-
Transforming nursing education to enhance integrated nursing competency: a Delphi-based methodological study on symptom-based clinical reasoning
-
Jeung-Im Kim, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park, Ju-Eun Song, Eunjung Ryu, JuHee Lee, YeoJin Im
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):39-50. Published online February 5, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25151
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
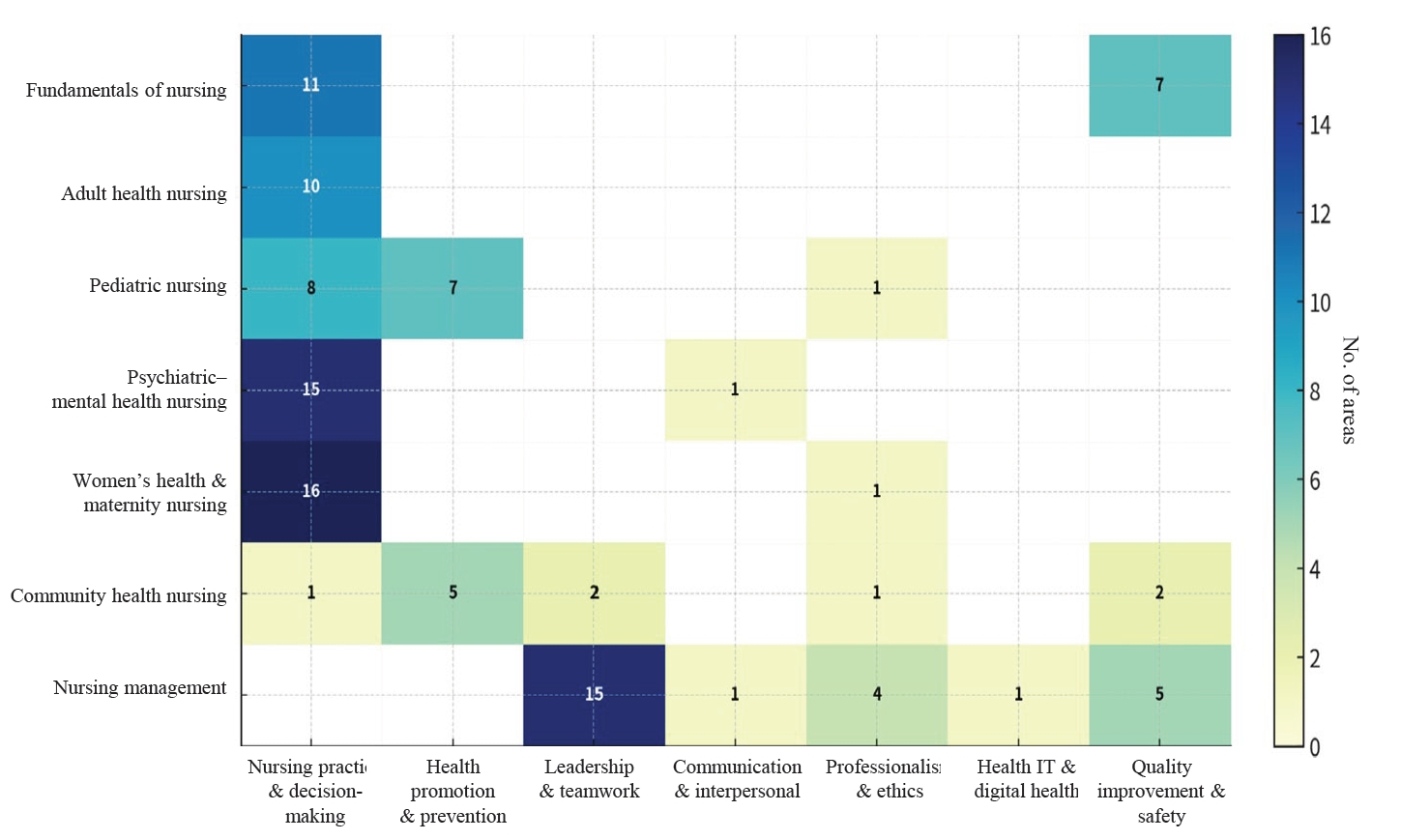
This study aimed to address the shift toward competency-based education and the planned 2028 “Integrated Nursing” National Licensing Examination (NLE), this study aimed to establish structural alignment among NLE domains, the seven integrated nursing competencies (INCs), and curriculum goals, with a particular focus on implementing symptom-based clinical reasoning (SBCR).
Methods
This Delphi-based methodological study included seven content experts for content validity index (CVI) assessment and 24 nursing education experts who participated in a consensus workshop. The item-level CVI and the scale-level CVI/average were calculated to confirm the linkage between INCs and NLE domains. In addition, qualitative analysis of workshop materials and meeting records was conducted to derive 10 integrated learning topics and to develop an SBCR educational model for the key symptom of headache, grounded in Miller’s Clinical Competence Pyramid (levels 2–4).
Results
The analysis confirmed the validity of integrating the INCs within the overall curriculum structure. The resulting framework delineates staged learning objectives and core clinical questions designed to systematically enhance clinical reasoning, promote safe nursing practice, and support professional reflection within a unified curriculum.
Conclusion
This study provides a practical foundation for nursing curriculum redesign by facilitating a transition from fragmented, subject-based instruction to a holistic, patient-centered SBCR model. This approach aligns with the requirements of the integrated NLE and is expected to contribute to meaningful improvements in actual clinical competency.
-
Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
-
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):557-567. Published online November 19, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25119
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
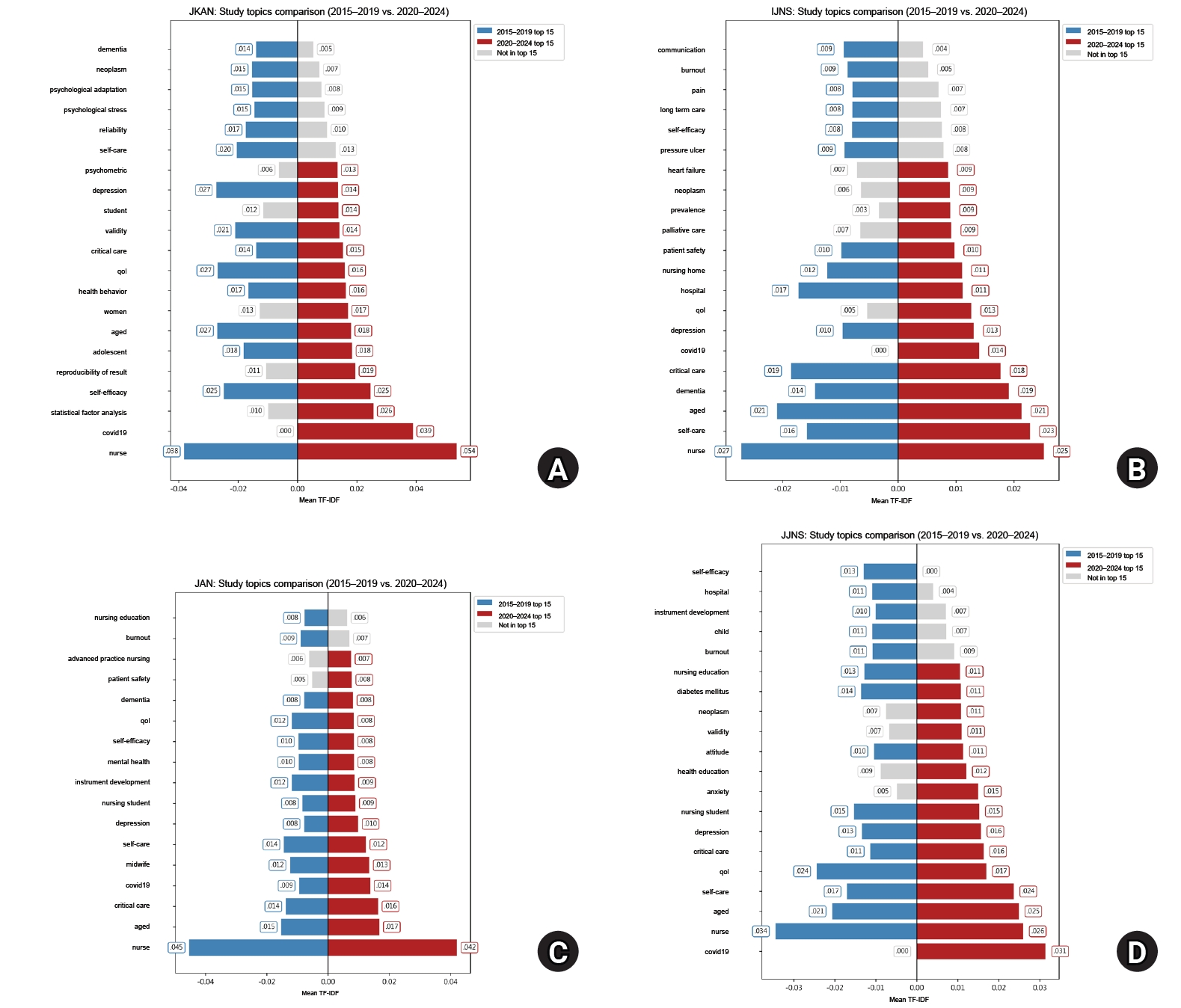
This study compared trends in research designs and keywords by analyzing the abstracts of four major nursing journals over the past decade, focusing on the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) in comparison with the International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), Journal of Advanced Nursing (JAN), and Japan Journal of Nursing Science (JJNS).
Methods
A bibliometric analysis was conducted, encompassing 5,522 abstracts published between 2015 and 2024. Research designs were first classified as “quantitative,” “qualitative,” or “other,” and then further sub-classified based on international evidence-based frameworks. Text preprocessing was also conducted, and term frequency–inverse document frequency was applied to evaluate keyword importance. The 2015–2019 and 2020–2024 periods were compared to examine changes in both research designs and keyword importance.
Results
Compared to IJNS, JAN, and JJNS, JKAN published more instrument development and analytic studies but fewer randomized controlled trials and systematic reviews. Over time, the number of instrument development and mixed-methods studies in JKAN increased, while high-evidence designs remained scarce. Keyword analysis showed JKAN’s emphasis on psychosocial themes such as self-efficacy, quality of life, and depression, whereas the other journals more often highlighted policy- and institution-related topics. Across journals, COVID-19 and patient safety emerged as important themes after 2020.
Conclusion
JKAN demonstrates strengths in methodological diversity within quantitative research and in digital health–related analytics. However, high-evidence study designs and policy-oriented keywords are underrepresented in JKAN. Strategic expansion toward randomized controlled trials, systematic review, global and digital health, and policy-relevant research is recommended to strengthen JKAN’s international competitiveness.
-
A review of domestic and international contexts for establishing a communication platform for early-career nurse scientists
-
Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Hye Young Kim, Mi Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Yeonsoo Jang, Sangeun Jun
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):317-325. Published online May 27, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25041
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
As nursing continues to advance through digital health, clinical specialization, and interdisciplinary research, early-career nurse scientists are central to advancing innovation. However, Korea lacks a structured platform to support their research, collaboration, and career development. This review aimed to identify the needs of early-career nurse scientists and examine international best practices to guide the creation of an effective communication platform.
Methods
This study involved a secondary analysis of the final report from the project “Establishment of a communication platform for young nursing scientists,” carried out by the Korean Society of Nursing Science. The report comprises data from focus group interviews with domestic graduate students and early-career researchers, a literature review of international communication and support systems, and a global policy analysis related to young nursing scientists. Based on this report, the present review synthesizes key findings and draws implications for the development of a communication platform in Korea.
Results
International examples, such as grant writing programs, mentoring initiatives, and digital collaboration hubs, showed positive outcomes in strengthening research capacity and promoting the professional growth of nurse scientists. Based on these findings, key considerations for platform development include: (1) establishing clear leadership and a participatory governance model; (2) providing demand-driven content such as research guides, mentoring, and mental health resources; (3) implementing mechanisms to ensure sustainability, content quality, and user data protection; and (4) designing an integrated platform that fosters synergy across research, policy development, education, and global networking.
Conclusion
A digital platform for early-career nurse scientists should function not merely as an information portal, but also as dynamic infrastructure for collaboration, mentorship, and growth. It is recommended that the Korean Society of Nursing Science spearhead this initiative, with governmental support, to enhance the research capacity and expand the global engagement of Korean nursing scientists.
-
Practical Consideration of Factor Analysis for the Assessment of Construct Validity
-
Jin-Hee Park, Jeung-Im Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(6):643-647. Published online December 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.51601
-
-
 PDF PDF
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Hotel employees’ attitudes towards multitasking: scale development and validity testing
Tuğrul Ayyildiz, Erdogan Koc, Muhammed Baykal, Ahu Yazıcı Ayyıldız
Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Insights.2025; 8(7): 2517. CrossRef - Turkish adaptation of the clinical reasoning evaluation simulation tool (CREST-TR): a validity and reliability study
Cigdem Bayzat, Leyla Dinc
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Translation and psychometric evaluation of the Persian version of the nurse team resilience scale in the context of cardiopulmonary resuscitation
Mobina Rajaee, Mehrsa Basiri Moghaddam, Alireza Jafari, Mahdi Basiri Moghaddam
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Logistic Capabilities as a Performance Enabler for Online Retailers
Jagdish Bhagwat, Rekha Attri
Vikalpa: The Journal for Decision Makers.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validity of the Musculoskeletal Tumor Society Score for lower extremity in patients with bone sarcoma or giant cell tumour of bone undergoing bone resection and reconstruction surgery in hip and knee
Nikolai Sherling, Müjgan Yilmaz, Christina Enciso Holm, Michael Mørk Petersen, Linda Fernandes
BMC Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - African American race is associated with worse sleep quality in heavy smokers
Aaron D. Baugh, Megan Acho, Abraham Arhin, Igor Barjaktarevic, David Couper, Gerard Criner, Meilan Han, Nadia Hansel, Jerry Krishnan, Katherine Malcolm, Andrew Namen, Stephen Peters, Helena Schotland, Mudiaga Sowho, Michelle Zeidler, Prescott Woodruff, Ne
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.2023; 19(8): 1523. CrossRef - Development and validation of the 23-item preterm birth risk assessment scale-Korean version
Jeung-Im Kim
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Conceptual Integration and Empirical Validation of a Unified Taxonomy: Quantitative Data Analysis for Virtual Learning Environments
Melanie Moreno-Barahona, Blanca Fraijo-Sing, Ghozlane Fleury-Bahi, Oscar Navarro-Carrascal, Cesar Tapia-Fonllem
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,747
View
-
62
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
Information and General Guidance for Healthcare Professionals in the Fourth Wave of COVID-19
-
Jeung-Im Kim, Mi Yu, Soyoung Yu, Jin-Hee Park
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2021;51(4):395-407. Published online August 31, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21137
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- The COVID-19 curve seesawed and reached the fourth pandemic in July 2021. Since the first three waves, the focus has been on achieving herd immunity through vaccination while a lot of manpower is used for quarantine. However, we have not been able to prevent the fourth wave. The causes are thought to be related to people who doubt the safety of the vaccine and refuse it or violate quarantine guidelines such as social distancing. This study examined guidelines for preventing and controlling COVID-19, the accuracy of vaccination-related information, and described quarantine measures including for those who completed vaccination. In conclusion, prevention and vaccination are the most effective countermeasures against COVID-19. We recommend people vaccination with self-quarantine. Also, it is necessary to make large investments to protect and support nurses in future pandemics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Halal Indonesia: creating global nation branding through communication and diplomacy
Nurprapti Wahyu Widyastuti, Marchela Rahesta, Isti Nursih Wahyuni
Jurnal Studi Komunikasi (Indonesian Journal of Communications Studies).2025; 9(2): 577. CrossRef - COVİD-19 Pandemisinde Diş Hekimlerinin Dezenfeksiyon, Antisepsi ve Sterilizasyon Uygulamalarına Bakışı
Pelin ÖZMEN, Serdar SÜTCÜ, Haluk KÖSE
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2023; 12(3): 348. CrossRef - The thoughts of parents to vaccinate their children against COVID‐19: An assessment of situations that may affect them
Melike Y. Çelik
Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatric Nursing.2022; 35(2): 189. CrossRef - Vaccination process evaluation at COVID-19 vaccination centers in Lebanon: a national study
Abeer Zeitoun, Souheil Hallit, Maya Helali, Sirine Chehade, Carla Allam, Aya Ibrahim, Hani Dimassi, Rita Karam
Journal of Pharmaceutical Policy and Practice.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Theoretical effectiveness of steam inhalation against SARS-CoV-2 infection: updates on clinical trials, mechanism of actions, and traditional approaches
Md. Nafees Rahman Chowdhury, Yasin Arafat Alif, Safaet Alam, Nazim Uddin Emon, Fahmida Tasnim Richi, S. M. Neamul Kabir Zihad, Md. Tohidul Islam Taki, Mohammad A. Rashid
Heliyon.2022; 8(1): e08816. CrossRef - Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 66. CrossRef - Effectiveness and Utility of Virtual Reality Infection Control Simulation for Children With COVID-19: Quasi-Experimental Study
Mi Yu, Mi Ran Yang
JMIR Serious Games.2022; 10(2): e36707. CrossRef - Healthcare Considerations for Special Populations during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review
Jeung-Im Kim, YeoJin Im, Ju-Eun Song, Sun Joo Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2021; 51(5): 511. CrossRef
-
2,694
View
-
15
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
-
Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(4):501-512. Published online August 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20167
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze articles published in the Journal of the Korean Academy of Nursing (JKAN) between 2010 and 2019, along with those published in three international nursing journals, to improve JKAN’s international reputation.
Methods
The overall characteristics of JKAN’s published papers and keywords, study participants, types of nursing interventions and dependent variables, citations, and cited journals were analyzed. Additionally, the keywords and study designs, publication-related characteristics, journal impact factors (JIF), and Eigenfactor scores of International Journal of Nursing Studies (IJNS), International Nursing Review (INR), Nursing & Health Sciences (NHS), and JKAN were analyzed and compared.
Results
Among the four journals, JKAN’s score was the lowest in both the journal impact factor and Eigenfactor score. In particular, while the JIF of INR and NHS has been continuously increasing; JKAN’s JIF has remained static for almost 10 years. The journals which had cited JKAN and those which JKAN had cited were mainly published in Korean.
Conclusion
JKAN still has a low IF and a low ranking among Social Citation Index (E) journals during the past 10 years, as compared to that of four international journals. To enhance JKAN’s status as an international journal, it is necessary to consider publishing it in English and to continuously improve the conditions of other publications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 557. CrossRef - Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Korean Society of Nursing Science and Contemplating Direction to Move Forward
Kyung-Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 641. CrossRef
-
2,422
View
-
28
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Validity and Reliability of the Korean Version of the Menopause-Specific Quality of Life
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):487-500. Published online June 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20049
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the validity and reliability of the Korean version of Menopause-Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL).
Methods
The MENQOL was translated into Korean according to algorithm of linguistic validation process. A total of 308 menopausal womenwere recruited and assessed using the Korean version of MENQOL (MENQOL-K), the World Health Organization Quality of Life BriefVersion (WHOQOL-BREF), and Center for Epidemiological Studies Depression Scale (CES-D-K). In estimating reliability, internal consistencyreliability coefficients were calculated. Validity was evaluated through criterion validity and construct validity with confirmatory factor analysesusing SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 25.0 software.
Results
In item analyses, the “increased facial hair” symptom was excluded because of thelow contribution of MENQOL-K. The confirmatory factor analysis supported good fit and reliable scores for MENQOL-K model, and thefour-factor structure was validated (x2=553.28, p <.001, NC=1.84, RMSEA=.05, AGIF=.85, AIC=765.28). The MENQOL-K consists of 28 itemsin 4 domains, including vasomotor (3 items), psychosocial (7 items), physical (15 items), and sexual subscales (3 items). There was an acceptablecriterion validity with moderately significant correlation between MENQOL-K and WHOQOL-BREF. The Cronbach’s a for the 4subsacles ranged from .80 to .93.
Conclusion
The MENQOL-K is a valid and reliable scale to measure condition-specific quality of life forperimenopausal and postmenopausal women. It can be used to assess the impact of menopausal symptoms on the quality of life of Koreanwomen in clinical trials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Longitudinal analysis of alcohol consumption pattern and menopause‐specific quality of life in middle‐aged women undergoing the menopausal transition
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yoonyoung Jang, Ga‐young Lim, Yoo‐Jung Kim, Seungho Ryu
Addiction.2026; 121(3): 586. CrossRef - Examining the relationship between symptoms and quality of life related to menopausal period of women with gynecologic cancer: a cross-sectional study
Ahsen Demirhan Kayacik, Gulsah Kok
Supportive Care in Cancer.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The 3-dimensionel Ovarian Volume Assessment to Evaluate Whether Menopausal Related Symptoms and Hormone Levels Correlate with the Ovarian Volume
Gizem Işık Solmaz, İsmail Güler, Esra İşçi Bostancı, Serhan Can İşcan, Nuray Bozkurt, Mehmet Anıl Onan
Gazi Medical Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Aerobic Exercise Vs Surya Namaskar on Quality of Life in Postmenopausal Women Using Menopause Specific Quality of Life (MENQOL) Questionnaire
Dr. Dhanashree P. Shinde (PT), Alphina E. Jules
International Journal of Advanced Research in Science, Communication and Technology.2025; : 51. CrossRef - Longitudinal patterns and group heterogeneity of depressive symptoms during menopausal transition in middle-aged Korean women
Yoonyoung Jang, Yoosoo Chang, Junhee Park, Sang Won Jeon, Byungtae Seo, Jae Ho Park, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Early-onset vasomotor symptoms and development of depressive symptoms among premenopausal women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Jungeun Park, Yoosun Cho, Chanmin Kim, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 354: 376. CrossRef - Association between Menopausal Women’s Quality of Life and Aging Anxiety: The Role of Life Satisfaction and Depression
Seunghee Lee, Mijung Jang, Dohhee Kim, KyooSang Kim
Medicina.2024; 60(8): 1189. CrossRef - Vasomotor and other menopause symptoms and the prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health metrics among premenopausal stage women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Min-Jung Kwon, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Menopause.2023; 30(7): 750. CrossRef - Research trends in the Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing from 2011 to 2021: a quantitative content analysis
Ju-Hee Nho, Sookkyoung Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2023; 29(2): 128. CrossRef - Low anti-Müllerian hormone levels are associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms among premenopausal women
SunJu NamGoung, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Hoon Kim, In Young Cho, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Hyun-Young Park, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Min-Jung Kwon, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is associated with an increased risk of incident early-onset vasomotor symptoms
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Ideal Cardiovascular Health Metrics and Risk of Incident Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms Among Premenopausal Women
Hye Rin Choi, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Jeonggyu Kang, Min-Jung Kwon, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2666. CrossRef - Alcohol Consumption Patterns and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Premenopausal Women
Ria Kwon, Yoosoo Chang, Yejin Kim, Yoosun Cho, Hye Rin Choi, Ga-Young Lim, Jeonggyu Kang, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Jihwan Park, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun-Young Park, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(11): 2276. CrossRef - Metabolically healthy and unhealthy obesity and risk of vasomotor symptoms in premenopausal women: cross‐sectional and cohort studies
Sunju Namgoung, Yoosoo Chang, Chae‐Yeon Woo, Yejin Kim, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga‐Young Lim, Hye Rin Choi, Kye‐Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Juhee Cho, Eliseo Guallar, Hyun‐Young Park, Seungho Ryu
BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2022; 129(11): 1926. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk of Early-Onset Vasomotor Symptoms in Lean and Overweight Premenopausal Women
Yoosun Cho, Yoosoo Chang, Hye Rin Choi, Jeonggyu Kang, Ria Kwon, Ga-Young Lim, Jiin Ahn, Kye-Hyun Kim, Hoon Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Di Zhao, Sanjay Rampal, Juhee Cho, Hyun-Young Park, Eliseo Guallar, Seungho Ryu
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2805. CrossRef
-
3,371
View
-
132
Download
-
14
Web of Science
-
15
Crossref
-
Development of Caring as a Human Science: 50 Years of History of the Korean Society of Nursing Science
-
Jeung-Im Kim, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im, Jin-Hee Park, Soyoung Yu, Sun Joo Jang, Da-Hee Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(3):313-332. Published online June 30, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20142
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This year 2020 marks the 50th anniversary of the founding of the Korean Society of Nursing Science (KSNS). This study wasaimed to explore development of caring and describe the 50 years of history of KSNS within the sociocultural context of Korea regardingacademic footsteps, meanings, and implications for the future.
Methods
This study used a historical research methodology using a literaturereview and bibliometric analysis. Relevant literature was reviewed and the published abstracts in the Journal of Korean Academy ofNursing (JKAN) were analyzed using VOSviewer.
Results
Birth control and family planning in the 1970s was the main research topic. In the1980s, the development of nursing concepts, theories, and philosophies was the mission of KSNS to extend the disciplinary boundary. In the1990s, the progress of KSNS to become one of the woman-dominant healthcare professionals was the mission in the given period. Expandingthe frontiers of KSNS to the extent of global standards was the undertaking of the nursing scholars in the 2000s. Lastly, in the 2010s,the quality and quantity improvement of KSNS and JKAN is expected to make our future even prosperous. The map visualization of the 50years of research accumulation showed the comparable opposition of quantitative vs. qualitative research methodologies, equation modeling,and instrument development.
Conclusion
These clusters of research demonstrates the efforts to make nursing evidence by Koreannursing scholars for the last five decades. The growth in the slope of KSNS and outcomes of JKAN are to carry on to an unimaginable extentin the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Ten-year trends in research designs and keywords: a bibliometric comparison of the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing and leading international nursing journals
Jin-Hee Park, Hyun Kyoung Kim, Gaeun Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 557. CrossRef - Editorials in February Issue of Asian Nursing Research
Asian Nursing Research.2024; 18(1): 1. CrossRef - PERCURSO METODOLÓGICO PARA CONSTRUÇÃO DE DEFINIÇÕES OPERACIONAIS DE DIAGNÓSTICOS DE ENFERMAGEM
Thaís Rodrigues de Albuquerque, Francisco Henryque Soares Morais, Glauberto da Silva Quirino, Marcos Antônio Gomes Brandão, Cândida Caniçali Primo, Rachel de Sá Barreto Luna Callou Cruz
Enfermagem em Foco.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lived experiences of work-life balance among doctoral nursing students: a qualitative descriptive study
Ji Yeon Lee, Yong Sook Yang, Gi Wook Ryu, Kyoungjin Lee
International Journal of Qualitative Studies on Health and Well-being.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Telephone Counseling of Patients in Chemotherapy Using Text Mining Technique
Seoyeon Kim, Jihyun Jung, Heiyoung Kang, Jeehye Bae, Kayoung Sim, Miyoung Yoo, Eunyoung, E. Suh
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 46. CrossRef - Fourth Industrial Revolution and Nursing Research
Young Whee Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(1): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of Research Topics and Trends in the Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing to Improve Its International Influence
Soyoung Yu, Jeung-Im Kim, Jin-Hee Park, Sun Joo Jang, Eunyoung E. Suh, Ju-Eun Song, YeoJin Im
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(4): 501. CrossRef - Commemorating the 50th Anniversary of Korean Society of Nursing Science and Contemplating Direction to Move Forward
Kyung-Sook Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2020; 50(5): 641. CrossRef
-
2,804
View
-
33
Download
-
7
Web of Science
-
8
Crossref
-
Psychoeducational Approach to Distress Management of Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Mison Chun, Yong Sik Jung, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(6):669-678. Published online January 15, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.6.669
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of integrated psychoeducational program for distress management of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer.
Methods
A quasi-experimental trial was conducted. The participants consisted of 47 female patients with breast cancer assigned to an intervention group (n=25) and control group (n=22). The intervention group participated in integrated psychoeducational program, consisting of individual face-to-face education and telephone-delivered health-coaching sessions. Data were collected at three time points: pre-intervention (T1), post-intervention (T2), and 6-month follow-up (T3). Study instruments were Distress thermometer, Supportive Care Needs Survey Short Form 34 and Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast.
Results
Compared with the control group, breast cancer patients in the intervention group reported lower distress and supportive care needs than the control group. The intervention group reported higher quality of life (QOL) overall and higher emotional well-being than the control group.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that the integrated psychoeducational program is an effective intervention for reducing distress and supportive care needs and increasing QOL of newly diagnosed patients with breast cancer. Oncology nurses need to provide psychoeducational intervention to support patients with breast cancer in managing their distress and helping them adjust to their life.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Analysis of Breast Cancer Nursing Education Content and Educational needs for Breast Cancer Patient Nursing Perceived by Nurses
Young-Hee Je, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2025; 25(1): 1. CrossRef - Effectiveness of a Tailored Psychoeducational Intervention for Patients With Advanced Cancer in Indonesia: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nurul Huda, Made Satya Nugraha Gautama, Wan Nishfa Dewi, Agung Waluyo, Hsiu Ju Chang, Malissa Kay Shaw
Journal of Nursing Scholarship.2025; 57(5): 848. CrossRef - Evidence on the benefits of mind-body Qigong exercise in women with breast cancer
Michel Marcos Dalmedico, Jackson Adriano Canavarro Ribeiro, Juliana Londero Silva Avila, Prisley Pereira de Oliveira, Paula Karina Hembecker, Sergio Ossamu Ioshii
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Psychological Distress and Influencing Factors in Newly Diagnosed Patients with Breast Cancer: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Min Hee Hur, Yu Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(4): 311. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions for Patients with Breast Cancer: A Meta-analysis
Kyu-Sic Hwang, Kuy-Haeng Lee, Chan-Mo Yang, Hye-Jin Lee, Sang-Yeol Lee
Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience.2023; 21(1): 118. CrossRef - The development of a lifestyle modification mobile application, “Health for You” for overweight and obese breast cancer survivors in Korea
Su-Jin Seo, Ju-Hee Nho, Youngsam Park
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 243. CrossRef - Development and Effect of the Integrated Health Promotion Program for Cancer Survivors Living at Home
Hee Sang Yoon, Eun A Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2021; 32(1): 51. CrossRef - Adjustment to life with metastatic cancer through psychodrama group therapy: A qualitative study in Turkey
Songül Kamışlı, Bahar Gökler
Perspectives in Psychiatric Care.2021; 57(2): 488. CrossRef - Integration of longitudinal psychoeducation programmes during the phases of diagnosis, management and survivorship of breast cancer patients: A narrative review
Athena Michaelides, Constantina Constantinou
Journal of Cancer Policy.2020; 23: 100214. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Mastectomy for Breast Cancer
Kavitha Konnakkaparambil Ramakrishnan, Sreekumar Damodaran
Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and Healthcare.2020; 7(28): 1368. CrossRef - Mediating and Moderating Factors of Adherence to Nutrition and Physical Activity Guidelines, Breastfeeding Experience, and Spousal Support on the Relationship between Stress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Survivors
Nam Mi Kang, Won-Ho Hahn, Suyeon Park, Jung Eun Lee, Young Bum Yoo, Chung Ja Ryoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(20): 7532. CrossRef - Uncertainty and unmet care needs before and after surgery in patients with gastric cancer: A survey study
Ji Yea Lee, Yeonsoo Jang, Sanghee Kim, Woo Jin Hyung
Nursing & Health Sciences.2020; 22(2): 427. CrossRef - Effects of Different Exercise Interventions on Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tetiana Odynets, Yuriy Briskin, Valentina Todorova
Integrative Cancer Therapies.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,840
View
-
41
Download
-
13
Crossref
-
Development and Validation of the Cancer-Specific Posttraumatic Growth Inventory
-
Young-Mi Jung, Jin-Hee Park
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(3):319-331. Published online January 15, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.3.319
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to develop a scale to evaluate posttraumatic growth in patients with cancer and to examine the validity and reliability of the scale.
Methods
A literature review, semi-structured patient interviews and an expert panel consultation produced a 27 preliminary item questionnaire. Participants were 150 cancer patients recruited to test the reliability and validity of the preliminary scale. Data were analyzed using item analysis, exploratory factor analysis, convergent validity and internal consistency.
Results
Item reduction and exploratory factor analysis led to 23 items, grouped into five subscales which were labelled new possibilities (6 items), coping skills (5 items), preciousness of life (5 items), relating to others (4 items), and personal strength (3 items). Convergent validity was evaluated by total correlation with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-General (r=.45, p<.001). The final scale demonstrated satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach's a =.94).
Conclusion
Findings from this study indicate that the Cancer-Specific Posttraumatic Growth Inventory has validity and reliability and is considered to be appropriate for assessing posttraumatic growth in patients with cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Transcultural adaptation and Mexican validation of the posttraumatic growth inventory (PTGI-X-Mx) in a palliative oncology population
Leticia Ascencio Huertas, Fernando Austria Corrales, Claudia Iveth Astudillo García, Carlos Alejandro García Benitez, Silvia Allende-Pérez
Palliative and Supportive Care.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efecto de un nuevo modelo de gestión de la organización de enfermería basado en la investigación apreciativa en pacientes con tumores ginecológicos en el periodo perioperatório
Chuntao Fang, Jing Yang
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of a new nursing organization management mode constructed by appreciative inquiry on gynecological tumor patients in the perioperative period
Chuntao Fang, Jing Yang
Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da USP.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer Coping, Family Support, and Posttraumatic Growth in Female Genital Cancer Patients
Hee Nam An, Jeong Hye Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2023; 23(1): 38. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Post-Traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer Based on a Model of Post-Traumatic Growth
Hee Yeon Park, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 65. CrossRef - Psychometric property of an instrument 1: content validity
Eun-Hyun Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(1): 10. CrossRef - Impact of Posttraumatic Growth and Health Promoting Behavior on Quality of Life in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Mi-Ae Kim, Hyun-Ju Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2021; 28(1): 32. CrossRef - The Development and Validation of a Perceived Nursing Support Scale for Mothers of Preterm Infants
Mihae Im, Jina Oh
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(5): 317. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth of Gynecologic Oncology Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Sun Jeong Yun, Hye Young Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2019; 25(4): 409. CrossRef - Psychosocial Adjustment in Korean Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyejin Sun, Jia Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(5): 545. CrossRef - Development of a revised model of posttraumatic growth in the contexts of leisure and sport
Se-Hyuk Park
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2018; : 237. CrossRef
-
2,213
View
-
47
Download
-
11
Crossref
-
Effects of Psychoeducational Intervention for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(2):143-163. Published online April 28, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.2.143
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material
-
Purpose
This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis designed to investigate effects of psychoeducational intervention for cancer survivors.
Methods
Ten databases were searched. Two reviewers independently performed the selection of the studies, data extraction and assessment. The risk of bias was assessed using Cochrane Collaboration's tool. To estimate the effect size, meta-analysis of the studies was performed using Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and RevMan programs.
Results
Of 18,781 publications identified, 35 met inclusion criteria, and 25 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychoeducational intervention. Effect sizes (standardized mean difference [SMD]) were heterogeneous and random effects models were used in the analyses. Psychoeducational intervention was effective for quality of life (n=2,410, ES=0.23; 95% CI: 0.09~0.37), coping and self-efficacy (n=179, ES=0.68; 95% CI: 0.26~1.11), anxiety (n=1,786, ES=-0.26; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.15), depression (n=1,910, ES=-0.28; 95% CI: -0.37~-0.18), and psychological distress (n=2,242, ES=-0.31; 95% CI: -0.46~-0.17). Subgroup analysis showed that counseling was the most effective intervention for quality of life, and behavioral therapy was an effective intervention for all positive and negative outcomes. Publication bias was not detected except for psychological distress.
Conclusion
Psychoeducational intervention appears to be effective in improving quality of life and coping and self-efficacy, and it is effective in reducing psychological symptoms in cancer survivors. Behavioral therapy, especially, is commonly effective in improving psychosocial outcomes. However, low-quality evidence, variability in the designs of existing studies, and publication bias suggest that additional high-quality trials should be conducted in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Factors associated with post-treatment smoking among a diverse sample of cancer survivors in the US
Safa Elkefi, Corina T. Lelutiu-Weinberger, Jean-Marie Bruzzese, Alicia K. Matthews
Discover Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Group‐Based Support Interventions for Adolescents and Young Adults With Lymphoma: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Dalnim Cho, Sairah Ahmed, Stella Snyder, Juliet Kroll, Minxing Chen, Michael Roth, Kathrin Milbury
Psycho-Oncology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Mind Health of Persons with Cancer: Psycho-Oncology and Nursing
Park Eun Young
Journal of Clinical Psychooncology.2025; 11(1): 24. CrossRef - Psychosocial interventions for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and motor neuron disease and their caregivers: a scoping review
Juyeon Oh, Jiwon An, Kyongok Park, Youngok Park
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of telemedicine psychoeducational interventions for adults with non‐oncological chronic disease: A systematic review
Carmen Sánchez‐Gutiérrez, Eugenia Gil‐García, Adriana Rivera‐Sequeiros, José M. López‐Millán
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2022; 78(5): 1267. CrossRef - Cancer-Related Psychological Distress in Lymphoma Survivor: An Italian Cross-Sectional Study
Giulia Agostinelli, Barbara Muzzatti, Samantha Serpentini, Michele Spina, Maria Antonietta Annunziata
Frontiers in Psychology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of the Advanced Practice Nurse-Led Psychoeducational Program for Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hye Kyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(3): 245. CrossRef - Effects of Nurse-Led Intervention Programs Based on Goal Attainment Theory: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Bom-Mi Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(6): 699. CrossRef - Effects of Psychosocial Interventions on Physical Function and Depression in Stroke Patients: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Jinhyang YANG, Changwan KANG, Hye-Won PARK, Euna PARK
JOURNAL OF FISHRIES AND MARINE SCIENCES EDUCATION.2021; 33(2): 396. CrossRef - Development of A Nurse-Led Educational Intervention Program in Managing the Nutrition Impact Symptom Cluster in Patients with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma following the Medical Research Council Framework
Wenli Xiao, Carmen W Chan, Jinnan Xiao, Cho L Wong, Ka M Chow
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 8(6): 653. CrossRef - Chemotherapy Education and Support: A Model for Use in the Ambulatory Care Setting
Terri Jabaley, Patricia Rizzo, Nina Grenon, Clare Sullivan, Janet Bagley, Maritza Nassif, Renee Siegel, Meghan Underhill-Blazey
Clinical Journal of Oncology Nursing.2020; 24(4): E43. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy for Chronic Pain Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Hee-Sook Kang, Sung-Dong Hwang, Sang-Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2019; 28(3): 271. CrossRef
-
2,111
View
-
35
Download
-
12
Crossref
-
Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Survivors of Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Yong-Sik Jung, Youngmi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2016;46(3):454-462. Published online June 30, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2016.46.3.454
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
Posttraumatic growth (PTG) is defined as 'positive psychological change experienced as a result of a struggle with highly challenging life circumstances'. The purpose of this study was to identify the level of PTG and its correlates in Korean patients with breast cancer.
Methods
A sample of 120 participants was recruited from outpatients, who had successfully completed primary treatment of breast cancer at a university hospital., Data were collected from June to December, 2014 using Posttraumatic Growth Inventory, lllness Intrusiveness Rating Scale, Cancer Coping Questionnaire, Revised Life Orientation Test and The Multidimensional Scale of Perceived Social Support.
Results
Total score for the PTG was 79.18±17.54 in patients surviving breast cancer. Bivariate analyses indicated that PTG was positively associated with having a religion, perceived social support, greater optimism, cancer coping, and illness intrusiveness. Results of the regression analysis showed that cancer coping (β=.29, p=.001), optimism (β=0.28, p=.001) and illness intrusiveness (β=0.17, p=.037) were statistically significant in patients' PTG.
Conclusion
The research findings show that the variables of cancer coping, optimism and illness intrusiveness significantly explain PTG and these psychological variables can be used to provide improvement in PTG for patients with breast cancer
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The influence of locus of control, coping strategies and time perspective on post-traumatic growth in survivors with primary breast cancer
Alexandra-Cristina Paunescu, Marina Kvaskoff, Cyrille Delpierre, Lidia Delrieu, Guillemette Jacob, Myriam Pannard, Marie Préau
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Do caregivers of traumatic brain injury survivors experience post-traumatic growth? A mixed-methods study exploring the positive experiences of informal caregivers
Molly Hillyard, Ryan Westley, Jade Kettlewell, Melissa Brunner
Brain Impairment.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-traumatic growth and its influencing factors in first-episode stroke patients: a cross-sectional study
Minli Hu, Yue Ban, Zhihui Li, Yu He, Liping Deng, Xiaohua Xie
BMC Psychology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Influencing Resilience in Patients with Multiple Myeloma: A Cross-Sectional Study
Hae-Lyeon Jeon, Hye-Ah Yeom
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2024; 36(1): 41. CrossRef - Post-traumatic Growth Experiences of Breast Cancer Survivors: A Grounded Theory Approach
Seung-Kyoung Yang, Young-Suk Park, Eun-Joo Lee
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2024; 9(2): 79. CrossRef - Social Reintegration Experiences of Young Adult Cancer Survivors
Ji Seong Yi, Song Yi Lee
Behavioral Sciences.2024; 14(11): 1101. CrossRef - A Structural Equation Model for Posttraumatic Growth among Cured Patients with COVID-19
Soo Young An, Heejung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(3): 309. CrossRef - Effects of Post Traumatic Growth on Successful Aging in Breast Cancer Survivors in South Korea: The Mediating Effect of Resilience and Intolerance of Uncertainty
Su Jeong Yi, Ku Sang Kim, Seunghee Lee, Hyunjung Lee
Healthcare.2023; 11(21): 2843. CrossRef - Pathways to post-traumatic growth in Korean female cancer patients: the mediation effects of coping strategies and resilience
Sumi Choi, Dongil Kim, Ahyoung Cho, Sohyun An, Changhyun Kim, Inhwa Yoo
European Journal of Psychotraumatology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Structural Equation Model for Psychosocial Adjustment of Breast Cancer Survivors Based on Family Resilience Model
Jiyoung Seo, Myungsun Yi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2022; 34(2): 178. CrossRef - Cancer coping, healthcare professionals’ support and posttraumatic growth in brain-tumor patients
Jiyoung Kim, Nayeon Shin
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2022; 27(4): 780. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Post-Traumatic Growth in Patients with Breast Cancer Based on a Model of Post-Traumatic Growth
Hee Yeon Park, Ja Yun Choi
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 65. CrossRef - Factors influencing posttraumatic growth in ovarian cancer survivors
Jeong Min Oh, Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
Supportive Care in Cancer.2021; 29(4): 2037. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Supportive Care Needs of Colorectal Cancer Survivors
Hyekyung Kim, Yang-Sook Yoo
Asian Nursing Research.2021; 15(1): 60. CrossRef - Factors associated with post-traumatic growth in male patients with rectal cancer: A cross-sectional study
Yuri Kim, Yoonjung Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2021; 54: 102028. CrossRef - A Structural Model on the Post-Traumatic Growth of Police Officers
Seung Woo Han, Eun Suk Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2020; 31(3): 348. CrossRef - Stacking Ensemble Technique for Classifying Breast Cancer
Hyunjin Kwon, Jinhyeok Park, Youngho Lee
Healthcare Informatics Research.2019; 25(4): 283. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Posttraumatic Growth in Cancer Survivors
Jeong-Sook Park, You-Jeong Kim, Young-Seun Ryu, Mi-Hyang Park
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(1): 30. CrossRef - The relationship between cancer‐related worry and posttraumatic growth in adolescent and young adult cancer survivors
Glynnis A. McDonnell, Alice W. Pope, Tammy A. Schuler, Jennifer S. Ford
Psycho-Oncology.2018; 27(9): 2155. CrossRef - The Influence of Spiritual Well-Being, Self-Esteem, and Perceived Social Support on Post-Traumatic Growth among Breast Cancer Survivors
Eun Young Seo, Suhye Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(4): 232. CrossRef
-
1,544
View
-
16
Download
-
20
Crossref
-
Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2015;45(1):118-128. Published online February 27, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2015.45.1.118
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
Evidence suggests that some patients with breast cancer experience cognitive difficulties following chemotherapy. This longitudinal study was done to examine the prevalence of cognitive impairment and trajectory of cognitive function over time in women with breast cancer, who received adjuvant chemotherapy.
Methods
Participants were 137 patients with breast cancer. They completed neuropsychological tests and the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Cognitive Function before adjuvant therapy (pretest), toward the end of adjuvant therapy (posttest), and 6 months after the completion of adjuvant therapy (follow-up test). Of the patients, 91 were treated with adjuvant chemotherapy and 46 patients who did not receive chemotherapy made up the comparison group. A reliable-change index and repeated-measure ANOVA were used for statistical analyses.
Results
At the posttest point, over 30% of patients showed complex cognitive impairment and reported greater difficulty in subjective cognitive function. At the follow-up test point, 22.0% of patients exhibited complex cognitive impairment and 30.8% of patients complained of subjective cognitive impairment. Repeated-measure ANOVA showed significant decreases after receiving chemotherapy followed by small improvements 6 months after the completion of chemotherapy in cognitive domains of change for attention and concentration, memory, executive function, and subjective cognitive function.
Conclusion
These results suggest that chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer may be associated with objective and subjective cognitive impairments. Further studies are needed to explore the potential risk factors and predictor of chemotherapy-related cognitive changes. Also nursing interventions for prevention and intervention of cognitive impairments should be developed and tested.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Impact of nonpharmacological interventions on cognitive impairment in women with breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jin-Hee Park, Su Jin Jung, Lena J. Lee, Junghyun Rhu, Sun Hyoung Bae
Asia-Pacific Journal of Oncology Nursing.2023; 10(4): 100212. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Self-reported Memory Problems of Adult Cancer Survivors Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019
Sangjin Ko
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 51. CrossRef - Brain network deficits in breast cancer patients after early neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A longitudinal MRI study
Jing Yang, Yongchun Deng, Daihong Liu, Yong Tan, Meng Lin, Xiaoyu Zhou, Jing Zhang, Hong Yu, Yixin Hu, Yu Tang, Shixi Jiang, Jiuquan Zhang
Journal of Neuroscience Research.2023; 101(7): 1138. CrossRef - Frailty and its associated factors among older adults with cancer undergoing chemotherapy as outpatients: A cross-sectional study
Misun Jeon, Hyoeun Jang, Arum Lim, Sanghee Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2022; 60: 102192. CrossRef - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Distinct sleep disturbance and cognitive dysfunction profiles in oncology outpatients receiving chemotherapy
Vivian Huang, Lynda Mackin, Kord M. Kober, Steven M. Paul, Bruce A. Cooper, Yvette P. Conley, Marilyn J. Hammer, Jon D. Levine, Christine Miaskowski
Supportive Care in Cancer.2022; 30(11): 9243. CrossRef - Measurement, outcomes and interventions of cognitive function after breast cancer treatment: A narrative review
Miaomiao Jia, Xiaojun Zhang, Liyuan Wei, Jinnan Gao
Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology.2021; 17(4): 321. CrossRef - Improving preoperative breast reconstruction consultations: a qualitative study on the impact of personalised audio-recordings
Josipa Petric, Bahara Sadri, Phillipa van Essen, Nicola Ruth Dean
BMC Women's Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Study on Neurologic and Cognitive Dysfunction in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy with Resting State fMRI
Fenshan Zheng, Peiying Cao, Jie Zhou, Chunyu Li, John Norris
World Neurosurgery.2021; 149: 388. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Computerized programs for cancer survivors with cognitive problems: a systematic review
Yoonjung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2019; 13(6): 911. CrossRef - Cancer treatment effects on cognition and depression: The moderating role of physical activity
Margaret F. Bedillion, Emily B. Ansell, Gwendolyn A. Thomas
The Breast.2019; 44: 73. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Depression following Chemotherapy in Women with Breast Cancer: A Prospective Study
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee, Hyun Ah Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2018; 18(2): 66. CrossRef - Mulheres Submetidas à Quimioterapia e suas Funções Cognitivas
Camila Vasconcelos Carnaúba Lima, Raner Miguel Ferreira Póvoa
Psicologia: Ciência e Profissão.2017; 37(4): 970. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-induced prospective memory impairment in breast cancer patients with different hormone receptor expression
Wen Li, Chen Gan, Yue Lv, Shanghu Wang, Huaidong Cheng
Medicine.2017; 96(13): e6514. CrossRef - Altered network efficiency of functional brain networks in patients with breast cancer after chemotherapy
Han Xuan, Chen Gan, Wen Li, Zhonglian Huang, Longsheng Wang, Qianqian Jia, Zhendong Chen, Huaidong Cheng
Oncotarget.2017; 8(62): 105648. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - Effect of Cancer Symptoms and Fatigue on Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Depression in People with Gastrointestinal Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Jung Ran Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(3): 420. CrossRef - A review of traditional Korean medical treatment for cancer-related cognitive impairment
Hye-Yoon Lee, Jung-Eun Kim, Mikyung Kim, Joo-Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Medicine.2016; 37(3): 74. CrossRef - Cognitive outcome after radiotherapy in brain tumor
Thomas Durand, Marie-Odile Bernier, Isabelle Léger, Hervé Taillia, Georges Noël, Dimitri Psimaras, Damien Ricard
Current Opinion in Oncology.2015; 27(6): 510. CrossRef - Changes of Symptom Distress and Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients Receiving Adjuvant Therapy
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Young-Mi Jung
Asian Oncology Nursing.2015; 15(2): 67. CrossRef
-
1,418
View
-
12
Download
-
21
Crossref
-
A Meta-analysis of Chemotherapy related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2012;42(5):644-658. Published online October 12, 2012
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2012.42.5.644
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the cognitive effects of chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
Methods
Using several databases, prospective studies were collected up to August 2011. Of 2,106 publications identified, 12 met the inclusion criteria, and 8 studies were used to estimate the effect size of chemotherapy on cognitive impairment.
Results
Twelve studies were done since 2005 and most of the research was performed in Europe or North America. Eight studies were used to generate effect size across the cognitive domains of attention/concentration, verbal and visual memory, executive function, visuospatial skill, language, and subjective cognitive function. Each of the cognitive domains showed small effect sizes (-0.02 ~ -0.26), indicating diminished cognitive function for the chemotherapy group compared with non-chemotherapy groups.
Conclusion
Finding suggests that breast cancer patients who undergo chemotherapy may experience mild cognitive decline. Further study is needed to generate knowledge and guideline for interventions to address chemotherapy related cognitive impairment in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Experience of Chemotherapy Related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Cancer
Pok Ja Oh, Ji Hyun Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(1): 1. CrossRef - Effects of smart-care services program for breast cancer survivors
Bok Yae Chung, Sung Jung Hong
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(2): 95. CrossRef - Changes of Cognitive Function and Fatigue following Chemotherapy in Patients with Gastrointestinal Cancer: A Prospective Controlled Study
Pok-Ja Oh, Sun Mi Moon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2019; 19(3): 126. CrossRef - Effects of compensatory cognitive training intervention for breast cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a pilot study
Jin-Hee Park, Yong Sik Jung, Ku Sang Kim, Sun Hyoung Bae
Supportive Care in Cancer.2017; 25(6): 1887. CrossRef - Impact of Cognitive Function and Cancer Coping on Quality of Life among Women with Post-chemotherapy Breast Cancer
Yoon Jung Kim, Sook Jung Kang
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2016; 22(3): 182. CrossRef - Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment and Quality of Life in People with Colon Cancer: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Distress
Pok Ja Oh, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2016; 46(1): 19. CrossRef - QLU-C10D: a health state classification system for a multi-attribute utility measure based on the EORTC QLQ-C30
M. T. King, D. S. J. Costa, N. K. Aaronson, J. E. Brazier, D. F. Cella, P. M. Fayers, P. Grimison, M. Janda, G. Kemmler, R. Norman, A. S. Pickard, D. Rowen, G. Velikova, T. A. Young, R. Viney
Quality of Life Research.2016; 25(3): 625. CrossRef - The Impact of Cancer on Psychological and Social Outcomes
Daniel Sj Costa, Rebecca Mercieca‐bebber, Claudia Rutherford, Liam Gabb, Madeleine T King
Australian Psychologist.2016; 51(2): 89. CrossRef - Prevalence and Characteristics of Chemotherapy-related Cognitive Impairment in Patients with Breast Cancer
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae, Yong-Sik Jung, Young-Mi Jung
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(1): 118. CrossRef
-
1,191
View
-
5
Download
-
9
Crossref
-
A Systematic Review of Psychological Distress as a Risk Factor for Recurrent Cardiac Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
-
Jin-Hee Park, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):704-714. Published online October 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.704
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to determine whether psychological distress is an independent risk factor for recurrent cardiac events in patients with coronary artery disease (CAD).
Methods
A prospective cohort of studies that measured psychological distress and the incidence of recurrent cardiac events in the adult population were included. Three computerized databases were assessed (PubMed, CINAHL, and PSYCINFO). Meta-analysis was conducted using a random-effects model to determine summary estimates of risks of major recurrent cardiac events associated with each psychological distress. Of 506 publications identified, 33 met inclusion criteria, and 24 studies were used to estimate effect size of psychological distress on recurrent cardiac events.
Results
Mean number in the research sample was 736 and mean time of follow-up was 4.0 years. Depression, anxiety, anger, and hostility as psychological factors were studied. According to estimation of effect size using random model effect, depression (OR=1.39, 95% CI: 1.22-1.57), anxiety (OR=1.22, 95% CI: 0.96-1.56), and anger/hostility (OR=1.29, 95% CI: 1.07-1.57) CAD patients in significantly increased risk for recurrent cardiac events.
Conclusion
Finding suggests that psychological distress in forms of depression, anxiety, anger, and hostility impact unfavorably on recurrent cardiac events in CAD patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - NAMS task force report on mental stress
Rajesh Sagar, Kaushik Chatterjee, Sandeep Thareja, Anurag Timothy, A.S. Yadav, Prateek Yadav, Rajinder Dhamija, S.V. Madhu, Preethy Kathiresan, Pratibha Prasad, Swati Kedia Gupta, Kalpana Srivastava
Annals of the National Academy of Medical Sciences (India).2025; 61: 66. CrossRef - Impact of Type D Personality and Health Literacy on Resilience of Inpatients with Cardiovascular Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study
Da Eun Kim, Seon Young Hwang
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2023; 35(1): 23. CrossRef - The Effect of Perceived Stress, Fine Dust Risk Perception, and Resilience on Stress Response in Patients with Respiratory and Circulatory Disorders
Jin-Hee Park, Kuem-Sun Han
STRESS.2021; 29(1): 21. CrossRef - Associations of depression and anxiety with cardiovascular risk among people living with HIV/AIDS in Korea
Kyong Sil Park, Seon Young Hwang, Bo Youl Choi, June Kim, Sang Il Kim, Woo-Joo Kim, Chun Kang
Epidemiology and Health.2020; 43: e2021002. CrossRef - Impact of Type D Personality on Depression, Anxiety, and Health-related Quality of Life among Coronary Artery Disease Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Sun Hyoung Bae, Jin-Hee Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 219. CrossRef - Analysis of the relationship between community characteristics and depression using geographically weighted regression
Hyungyun Choi, Ho Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2017; 39: e2017025. CrossRef - Influencing Effects of Type D Personality on Symptom Experiences and Quality of Life in Patients with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Eun Hee Jo, Sun Hee Han, Myung Ha Lee, Sung Reul Kim
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(5): 536. CrossRef - Depression and Anxiety as Predictors of Recurrent Cardiac Events 12 Months After Percutaneous Coronary Interventions
Jin-Hee Park, Seung-Jea Tahk, Sun Hyoung Bae
Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing.2015; 30(4): 351. CrossRef - Anger, anger expression, cardiovascular risk factors, and gastrointestinal symptoms by hwa-byung symptoms in Korean adult women
Young-Joo Park, Sook-Ja Lee, Nah-Mee Shin, Hyunjeong Shin, Hyun Cheol Kang, Yoon Tae Jin, Song I. Jeon, Inhae Cho
Applied Nursing Research.2015; 28(4): 398. CrossRef - Risk Factor–tailored Small Group Education for Patients with First-time Acute Coronary Syndrome
Seon Young Hwang, Jin Shil Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2015; 9(4): 291. CrossRef - Influences of Knowledge, Self-efficacy, and Social Support on Sick Role Behavior in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Soonhee Kim, Sunhee Lee
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2014; 28(2): 228. CrossRef - Factors Influencing the Quality of Life in Low- Income Elders Living at Home: A Literature Review
Chung-Min Cho
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2013; 27(2): 372. CrossRef - Effects of a psychoeducational intervention for secondary prevention in Korean patients with coronary artery disease: A pilot study
Jin‐Hee Park, Seung‐Jae Tahk, Sun Hyoung Bae, Youn‐Jung Son
International Journal of Nursing Practice.2013; 19(3): 295. CrossRef - Stress and cardiovascular disease
Jung Jin Cho
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2013; 56(6): 462. CrossRef
-
1,326
View
-
11
Download
-
14
Crossref
-
The Effects of Case-Based Learning Using Video on Clinical Decision Making and Learning Motivation in Undergraduate Nursing Students
-
Moon-Sook Yoo, Jin-Hee Park, Si-Ra Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(6):863-871. Published online December 31, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.6.863
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of case-base learning (CBL) using video on clinical decision-making and learning motivation.
Methods
This research was conducted between June 2009 and April 2010 as a nonequivalent control group non-synchronized design. The study population was 44 third year nursing students who enrolled in a college of nursing, A University in Korea. The nursing students were divided into the CBL and the control group. The intervention was the CBL with three cases using video. The controls attended a traditional live lecture on the same topics. With questionnaires objective clinical decision-making, subjective clinical decision-making, and learning motivation were measured before the intervention, and 10 weeks after the intervention.
Results
Significant group differences were observed in clinical decision-making and learning motivation. The post-test scores of clinical decision-making in the CBL group were statistically higher than the control group. Learning motivation was also significantly higher in the CBL group than in the control group.
Conclusion
These results indicate that CBL using video is effective in enhancing clinical decision-making and motivating students to learn by encouraging self-directed learning and creating more interest and curiosity in learning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effect of a Hybrid Simulation-based Patient Safety Education Program on Patient Safety Knowledge, Attitudes, Performance Confidence and Decision-Making Abilities in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Hyun-Sook Jeong, Mi Yang Jeon
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2025; 32(4): 432. CrossRef - Advancing Healthcare Education: A Comprehensive Review of Case-based Learning
T. Safiya Sultana, R. Mrinal Gite, D. Akshaya Tawde, Chandrakanth Jena, Karishma Khatoon, Mitali Kapoor
Indian Journal of Continuing Nursing Education.2024; 25(1): 36. CrossRef - Örnek Olay Eğitim Yönteminin Hemşirelik Eğitimi Açısından Öneminin Belirlenmesi ve Hemşirelikte Yönetim Eğitimine Bakış Açısı Kazandırılması: Bir Sistematik Derleme
Aysun Yerköy Ateş, Samet Yerköy
Hemşirelik Bilimi Dergisi.2024; 7(2): 130. CrossRef - The effect of case‐based teaching method on professional competence and clinical decision‐making levels of public health nursing students: A sequential explanatory mixed‐methods study
Adem Sümen, Derya Adibelli
Public Health Nursing.2024; 41(3): 446. CrossRef - The development and effects of an online-based community psychiatric nursing practice program with the ARCS model
Pan Heui Kim, Hee Sook Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(1): 5. CrossRef - The Impact of Online Learning Methods on Nursing Students' Motivation During the Covid-19 Pandemic: A Mixed Method Study
Nihal Yıldız Emre, İnci Mercan Annak, Keziban Öztürk, Nevra Kalkan, Burcu Opak Yücel, Burçin Irmak, Hülya Bulut, Sevil Güler
Middle Black Sea Journal of Health Science.2024; 10(2): 127. CrossRef - Video-based approaches in health education: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mariana Morgado, João Botelho, Vanessa Machado, José João Mendes, Olusola Adesope, Luís Proença
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Case-based Learning Video and Learning Motivation among Midwifery Students
Ulfa Farrah Lisa, Feri Anita Wijayanti
EMBRIO.2023; 15(1): 75. CrossRef - Effects of Situation-Based Flipped Learning and Gamification as Combined Methodologies in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Haeran Kim, Boyoung Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(4): 644. CrossRef - The experiences of nursing master's students with dialogic case-based learning in an evidence-based nursing course: A qualitative study
Jiannan Yao, Xiuying Zhang, Hui Xue, Mingyue Zhu, Jia Wang, Qiuchen Wang, Zhiming Chen, Hua Yuan
Nurse Education Today.2022; 114: 105395. CrossRef - The Effect of Cine-education Method on Mental Diseases Beliefs and Stigmatization Tendency in Student Nurses
Burcu DEMİR GÖKMEN, Metin YILDIZ
Turkish Journal of Science and Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The mediating effect of self-efficacy on the relationship between social anxiety and communication ability in nursing students
Mi-Jin You, Hye-Sook Han
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 298. CrossRef - Evaluation and analysis of the effect of continuing education on nurses' physical restraint knowledge, attitude, and behavior
Luo Yang, Ling Tang, Hong Guo, Yan-Ling Shen, Li Li, Qing-Xia Liu, Hai-Yan Wang, Yan-Juan Liu
Journal of Integrative Nursing.2020; 2(1): 11. CrossRef - Uzun Vaka Olarak Sinema Filmlerinin Kullanımına Bir Örnek: The Doctor
Müesser ÖZCAN, Edip Güvenç ÇEKİÇ, Ümmühani ÖZEL TÜRKCÜ, Hülya ELBE
Tıp Eğitimi Dünyası.2019; 18(54): 63. CrossRef - Practice and effectiveness of “nursing case-based learning” course on nursing student's critical thinking ability: A comparative study
Shasha Li, Xuchun Ye, Wenting Chen
Nurse Education in Practice.2019; 36: 91. CrossRef - Examining the impact of case-based learning on student engagement, learning motivation and learning performance among university students
Syed Ali Raza, Wasim Qazi, Bushra Umer
Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education.2019; 12(3): 517. CrossRef - Development and Effects of E-Learning Program for Clinical Questioning in Evidence-Based Practice Using Case-Based Animation for Nurses
Miri Jeong, Myonghwa Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2018; 30(6): 643. CrossRef - Effects of Communication Empowerment Program Based on Situated Learning Theory for Nursing Students
Soo Jin Kim, Boyoung Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 708. CrossRef - Using Quick Response Codes to Increase Students' Participation in Case-Based Learning Courses
Kai-Yin Lin, Daniel Chia-En Teng
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2018; 36(11): 560. CrossRef - The impact of using standardized patients in psychiatric cases on the levels of motivation and perceived learning of the nursing students
Gamze Sarikoc, Celale Tangul Ozcan, Melih Elcin
Nurse Education Today.2017; 51: 15. CrossRef - Comparison of the effectiveness of two styles of case-based learning implemented in lectures for developing nursing students’ critical thinking ability: A randomized controlled trial
Shaohua Hong, Ping Yu
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2017; 68: 16. CrossRef - An Effect of the Application of Educational Electronic Nursing Record System for Nursing Students
Se Young Kim, Insook Lee, Shinmi Kim, Kisook Kim, Bohyun Park, Yoon Goo Noh
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2016; 22(3): 396. CrossRef - The Influence of Case-Based Learning using video In Emergency care of infant and toddlers
Hye-Young Cho, Kyoung-Ah Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2016; 17(12): 292. CrossRef - DIJITAL ÖRNEK OLAYA DAYALI ÖĞRENME YAKLAŞIMININ ÖĞRETMEN ADAYLARININ AKDADEMIK GÜDÜLENMELERI ÜZERINDEKI ETKISI
ilker KÖSTERELİOĞLU, Fatih SALTAN, Meltem AKIN KÖSTERELİOĞLU
Hitit Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effects of Case-Based Learning (CBL) on Learning Motivation and Learning Satisfaction of Nursing Students in a Human Physiology Course
Na Hyun Kim, Ji Yeon Park, Sang Eun Jun
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2015; 17(1): 78. CrossRef - Effects of case‐based learning on communication skills, problem‐solving ability, and learning motivation in nursing students
Moon‐Sook Yoo, Hyung‐Ran Park
Nursing & Health Sciences.2015; 17(2): 166. CrossRef - Effects of Case-Based Learning on Clinical Decision Making and Nursing Performance in Undergraduate Nursing Students*
Mi-Eun Jeong, Hyoung-Sook Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2015; 22(3): 308. CrossRef - Effects of Basic Clinical Practice Program in Academic Motivation, Critical Thinking and Clinical Nursing Competence of Nursing Students
In-Soon Seo, Su-Min Oh, Dongwon Choi, Hee-Ok Park, Rye-Won Ma
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2014; 15(4): 2276. CrossRef - Effects of a Blended Learning Program on Ethical Values in Undergraduate Nursing Students
Sang Dol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2014; 20(5): 567. CrossRef - Using student produced videos to increase knowledge of self-care topics and nonprescription medications
Jeanne E. Frenzel, Elizabeth T. Skoy, Heidi N. Eukel
Currents in Pharmacy Teaching and Learning.2013; 5(1): 44. CrossRef - The Development and Evaluation of a New Educational Program, Introduction to Clinical Nursing, for Third Year Nursing Students
Kyung-Ae Song, Hyun-Jung Park, Hye-A Yeom, Jong-Eun Lee, Ga-Eul Joo, Hee-Ju Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 322. CrossRef
-
1,718
View
-
29
Download
-
31
Crossref
-
Factors Influencing Relocation Stress Syndrome in Patients Following Transfer from Intensive Care Units
-
Jin-Hee Park, Moon-Sook Yoo, Youn-Jung Son, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(3):307-316. Published online June 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.3.307
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the levels of relocation stress syndrome (RSS) and influencing the stress experienced by Intensive Care Unit (ICU) patients just after transfer to general wards.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 257 patients who transferred from the intensive care unit. Data were collected through self-report questionnaires from May to October, 2009. Data were analyzed using the Pearson correlation coefficient, t-test, one-way ANOVA, and stepwise multiple linear regression with SPSS/WIN 12.0.
Results
The mean score for RSS was 17.80±9.16. The factors predicting relocation stress syndrome were symptom experience, differences in scope and quality of care provided by ICU and ward nursing staffs, satisfaction with transfer process, length of stay in ICU and economic status, and these factors explained 40% of relocation stress syndrome (F=31.61, p<.001).
Conclusion
By understanding the stress experienced by ICU patients, nurses are better able to provide psychological support and thus more holistic care to critically ill patients. Further research is needed to consider the impact of relocation stress syndrome on patients' health outcomes in the recovery trajectory.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - A phenomenological study on the experiences of patient transfer from the intensive care unit to general wards
Eun-Young Lee, Jin-Hee Park, Alvisa Palese
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(7): e0254316. CrossRef - Development and psychometric evaluation of the Relocation Stress Syndrome Scale-Short Form for patients transferred from adult intensive care units to general wards
Mi Hwa Won, Youn-Jung Son
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2020; 58: 102800. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Transition Nursing Program for Patients and Family Caregivers at a Neurological ICU in Korea
Sun Hee Yun, Eui Geum Oh, Yang Sook Yoo, So Sun Kim, Yeon Soo Jang
Clinical Nursing Research.2017; 26(1): 27. CrossRef - The Effects of Aromatherapy on Intensive Care Unit Patients’ Stress and Sleep Quality: A Nonrandomised Controlled Trial
Eun Hee Cho, Mi-Young Lee, Myung-Haeng Hur, Nativ Dudai
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - A tailored relocation stress intervention programme for family caregivers of patients transferred from a surgical intensive care unit to a general ward
Seul Lee, HyunSoo Oh, YeonOk Suh, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2017; 26(5-6): 784. CrossRef - Clinical validity of a relocation stress scale for the families of patients transferred from intensive care units
HyunSoo Oh, Seul Lee, JiSun Kim, EunJu Lee, HyoNam Min, OkJa Cho, WhaSook Seo
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2015; 24(13-14): 1805. CrossRef
-
1,427
View
-
12
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Factors Influencing Learning Achievement of Nursing Students in E-learning
-
Jin-Hee Park, Eunha Lee, Sun Hyoung Bae
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(2):182-190. Published online April 30, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.2.182
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
This study was done to identify self-directed learning readiness, achievement goal orientations, learning satisfaction and learning achievement, and to evaluate the factors affecting learning achievement for nursing students using a web-based Health Assessment e-Book.
Methods
The research design was a cross-sectional study with a structured questionnaire and data were collected before using the web-based Health Assessment e-Book and 1 week after finishing. The participants were 80 nursing students who were taking the Health Assessment class from March to June 2009.
Results
Mean score for subjective learning achievement was 31.26 and for objective learning achievement, 69.25. Subjective and objective learning achievement were positively correlated with self-directed learning readiness, mastery goal, attitude toward distance education, and learning satisfaction. In subjective learning achievement, learning satisfaction and mastery goal were significant predictive factors and explained 64% of the variance. Objective learning achievement was significantly predicted by learning satisfaction and self-directed learning readiness, which explained 24% of the variance.
Conclusion
Learning satisfaction, mastery goal and self-directed learning readiness were found to be very important factors associated with learning achievement for nursing students using a web-based Health Assessment e-Book. To provide high quality and effective web-based courses and to improve nursing students' learning achievement and learning satisfaction, educators should consider the learner's characteristics from the initial stages of lecture planning.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Exploring the effectiveness of different “escape room simulation teaching” methods on clinical preceptors’ knowledge and skills in judging and handling violent situations in the healthcare profession
Huang-Chin Wu, Han-Jen Hsu, Yi-Ting Chou, Chun-Ju Lin, Chun-Hong Shen, Ruey Chen
Interactive Learning Environments.2025; 33(8): 4932. CrossRef - The effectiveness of 3D cadaver simulation learning on the perceived learning achievement, satisfaction, and flow state of nursing students
Hyeongyeong Yoon
Clinical Simulation in Nursing.2024; 97: 101645. CrossRef - The influence of self-directed learning ability and self-leadership on the learning satisfaction and academic achievement of nursing students who experienced blended learning
Sungjun Kim, Ji Young Lim, Hwasoon Kim, Kyoung Ja Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2024; 30(3): 232. CrossRef - A study on the factors influencing users’ willingness to continue using online learning platforms
Junren Ming, Qiuyu Zhu, Yu Cheng, Ruide Tu, Rong Chen
Procedia Computer Science.2024; 242: 492. CrossRef - Students’ learning preferences for forms and activities – suggestions for academic teachers
Hubert Wojciechowski, Łukasz Hadaś, Roman Domański
Przegląd Organizacji.2023; : 416. CrossRef - HOW ATTITUDES TOWARDS E-LEARNING AFFECTED THE ACADEMIC ACHIEVEMENT DURING THE COVID-19 PANDEMIC: AN EXAMPLE OF A NURSING SKILLS TEACHING
Oznur GURLEK KISACIK, Munevver SONMEZ, Azize OZDAS
Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education.2023; 24(1): 129. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Attitudes of Nursing Students Towards Web-Based Learning and their Readiness for Online Learning
İlkay ÇULHA
Artuklu International Journal of Health Sciences.2023; 3(3): 253. CrossRef - The effects of collaborative reasoning strategies on improving primary school students’ argumentative decision-making skills
Mohsen Bayat, Seyyed Kazem Banihashem, Omid Noroozi
The Journal of Educational Research.2022; 115(6): 349. CrossRef - Academic Success of Online Learning in Undergraduate Nursing Education Programs in the COVID-19 Pandemic Era
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Ju Jeong
Journal of Professional Nursing.2022; 38: 6. CrossRef - Self-Directed Learning versus Problem-Based Learning in Korean Nurse Education: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Jaehee Jeon, Sihyun Park
Healthcare.2021; 9(12): 1763. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Academic Achievement of Nursing College Students in a Flipped Learning Simulation Practice
Minkyung Gu, Sohyune Sok
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 5970. CrossRef - The Effect of Self-directed Learning Strategies on e-Learning Pre-learning of Nursing Students: Focusing on the Flow Experience
Ju Young Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2020; 27(1): 52. CrossRef - Effects of Flipped Learning on the Critical Thinking Disposition, Academic Achievement and Academic Self-efficacy of Nursing Students: A Mixed Methods Study
Ju Cha, Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2020; 26(1): 25. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Students’ Preferences for Online and Blended Learning:
Motivational vs. Cognitive
Sinan Keskin, Halil Yurdugül
European Journal of Open, Distance and E-Learning.2020; 22(2): 72. CrossRef - Measuring Teachers-As-Learners’ Digital Skills and Readiness to Study Online for Successful e-Learning Experience
Evija Mirķe, Sarma Cakula, Lilian Tzivian
Journal of Teacher Education for Sustainability.2019; 21(2): 5. CrossRef - Differences in Non‐Cognitive Factors Influencing the Academic Achievement of Medical and Nursing Students: Focusing on Achievement Goal Orientation and Self‐Regulated Learning
Eun A Park, Kyung Hee Chun
Korean Medical Education Review.2014; 16(1): 32. CrossRef - Academic Achievement, Self-directed Learning, and Critical Thinking Disposition According to Learning Styles of Nursing Students
Sun-Hee Yang, Eun-Ho Ha, Og-Cheol Lee, In-Ok Sim, Young-Mi Park, Hyun-A Nam, Jeong-Sook Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(3): 334. CrossRef - Development and Effects of an e-Learning Program in Operating Room Nursing for Nursing Students
Eun Hee Park, Seon Young Hwang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(1): 36. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Problem Solving Abilities of Freshmen Nursing Students
Yun Min Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2010; 16(2): 190. CrossRef
-
1,803
View
-
151
Download
-
19
Crossref
|