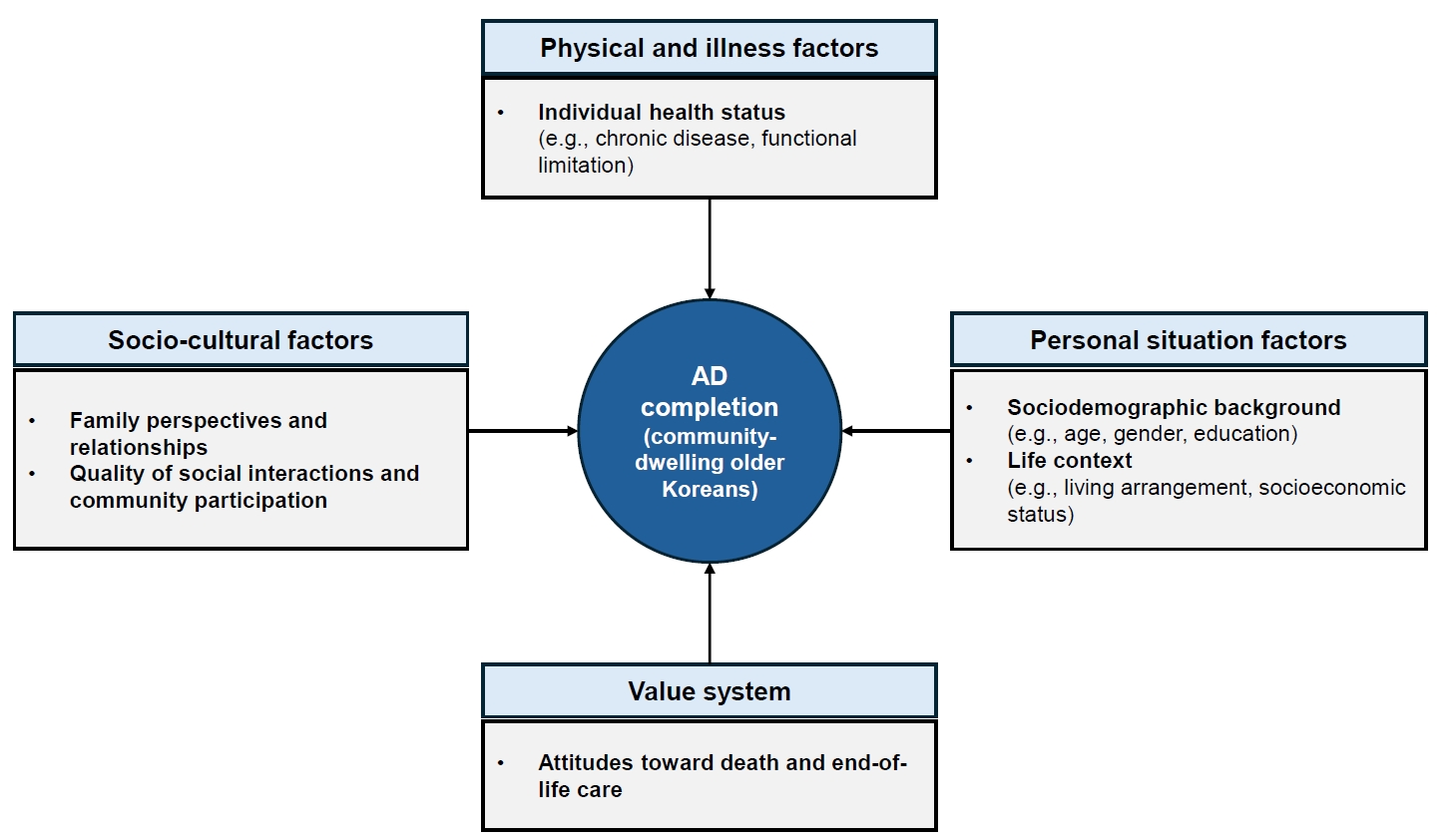
- Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
- Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
- 1,315 View
- 115 Download

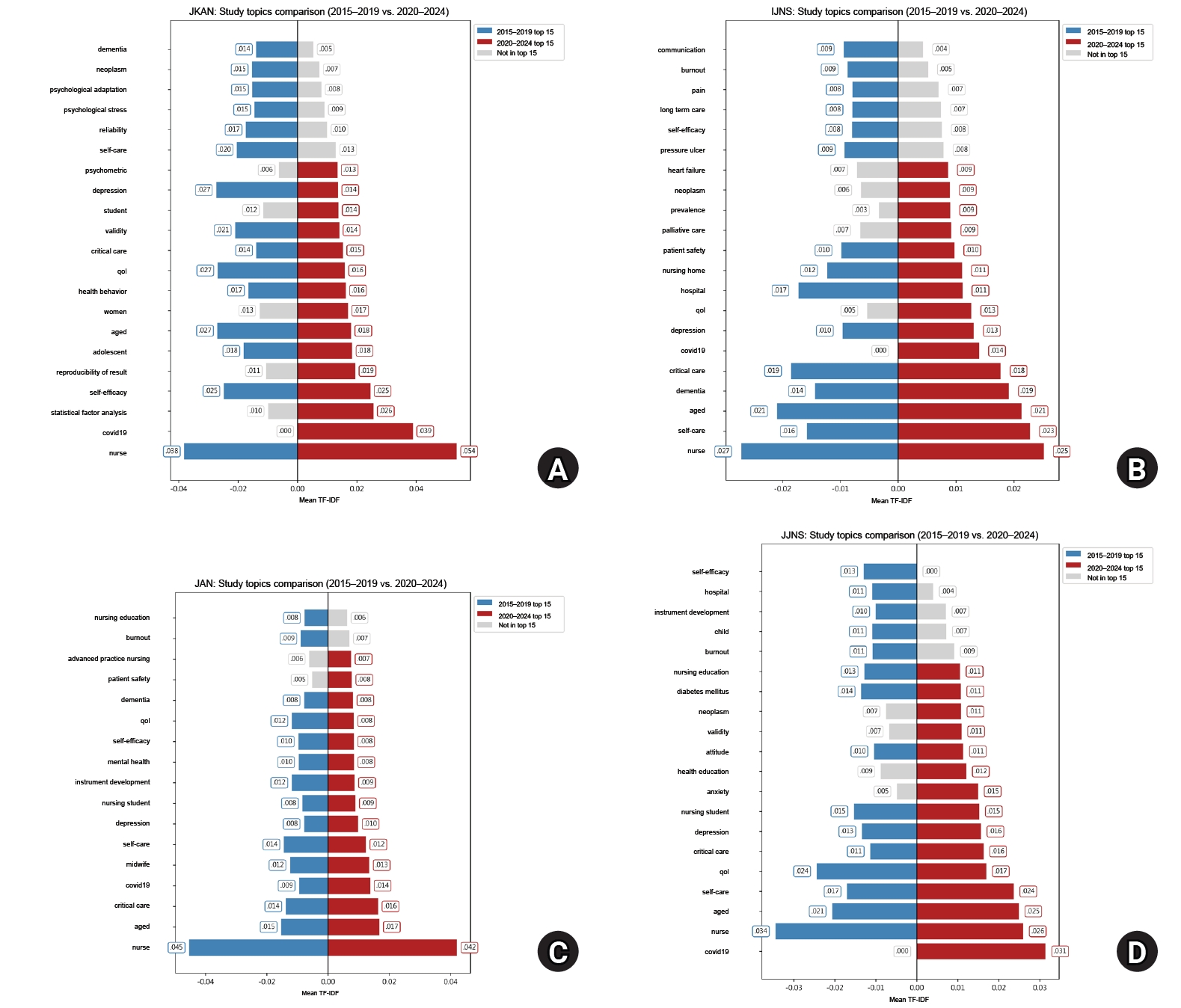
- Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
- Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):557-567. Published online November 19, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25119
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study compared trends in research designs and keywords by analyzing the abstracts of four major nursing journals over the past decade, focusing on the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) in comparison with the International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), Journal of Advanced Nursing (JAN), and Japan Journal of Nursing Science (JJNS).
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted, encompassing 5,522 abstracts published between 2015 and 2024. Research designs were first classified as “quantitative,” “qualitative,” or “other,” and then further sub-classified based on international evidence-based frameworks. Text preprocessing was also conducted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency was applied to evaluate keyword importance. The 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 periods were compared to examine changes in both research designs and keyword importance.
Results
Compared to IJNS, JAN, and JJNS, JKAN published more instrument development and analytic studies but fewer randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews. Over time, the number of instrument development and mixed-methods studies in JKAN increased, while high-evidence designs remained scarce. Keyword analysis showed JKAN’s emphasis on psychosocial themes such as self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression, whereas the other journals more often highlighted policy- and institution-related topics. Across journals, COVID-19 and patient safety emerged as important themes after 2020.
Conclusion
JKAN demonstrates strengths in methodological diversity within quantitative research and in digital health–related analytics. However, high-evidence study designs and policy-oriented keywords are underrepresented in JKAN. Strategic expansion toward randomized controlled trials, systematic review, global and digital health, and policy-relevant research is recommended to strengthen JKAN’s international competitiveness.
- 786 View
- 83 Download

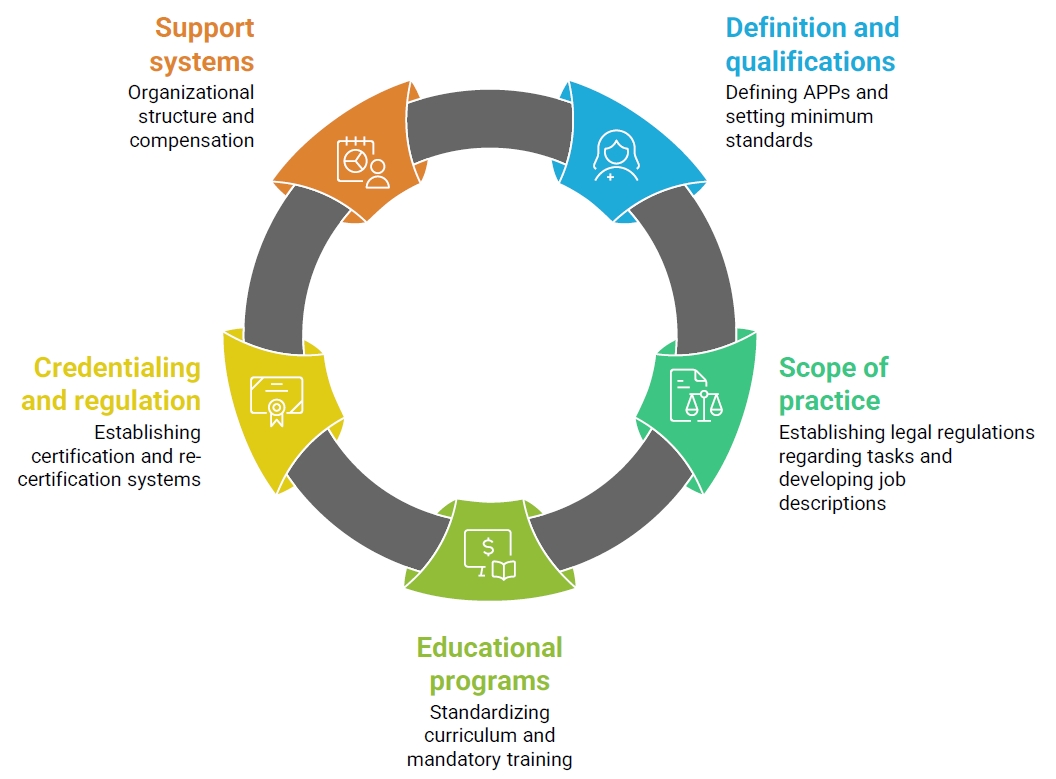
- Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
- Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):568-583. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25106
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to propose strategies for strengthening the nursing workforce by expanding their roles as advanced practice providers (APPs).
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was employed, consisting of five focus group interviews (FGIs) with 30 healthcare professionals (including 10 physicians) and a two-round Delphi survey with 49 experts. The FGIs explored practical insights from clinical settings, while the Delphi process validated and prioritized strategic recommendations through expert consensus.
Results
Four major themes emerged from the FGI analysis: (1) utilization of diverse APPs to ensure quality care, (2) expanding the scope of practice of APPs, (3) requirements to ensure the quality of APPs, and (4) strategies for sustainable management of the APP workforce. Building on these findings, the Delphi survey identified five strategic domains: “definition and qualifications,” “scope of practice,” “educational programs,” “credentialing and regulation,” and “support systems.” Key areas of consensus included the need for mandatory clinical experience and specialty training, legal clarification of role boundaries, standardized curricula with certification mechanisms, and institution-led support systems such as task-specific job descriptions and recredentialing processes.
Conclusion
To effectively strengthen APP roles, it is essential to build on the existing advanced practice nurse (APN) framework, which already includes structured curricula and national certification. Furthermore, integrative strategies should be developed to incorporate experienced clinical nurses without APN licenses into the APN system.
- 1,448 View
- 126 Download

- Effects of presenteeism on turnover intention in clinical nurses through the serial mediating roles of missed nursing care and job satisfaction: a cross-sectional predictive correlational study
- Hyeonseon Cheon, Seok Hee Jeong, Hyun Kyung Kim, Hyoung Eun Chang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):584-597. Published online November 10, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
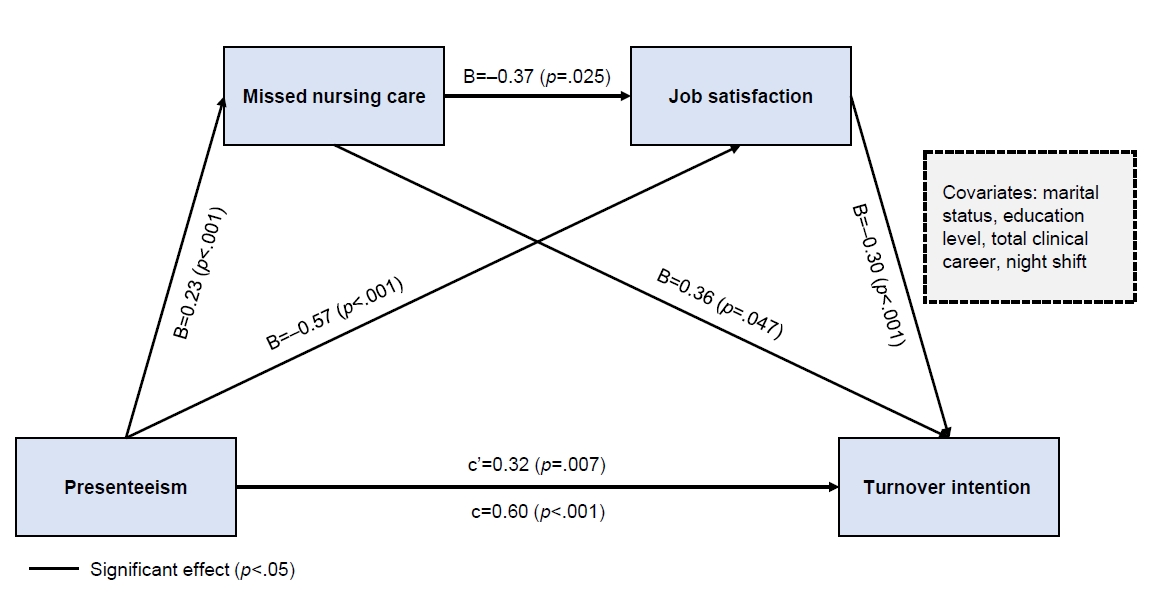
This study aimed to investigate the two-mediator serial mediation effect of missed nursing care and job satisfaction on the relationship between presenteeism and turnover intention in clinical nurses.
Methods
A cross-sectional predictive correlational study was conducted, and the participants were 208 clinical nurses working in advanced general hospitals in South Korea. Data were collected from October 6 to November 7, 2023 using self-reported questionnaires, including general characteristics, presenteeism, missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS/WIN ver. 29.0 and PROCESS macro ver. 4.2.
Results
Missed nursing care and job satisfaction exhibited a double mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. In addition, missed nursing care showed a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Job satisfaction had a mediating effect on the relationship between presenteeism and clinical nurses’ turnover intention. Presenteeism had a direct effect on missed nursing care, job satisfaction, and turnover intention. Missed nursing care exerted a direct effect on job satisfaction and turnover intention among clinical nurses. Job satisfaction had a direct effect on turnover intention.
Conclusion
To reduce nurses’ turnover intention, it is essential to develop and implement programs focused on preventing presenteeism. Additionally, organizational initiatives should prioritize active support for nurses’ health management, alleviating the shortage of nursing staff, augmenting job satisfaction, and improving the overall working environment.
- 1,365 View
- 175 Download

- Development of an end-of-life care competency scale for nurses in long-term care hospitals: a psychometric validation study
- Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):598-612. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure end-of-life care (EOLC) competency among nurses working in long-term care hospitals and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods
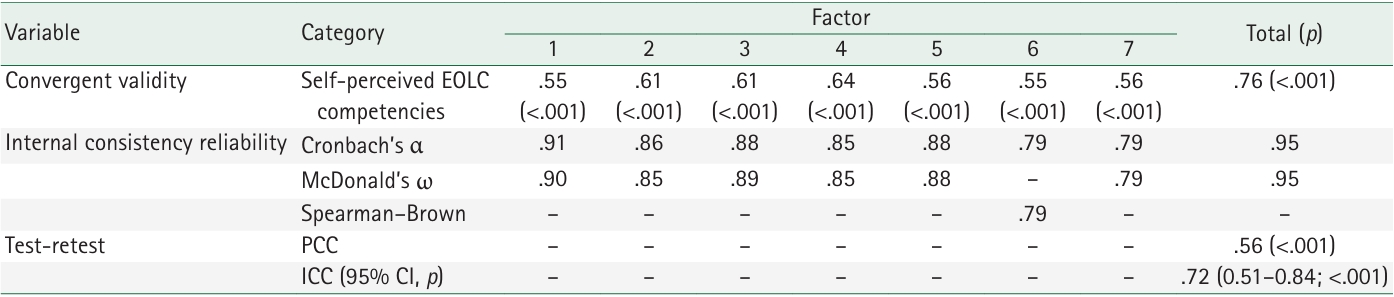
Preliminary items were developed based on attributes and indicators identified through a conceptual analysis of EOLC competency. The initial version of the scale was refined through expert content validity assessment, item revision, and a pilot test. The main survey was conducted among 460 nurses in long-term care hospitals, and 409 valid responses were analyzed after excluding 51 incomplete or invalid cases. Data were analyzed using software-assisted item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and assessments of convergent, discriminant, and criterion-related validity, as well as reliability testing.
Results
The initial 55 items were reduced to a final set of 30 items across seven dimensions. Model fit indices indicated good construct validity (χ²/degrees of freedom=1.91, standardized root mean square residual=.06, root mean square error of approximation=.07, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.91), with a total explained variance of 70.2%. The scale demonstrated strong criterion-related validity (r=.76, p<.001), high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α=.95; McDonald’s ω=.95), acceptable test–retest reliability (r=.56, p<.001), and an intraclass correlation coefficient of .72 (95% confidence interval, .51–.84; p<.001).
Conclusion
The developed scale is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing EOLC competency among nurses in long-term care hospitals. It can be effectively utilized for educational assessment, training evaluation, and the measurement of program effectiveness in end-of-life care.
- 821 View
- 91 Download

- Validity and reliability of the Security Neglect Subscale of the Child Neglect Scale in vulnerable Chinese children: a methodological study
- Zexi Su
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):613-620. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25089
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
Security neglect is common among vulnerable children. The Child Neglect Scale (CNS) is widely used to screen children for neglect. However, little is known about the accuracy of the Security Neglect Subscale when administered in isolation. This study aimed to examine the reliability and validity of the Security Neglect Subscale of the CNS among vulnerable children in China.
Methods
Cluster sampling was used, and 242 vulnerable children participated in the study. Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS ver. 28.0 and Amos ver. 28.0, and the test construct validity of the CNS Security Neglect Subscale was analyzed through confirmatory factor analysis. In addition, convergent and discriminant validity, as well as reliability, were evaluated.
Results
The construct validity of the nine-item CNS Security Neglect Subscale was confirmed by a two-factor structure. The modified model fit the data well, as shown by a normed chi-square of 2.48, a comparative fit index of .97, a Tucker-Lewis index of .96, and a root mean square error of approximation of .08. The model had acceptable convergent and discriminant validity for each structure. The Cronbach’s α coefficient was .87 overall, and values for the two factors ranged from .78 to .93.
Conclusion
The findings of this study support the satisfactory psychometric properties of the CNS Security Neglect Subscale, indicating its utility in evaluating security neglect in vulnerable children in China.
- 449 View
- 64 Download

- A qualitative exploration of acute stroke patients’ experiences with aphasia in Korea
- Jiyeon Kang, Hyunyoung Heo
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):621-633. Published online November 25, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25132
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to explore the lived experiences of patients with acute stroke-related aphasia within the Korean healthcare context.
Methods
A qualitative research design using inductive content analysis was employed, following the Consolidated Criteria for Reporting Qualitative Research guidelines. Fourteen adults with acute stroke-related aphasia participated in one-on-one, in-depth interviews conducted between January and May 2025. Participants were recruited through purposive sampling until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were analyzed using an inductive qualitative content analysis approach.
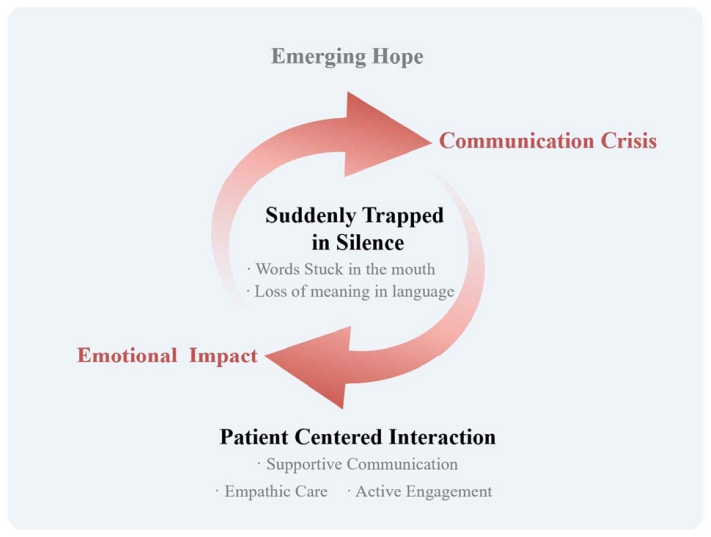
Results
Five main categories emerged: “suddenly trapped in silence” described the abrupt loss of language, including the inability to articulate intended words and understand others; “emotional impact” captured psychological shock and feelings of loss; “communication crisis” encompassed expressive difficulties, exclusion from decision-making, and social withdrawal; “patient-centered interaction” highlighted supportive communication, empathic care, and active engagement by others; and “emerging hope” reflected signs of recovery, self-directed efforts, and anticipation of improvement. These categories converged into the overarching theme, “communication beyond language,” illustrating how patients sought meaningful interaction despite linguistic limitations.
Conclusion
Acute aphasia extends beyond a language disorder to encompass profound emotional and social experiences. Although communication barriers exist, meaningful interaction remains possible through empathetic, person-centered approaches. Healthcare professionals should recognize that patients with aphasia retain cognitive competence despite expressive limitations. These findings underscore the need to integrate emotional sensitivity into clinical care and to develop training programs that enhance person-centered communication skills in stroke rehabilitation settings.
- 1,047 View
- 99 Download

Review Papers
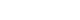
- Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
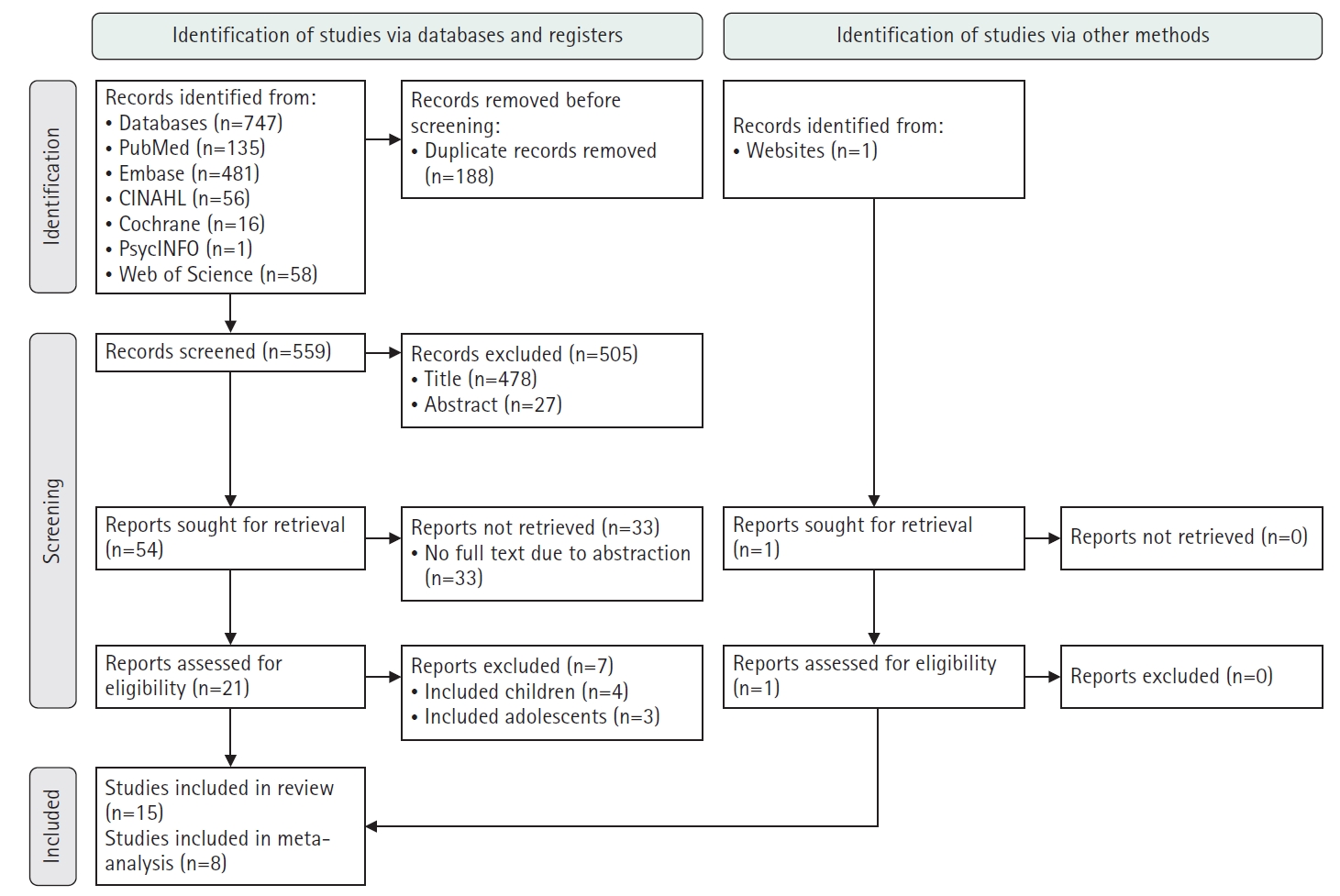
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
- 1,058 View
- 151 Download

- Variables influencing digital health literacy in older adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Jin Hwa Park, Eun Ju Mun
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):651-667. Published online November 27, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25112
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
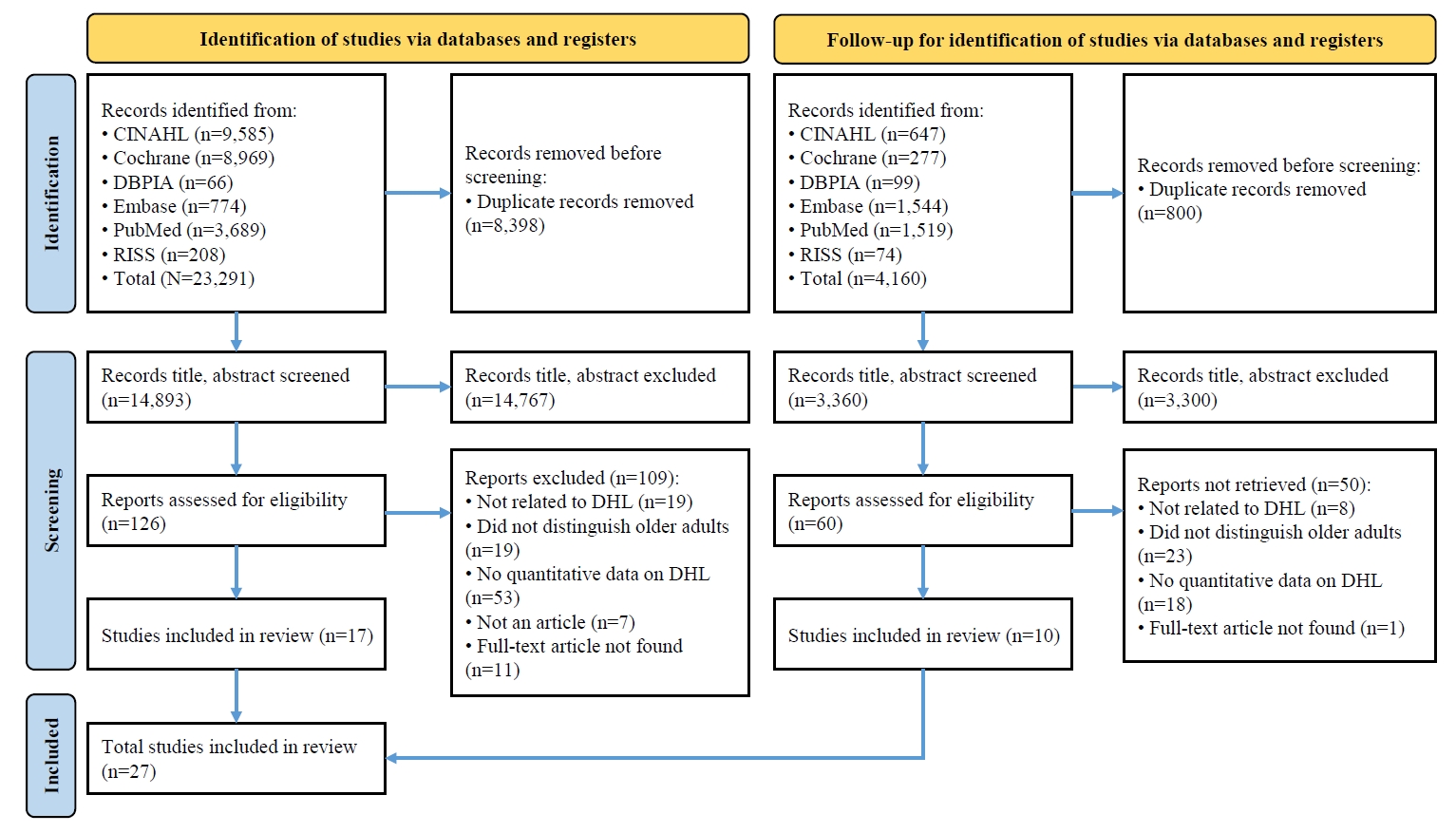
This study aimed to synthesize existing evidence on digital health literacy (DHL) among older adults and to estimate the associations between related influencing factors through a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. Literature searches were performed across PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, RISS, and DBPIA. The search and screening process was conducted from December 24, 2023, to March 31, 2025. Effect sizes (ESr) using correlation coefficient for each variable were calculated, and meta-analyses were performed using Microsoft Excel and R version 4.3.1.
Results
Forty-seven variables were identified, including two demographic, six physical, six behavioral, 23 psychosocial, and 10 cognitive factors. Meta-analysis results showed that physical, behavioral, psychosocial, and cognitive factors had significant effects on DHL. Among these, digital information level (ESr=.62; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55 to 0.69) within the cognitive domain and technophobia (ESr=−.55; 95% CI, −0.47 to −0.40) within the psychosocial domain demonstrated the largest ESr.
Conclusion
Among factors influencing DHL, digital information level and technophobia showed the strongest associations. These findings suggest that improving DHL in older adults requires a dual approach targeting both cognitive and psychosocial dimensions—enhancing digital information skills while reducing technophobia—to effectively support digital engagement and health empowerment in this population (PROSPERO registration number: CRD42023487486).
- 1,154 View
- 116 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION


 First
First Prev
Prev