-
Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
-
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):568-583. Published online November 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25106
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to propose strategies for strengthening the nursing workforce by expanding their roles as advanced practice providers (APPs).
Methods
A mixed-methods approach was employed, consisting of five focus group interviews (FGIs) with 30 healthcare professionals (including 10 physicians) and a two-round Delphi survey with 49 experts. The FGIs explored practical insights from clinical settings, while the Delphi process validated and prioritized strategic recommendations through expert consensus.
Results
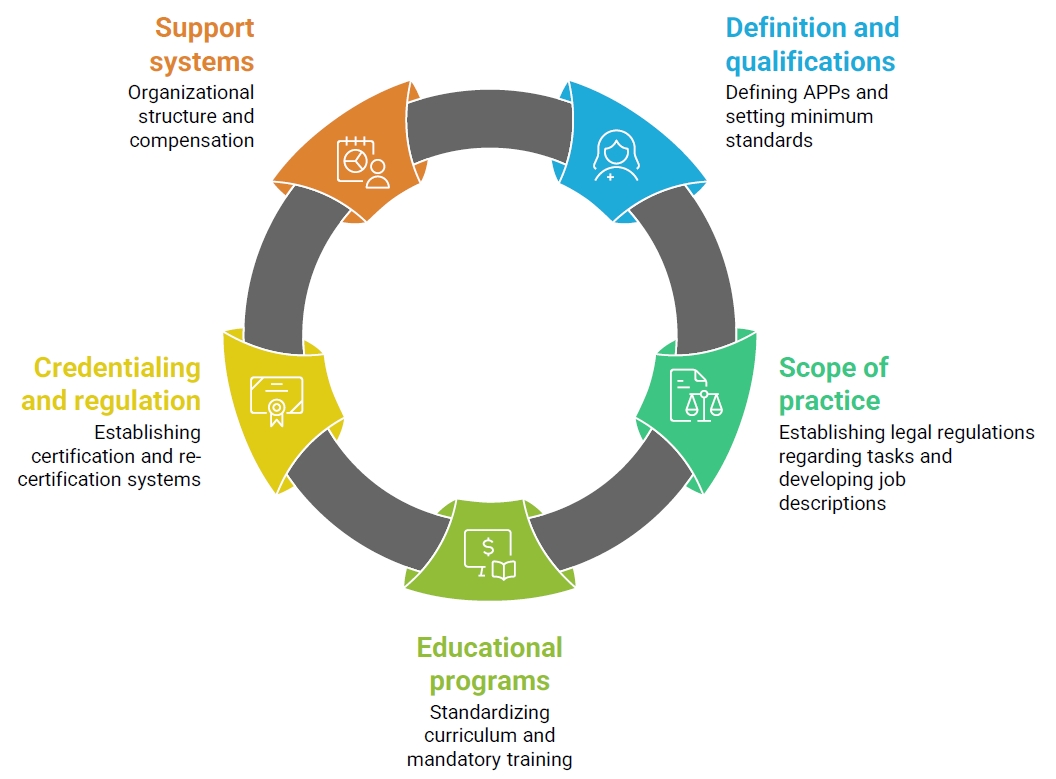
Four major themes emerged from the FGI analysis: (1) utilization of diverse APPs to ensure quality care, (2) expanding the scope of practice of APPs, (3) requirements to ensure the quality of APPs, and (4) strategies for sustainable management of the APP workforce. Building on these findings, the Delphi survey identified five strategic domains: “definition and qualifications,” “scope of practice,” “educational programs,” “credentialing and regulation,” and “support systems.” Key areas of consensus included the need for mandatory clinical experience and specialty training, legal clarification of role boundaries, standardized curricula with certification mechanisms, and institution-led support systems such as task-specific job descriptions and recredentialing processes.
Conclusion
To effectively strengthen APP roles, it is essential to build on the existing advanced practice nurse (APN) framework, which already includes structured curricula and national certification. Furthermore, integrative strategies should be developed to incorporate experienced clinical nurses without APN licenses into the APN system.
-
Development of an end-of-life care competency scale for nurses in long-term care hospitals: a psychometric validation study
-
Sookyeon Son, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):598-612. Published online November 27, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25113
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure end-of-life care (EOLC) competency among nurses working in long-term care hospitals and to evaluate its validity and reliability.
Methods
Preliminary items were developed based on attributes and indicators identified through a conceptual analysis of EOLC competency. The initial version of the scale was refined through expert content validity assessment, item revision, and a pilot test. The main survey was conducted among 460 nurses in long-term care hospitals, and 409 valid responses were analyzed after excluding 51 incomplete or invalid cases. Data were analyzed using software-assisted item analysis, exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses, and assessments of convergent, discriminant, and criterion-related validity, as well as reliability testing.
Results
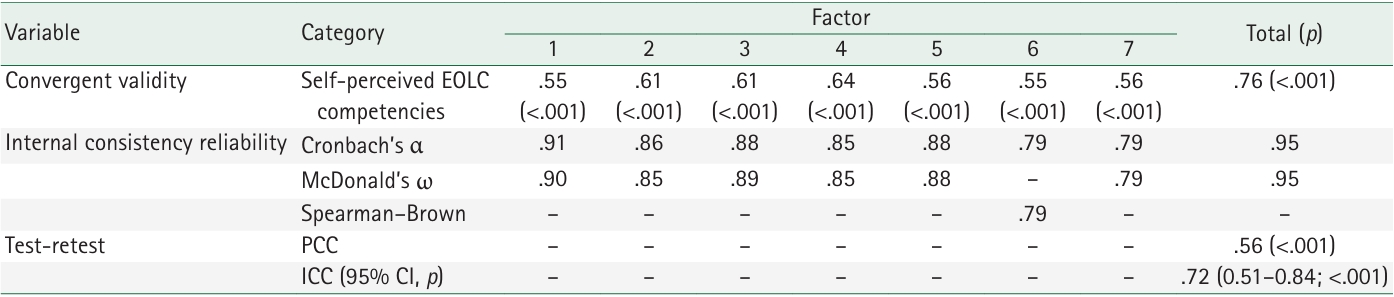
The initial 55 items were reduced to a final set of 30 items across seven dimensions. Model fit indices indicated good construct validity (χ²/degrees of freedom=1.91, standardized root mean square residual=.06, root mean square error of approximation=.07, Tucker-Lewis index=.90, comparative fit index=.91), with a total explained variance of 70.2%. The scale demonstrated strong criterion-related validity (r=.76, p<.001), high internal consistency (Cronbach’s α=.95; McDonald’s ω=.95), acceptable test–retest reliability (r=.56, p<.001), and an intraclass correlation coefficient of .72 (95% confidence interval, .51–.84; p<.001).
Conclusion
The developed scale is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing EOLC competency among nurses in long-term care hospitals. It can be effectively utilized for educational assessment, training evaluation, and the measurement of program effectiveness in end-of-life care.
-
Experiences of Patients and Their Families Receiving Medical Services Provided by Advanced Practice Nurses at Tertiary General Hospitals
-
Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Su Jung Choi, Ji Eun Han, Eun Kyung Kwon, Jeong Hee Park, Jeong Hye Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(4):594-606. Published online November 4, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24069
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to understand and describe the experiences of patients and their families who have received medical services from advanced practice nurses in tertiary general hospitals in Korea.
Methods
Data were collected through four focus group interviews with 20 patients and their families who had received medical services from advanced practice nurses for more than six months at four tertiary hospitals from November 29 to December 28, 2023. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using qualitative content analysis.
Results
The four themes extracted from the experiences of patients and their families were as follows: unfamiliar medical personnel encountered during the treatment process, healthcare professionals who exhibited excellence, companions to light my way through the tunnel of illness, and an advanced practice nurse system that must be activated urgently.
Conclusion
The study’s findings indicate that patients and their families view the care provided by advanced practice nurses as excellent, reliable, and holistic. Research suggests that advanced practice nurses are valuable healthcare professionals in team-based care. The findings suggest that hospitals should utilize an advanced practice nurse system to improve patient outcomes and ensure the quality of care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Legislation of Medical Support Tasks in the Nursing Act as a Foundation for Nursing Professionalism and Role Expansion
Su Jung Choi
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2025; 37(2): 69. CrossRef - Strategies for expanding the role of advanced practice providers in the Korean nursing workforce: a mixed-methods approach
Jeong Hye Kim, Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Suyoung Choi, Mimi Lee, Su Jung Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(4): 568. CrossRef - Nurses' Patient Care Experiences in a Changing Healthcare Environment Following One Year of Healthcare Policy Conflict - A Focus Group Interview
Eun Hee Kang, Yunhyung Kim, Jeong Hye Kim
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 280. CrossRef
-
4,482
View
-
266
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Experience of Nurses in Charge of COVID-19 Screening at General Hospitals in Korea
-
Boo Young Ha, Yun-Sook Bae, Han Sol Ryu, Mi-Kyeong Jeon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):66-79. Published online February 28, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21166
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to understand and describe the experiences of nurses in charge of COVID-19 screening at general hospitals in South Korea.
Methods
Data were collected through individual in-depth interviews with 14 nurses who had been working for more than a month at a screening clinic operated by two general hospitals from May 11 to July 20, 2021. Verbatim transcripts were analyzed using Colaizzi’s phenomenological analysis.
Results
As a result of analysis, four theme clusters were extracted from nurses’ experiences, as follow: the role of the hospital gatekeeper entrusted with managing the COVID-19 pandemic, struggling to maintain the protective barrier, boundlessness like a Mobius strip, and driving force to endure as a nurse in charge of COVID-19 screening.
Conclusion
The results of this study provide a deeper understanding of the lives of screening clinic nurses who are struggling with the COVID-19 situation. The results are expected to be useful in providing basic data for improving the infection control system and response strategies that can be applied to nursing practice in other pandemic situations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The Moderating Effect of Calling in the Relationship between Post-Traumatic Stress and Turnover Intention of Nurses Who Cared for COVID-19 Patients
Min Ju Woo, Bu Kyung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2025; 31(1): 75. CrossRef - Nurses’ Experience of Caring for Patients with COVID-19 in Residential Treatment Centers: A Qualitative Study
Jung Hwan Heo, Heeje Yun, Yeong Hun Park
Journal of Korean Association for Qualitative Research.2025; 10(3): 226. CrossRef - Improving Emerging Infectious Disease Control Based on the Experiences of South Korean Nurses During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Qualitative Systematic Review
Ha-Young Park, In-Sun Yeom
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2024; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - The impact of nurse’s sense of calling, organizational commitment, job stress, and nursing work environment on patient safety management activities in comprehensive nursing care service units during the covid-19 pandemic
YeJi Lee, Won Ju Hwang
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nurses’ intention to care of COVID-19 patients in hospitals dedicated to infectious disease in South Korea: application of the theory of planned behavior and verification of the moderating effect of ethical nursing competence
Mira Mo, Seongmi Moon, Eun Kyeung Song
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Perspectives of Frontline Nurses Working in South Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Combined Method of Text Network Analysis and Summative Content Analysis
SangA Lee, Tae Wha Lee, Seung Eun Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 584. CrossRef - Influence of Job Stress and Resilience on Burnout of Clinical Nurses Working in Small and Medium-Sized Hospital: Focusing on Comparing National Safety Hospital and COVID-19 Dedicated Hospital
Su-Young Jang, Young Ko
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 65. CrossRef
-
1,618
View
-
18
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
7
Crossref
-
Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Management of Liver Transplant Recipients
-
Mi-Kyeong Jeon, Yeon-Hwan Park
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2017;47(5):663-675. Published online January 15, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2017.47.5.663
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to construct and test a structural equation model of self-management of liver transplant recipients based on self-determination theory.
Methods
Participants were 275 outpatients who received liver transplantation. A structured self-report questionnaire was used to assess health care providers’ autonomy support, transplant-related characteristics, illness consequence perception, autonomy, competence, family relatedness, depression and self-management. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 24.0 and AMOS 24.0 program.
Results
The modified model showed a good fitness with the data: GFI=.96, RMSEA=.06, CFI=.96, NFI=.93, TLI=.93, PGFI=.43, PNFI=.49. The health care providers’ autonomy support, competence, family relatedness and depression were factors with a direct influence on the self-management of liver transplant recipients. The health care providers’ autonomy support and illness consequence perception had an indirect influence through competence, family relatedness and depression. However, the transplant-related characteristics and autonomy did not have a significant effect on self-management. This model explained 59.4% of the variance in self-management.
Conclusion
The result suggests that continuous education must be done to promote the competence of liver transplant recipients and to encourage the patient to positively perceive their current health condition with a view that enhances one's self-management. Additionally, the liver transplant recipients should be screened for depression, which would affect self-management. Most of all, health care providers, who have the most influence on self-management, should improve therapeutic communication and try to form a therapeutic relationship with the liver transplant recipients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Predictors of self-care in kidney transplant patients according to preoperative dialysis: A comparative study
Hyeiyeon Im, Hye-Young Jang
Heliyon.2024; 10(24): e40237. CrossRef - Structural equation modeling for associated factors with self-care behavior among young and middle-aged hypertensive patients: a cross-sectional study
Nam Jo Kim, Myung Kyung Lee
Contemporary Nurse.2023; 59(2): 99. CrossRef - Mediating Role of Hope Between Social Support and Self-Management Among Chinese Liver Transplant Recipients: A Multi-Center Cross-Sectional Study
Dan Zhang, Nannan Zhang, Hui Chang, Ying Shi, Zijun Tao, Xu Zhang, Qi Miao, Xiaofei Li
Clinical Nursing Research.2023; 32(4): 776. CrossRef - Factors associated with self‐management after hybrid revascularization in patients with peripheral artery disease: A structural equations model
So‐Young Kim, Yun Mi Lee, Youn‐Jung Son
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2023; 79(1): 170. CrossRef - Type D personality, cognitive illness perception, depression, approach coping, and self-management among older adults in long-term care hospitals: Structural equation modeling
Sunki Kim, Mona Choi, JuHee Lee, Heejung Kim, Kijun Song, Hye-Ja Park
Geriatric Nursing.2022; 48: 150. CrossRef - Factors influencing the self-management of kidney transplant patients based on self-determination theory: a cross-sectional study
Mi Kyung Sim, Sun Young Son, Man Ki Ju
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2022; 36(1): 37. CrossRef - Feasibility and preliminary effects of a theory-based self-management program for kidney transplant recipients: A pilot study
Hye Won Jeong, Chi Eun Song, Minjeong An, Lucy E. Selman
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(6): e0248947. CrossRef - Psychometric properties of the Chinese Version of the Readiness for Hospital Discharge Scale for people living with HIV
Chen Chen, Xiaoxia Zhang, Chulei Tang, Xueling Xiao, Zirong Tao, Honghong Wang
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2020; 7(2): 220. CrossRef - Mediation Effects of Basic Psychological Needs Between Autonomy Support from Healthcare Providers and Self-Management Among Cancer Survivors
Eun-Jung Bae, Yun-Hee Kim
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2019; 10(6): 385. CrossRef - Analysis of mortality prognostic factors using model for end-stage liver disease with incorporation of serum-sodium classification for liver cirrhosis complications
Yuna Kim, Kyunghee Kim, Insil Jang
Medicine.2019; 98(45): e17862. CrossRef - Structural Equation Modeling of Self-Care Behaviors in Kidney Transplant Patients Based on Self-Determination Theory
Hye Won Jeong, Hyang Sook So
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2018; 48(6): 731. CrossRef
-
1,356
View
-
24
Download
-
11
Crossref
|