-
Effects of social support on organizational commitment among experienced nurses experiencing department rotation: the mediating effect of organizational socialization
-
Young Jun Jang, Jeong A Jeong, Yu Seung Ban, Seon Hwa Park, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):364-376. Published online August 18, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25042
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
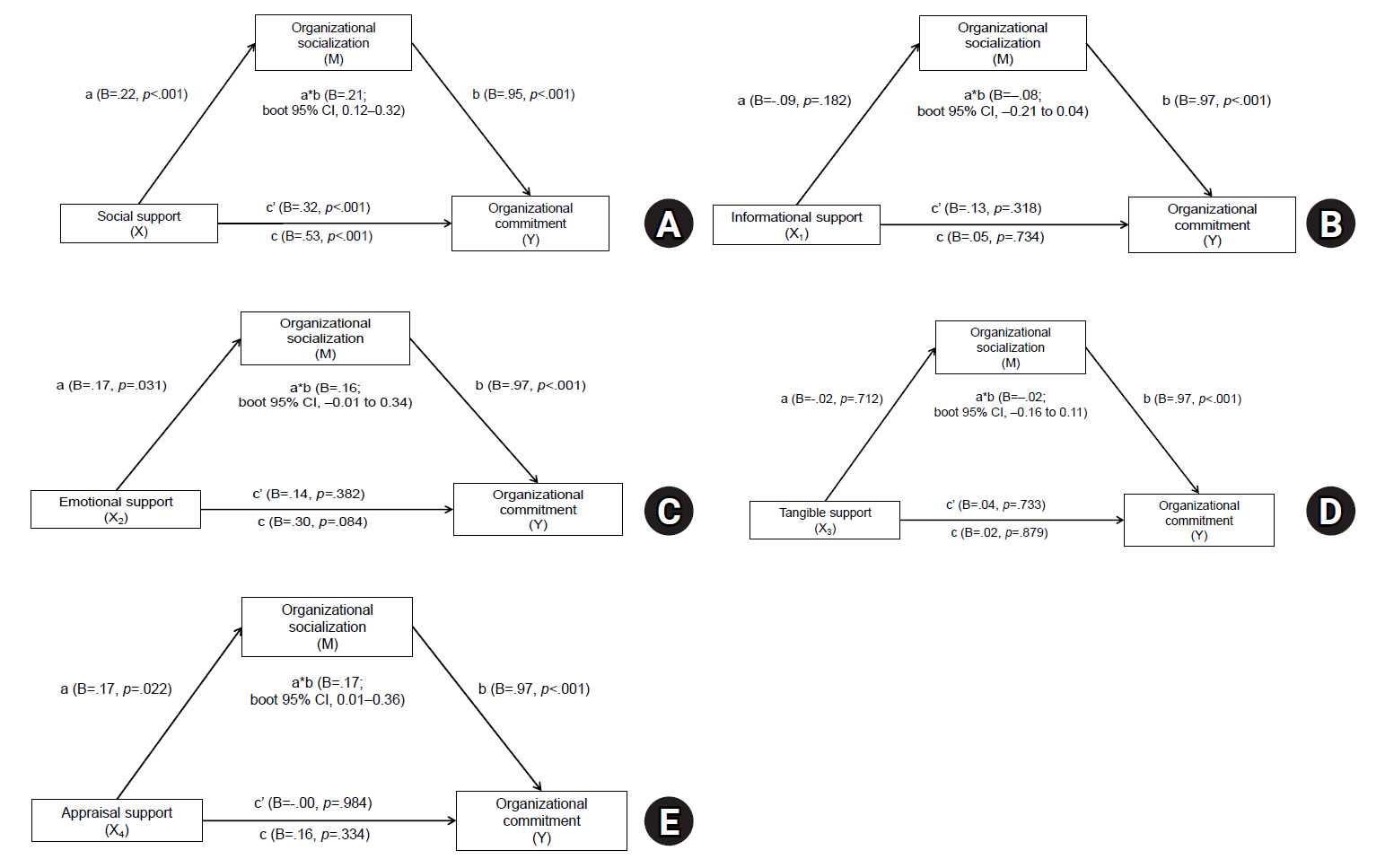
This study explored the mediating role of organizational socialization in the relationship between social support and organizational commitment among nurses in hospitals who had experienced department rotation.
Methods
A descriptive survey design was used with 202 nurses from a tertiary hospital who had experienced department rotation within the past 12 months. Data were collected via an online questionnaire from August 1 to August 30, 2024. Analyses included frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, Pearson correlation, and multiple regression. The mediating effect was tested using IBM SPSS WIN ver. 23.0 and the PROCESS macro (model 4) with 10,000 bootstrap resamples.
Results
Organizational socialization partially mediated the relationship between social support and organizational commitment (B=.21; bootstrapped 95% confidence interval, 0.12–0.32).
Conclusion
The findings suggest that both social support and organizational socialization play essential roles in improving nurses’ organizational commitment following department rotation. Thus, practical programs, such as mentoring systems, should be implemented that both enhance social support and actively promote organizational socialization. These efforts have the potential to help nurses adjust more effectively to new units and ultimately improve retention and performance within healthcare organizations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Effects of Nurses’ Dispatch Work Characteristics on Job Embeddedness, Organizational Commitment, and Turnover Intention
Eejee Jung, Gunjeong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(5): 560. CrossRef - Nurses' Experience Working with Substitute Nurses
Hye Mi Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 208. CrossRef
-
2,085
View
-
236
Download
-
2
Crossref
-
The Effect of Pain Relieving Intervention During Infiltration among Gamma Knife Surgery Patients for Stereotactic Frame Fixation
-
Young Jun Jang, Hyeon Ok Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2018;48(2):221-231. Published online January 15, 2018
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2018.48.2.221
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to compare the effects of three interventions on pain, blood pressure, and pulse rate during infiltration anesthesia in patients about to undergo gamma knife surgeries.
Methods
The three interventions employed in a university-affiliated Hospital in J City, South Korea were as follows: EMLA cream plus Vapocoolant spray (Vapocoolant, n=30), EMLA cream plus 10.0% Lidocaine spray (Lidocaine, n=30), and EMLA cream only (EMLA, n=30). The equivalent control-group pre test - post test study design was used. Pain was assessed subjectively using the numeric rating scale (NRS) and objectively using a Galvanic Skin Response (GSR) tester. NRS scores were assessed after infiltration anesthesia and the GSR was assessed during infiltration anesthesia. Blood pressure and pulse rate were assessed twice: before and after infiltration anesthesia. Data were collected between August 3, 2016 and March 24, 2017.
Results
NRS scores after infiltration anesthesia and the GSR during infiltration anesthesia were significantly lower in the Vapocoolant group than in the Lidocaine and EMLA groups (F=13.56, p<.001 and F=14.43, p<.001, respectively). The increase in systolic blood pressure (F=4.77, p=.011) and in pulse rates (F=4.78, p=.011) before and after infiltration anesthesia were significantly smaller in the Vapocoolant group than in the Lidocaine and EMLA groups; however, no significant differences were observed in diastolic blood pressures (F=1.51, p=.227).
Conclusion
EMLA cream plus Vapocoolant spray was the most effective intervention to relieve pain and to lower increase in systolic blood pressure and pulse rate caused by infiltration anesthesia for stereotactic frame fixation. Thus, application of Vapocoolant spray in addition to EMLA cream is highly recommended as a nursing intervention for patients undergoing gamma knife surgeries.
|