-
Perspectives of parents, teachers, and community leaders on adolescent sexual behavior across ecological contexts in Cambodia: a qualitative study
-
Youngran Yang, Gloria Park
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2026;56(1):108-122. Published online February 25, 2026
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25146
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study investigated the perspectives of parents, teachers, and community leaders regarding adolescents’ sexual behavior in Cambodia.
Methods
Grounded in the ‘ecological framework of adolescent health,’ this study employed a descriptive qualitative approach to explore the perspectives of key stakeholders, including 12 parents, eight teachers, and four community leaders. Drawing on in-depth, semi-structured individual and focus group interviews, the study examined risk and protective factors related to risky sexual behavior across family, school, community, social, cultural, and policy contexts. Data collection was conducted from December 5, 2022 to January 31, 2023.
Results
The integrated thematic analysis revealed six main themes. Parents positioned themselves as anxious protectors but struggled with limited opportunities for open conversation; teachers acted as observe-and-warn mediators, constrained by institutional authority, curricular boundaries, and rapidly shifting youth culture; and community leaders interpreted emerging trends through the lens of social change, eroding traditions, and weakening collective governance. Across groups, participants acknowledged the limitations of unilateral action and advocated for multilevel, collaborative solutions that bridge families, schools, and broader communities.
Conclusion
The study concluded that adolescent sexual behaviors should be understood from diverse perspectives. This finding highlights the need for culturally appropriate and sensitive measures supported by multisectoral systems operating at the family, school, community, civil society (e.g., non-governmental organizations), and national levels.
-
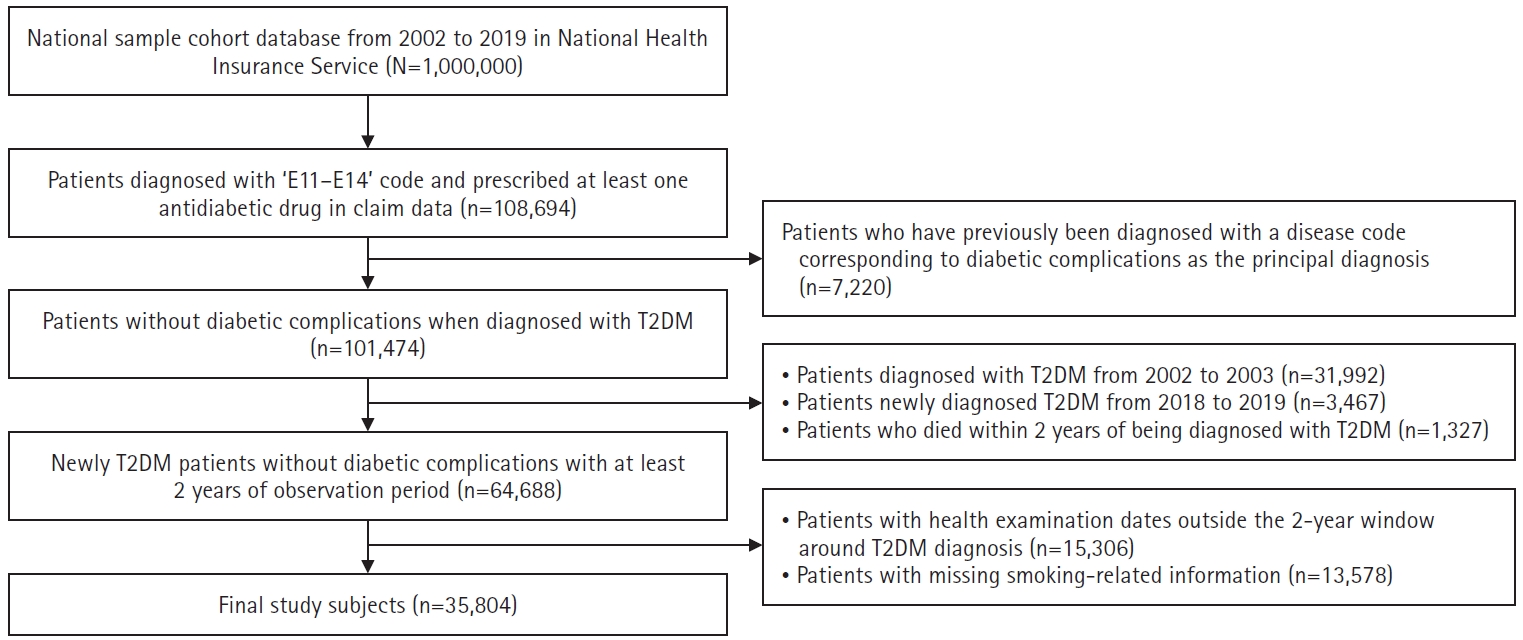
Impact of smoking on diabetes complications: a secondary analysis of the Korean National Health Insurance Service-health screening cohort (2002–2019)
-
Seonmi Yeom, Youngran Yang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):222-235. Published online April 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24109
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to examine the effects of smoking on the incidence of macrovascular and microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods
We analyzed 35,804 patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes between 2004 and 2017 using the Korean National Health Insurance Service–National Health Screening Cohort (2002–2019). Smoking status was categorized into never, former, and current smoking, with further classification based on duration of smoking and daily smoking amount. We conducted survival analysis using a Cox proportional hazards model.
Results
Both former and current smokers had significantly elevated risks of macrovascular complications compared to non-smokers, with hazard ratios (HRs) of 1.60 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.49–1.66) and 1.10 (95% CI, 1.08–1.17), respectively. Long-term smokers (over 30 years) had significantly higher risks of both macrovascular (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.29–1.42) and microvascular complications (HR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.30–1.42). Heavy smokers (over 2 packs/day) more frequently developed macrovascular (HR, 1.46; 95% CI, 1.30–1.64) and microvascular (HR, 1.78; 95% CI, 1.60–1.98) complications than never smokers. Notably, former smokers had increased risks of developing neuropathy (HR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.31–1.49), nephropathy (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.16–1.39), and retinopathy (HR, 1.49; 95% CI, 1.39–1.60).
Conclusion
Patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of smoking are at higher risk of developing macrovascular and microvascular complications. Smoking cessation, along with reducing smoking duration and amount, is crucial for lowering these risks.
-
Factors Influencing Sexual Experiences in Adolescents Using a Random Forest Model: Secondary Data Analysis of the 2019~2021 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey Data
-
Yoonseok Yang, Ju Won Kwon, Youngran Yang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):193-210. Published online May 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23134
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The objective of this study was to develop a predictive model for the sexual experiences of adolescents using the random forest method and to identify the “variable importance.” Methods: The study utilized data from the 2019 to 2021 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Web-based Survey, which included 86,595 man and 80,504 woman participants. The number of independent variables stood at 44. SPSS was used to conduct Rao-Scott χ2 tests and complex sample t-tests. Modeling was performed using the random forest algorithm in Python. Performance evaluation of each model included assessments of precision, recall, F1-score, receiver operating characteristics curve, and area under the curve calculations derived from the confusion matrix.
Results
The prevalence of sexual experiences initially decreased during the COVID-19 pandemic, but later increased. “Variable importance” for predicting sexual experiences, ranked in the top six, included week and weekday sedentary time and internet usage time, followed by ease of cigarette purchase, age at first alcohol consumption, smoking initiation, breakfast consumption, and difficulty purchasing alcohol.
Conclusion
Education and support programs for promoting adolescent sexual health, based on the top-ranking important variables, should be integrated with health behavior intervention programs addressing internet usage, smoking, and alcohol consumption. We recommend active utilization of the random forest analysis method to develop high-performance predictive models for effective disease prevention, treatment, and nursing care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Gender differences in the associations among adolescent problem behaviors: a secondary data analysis of the 2023 Korea Youth Risk Behavior Survey
Jaeyoung Lee, So Yeon Park
Child Health Nursing Research.2025; 31(3): 155. CrossRef
-
4,030
View
-
70
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Moderating the Effects of Health Behaviors on Sexual Intercourse among Adolescents: A CrossSectional Study Using the 2020 Adolescent Health Behavior Survey
-
Eunmi Lee, Youngran Yang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):499-510. Published online October 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22080
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study investigated the association between adolescent health behaviors (drinking, smoking, and drug use) and sexual intercourse, as well as the moderating effects of economic status, cohabitation with parents, and school type, among adolescents in Korea.
Methods
Secondary data from the 16th Adolescent Health Behavior Survey (2020) were used. A total of 395 schools and 54,948 middle and high school students participated in the study. Complex sample frequency analysis, the Rao–Scott test, and complex sample logistic regression analyses were performed.
Results
Sexual intercourse rates for men and women were 5.8% and 3.3%, respectively. Approximately 7.3% of high school students and 1.8% of middle school students reported having had sexual relations. Drinking (odds ratio [OR] = 3.15, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.82~3.52), smoking (OR = 6.75, 95% CI = 5.90~7.71), and drug use (OR = 3.03, 95% CI = 2.23~4.11) significantly increased the risk of sexual intercourse. Economic status and school type had moderating effects on the association between drinking and sexual intercourse.
Conclusion
Adolescent drinking, smoking, and drug use are associated with a higher risk of sexual experience. Thus, to reduce this risk, controlling alcohol consumption, smoking, and drug use is necessary. In addition, programs for healthy lifestyles and sexual intercourse should be differentiated according to the school type and the economic conditions of the adolescents’ households.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Public discourse on substance use behavior as a driver of public policy: a scoping review of South Korean academic and official literature
Meekang Sung, Jihye Han, Carrie G. Wade, Vaughan W. Rees
Addiction Research & Theory.2025; 33(4): 312. CrossRef
-
3,327
View
-
18
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
|