Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Triglyceride-glucose parameters as predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults: a secondary analysis of a Prospective Cohort Study
- Yu Jin Park, Miseon Shin, Hyun Seon Jeon, Eun Hee Yang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(2):205-221. Published online April 1, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24108
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
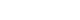
This study aimed to evaluate the association between triglyceride-glucose (TyG)–related parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus in Korean adults. Data were obtained from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES).
Methods
This secondary analysis examined data from 6,816 adults aged 40–69 years who participated in the KoGES from 2001 to 2020. TyG–related parameters, including the TyG index, TyG–body mass index (TyG–BMI), TyG–waist circumference (TyG–WC), and TyG–waist-to-height ratio (TyG–WHtR), were assessed. Cox proportional hazards models were employed to determine the association between these parameters and the incidence of diabetes mellitus, with adjustments made for demographic, lifestyle, and health-related characteristics.
Results
Higher levels of all TyG–related parameters were significantly associated with an increased risk of developing diabetes mellitus. Specifically, participants in the highest quartile of the TyG index, TyG–BMI, TyG–WC, and TyG–WHtR exhibited significantly higher hazard ratios for diabetes mellitus incidence compared with those in the lowest quartile (p<.001 for all). Notably, the TyG index demonstrated a stronger predictive value for diabetes mellitus than traditional measures such as the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance.
Conclusion
TyG–related parameters are robust predictors of diabetes mellitus incidence in Korean adults. These findings support the incorporation of TyG–related measures into clinical settings for the early identification and intervention of high-risk populations. Utilizing these parameters for early diagnosis and preventive strategies may significantly enhance diabetes mellitus management.
- 2,443 View
- 154 Download

- Glucose Tolerance and Insulin Secretion patterns by Body Mass Index(BMI) in Offspring of Parents with Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetes Mellitus
- Young Im Moon, Hye Ja Park, Young Ae Chang
- Journal of Nurses Academic Society 1997;27(3):694-704. Published online March 30, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jnas.1997.27.3.694
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was designed to assess the body fat distribution, and also to investigate the effects of body fat on glucose tolerance and on insulin secretion pattern by body mass in offspring of parents with NIDDM. The subjects consisted of twenty parents with NIDDM who had been admitted to the Department of Internal Medicine or had been seen in the outpatient clinic at Kangnam St. Mary's Hospital, Catholic University between February to March, 1995. Twenty offspring were randomly selected from forty six offspring of twenty healthy people without a family history of diabetes mellitus were matched by sex, age and body mass index(BMI). The results are as follows : 1. mean fasting serum glucose and insulin levels and insulin/glucose ratio were significantly greater in offspring than in the control subjects with BMI>or=25kg/m2 in the offspring and in the BMI<25kg/m2(P<0.05). 2. The total glucose area and insulin area were significantly greater in both the offsping and the control subjects with BMI>or=25kg/m2 than in both the offspring and the control subjects with BMI<25kg/m2(P<0.05). 3. Upper body skinfold thickness, Waist hip ratio(WHR), serum levels of total cholesterol and triglyceride(TG), total dietary calorie intake and protein intake in both the offspring and the control subjects with BMI>or=25kg/m2 were greater than those with BMI<25kg/m2(P<0.05). On the other hand, HDL-cholesterol in both the offspring and the control subjects with BMI 25kg/m2 was lower than those with BMI<25kg/m2(P<0.05). 4. The major variables influencing the total glucose area were subscapular skinfolds thickness and WHR and the major variables influencing the total insulin area were suprailiac skinfolds thickness, WHR, TG and free fatty acid. In the light of the results, glucose intolerance and insulin resistance were affected by body mass index, Upper body fat, WHR, and lipids(TG, Free fatty acid), it is implied that these are influencing factors on total glucose area and total insulin area. The identification of these factors might provide a useful tool to identify individuals at high risk of diabetes mellitus. Therefore, various nursing intervention programs to reduce obesity could be given to both the offspring of parents with NIDDM and to the obese healthy controls before diabetes mellitus develops.
- 459 View
- 0 Download

- Prevalence and Risk Factors for Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Fasting Glucose of Adults
- Hee Seung Kim, You Ja Ro, Nam Cho Kim, Yang Sook Yoo, Jin Sun Young, Jeong Ah Oh
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2000;30(6):1479-1487. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2000.30.6.1479
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study was conducted to draw out prevalence and the risk factors of diabetes mellitus and impaired fasting glucose for adults,(age 30-69). The subjects were 2096 adults, who had regular health examinations between January and December of 1999 at K Hospital in Seoul. The data was analyzed using chi-square test, unpaired t-test and logistic regression. Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose were diagnosed by ADA (American Diabetes Association, 1997) criteria. The results were as follows: 1. Mens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 7.9% and womens' prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus was 3.8%. Mens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 10.4% and womens' prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 6.5%. Prevalences of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with age. 2. Prevalence of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose of obese subjects (relative body weight>=162) was higher than that of overweight subjects (110<=relative body weight<=119) in men and women. 3. The diagnoses of Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose increased with systolic blood pressure and triglyceride. 4. Significant factors associated with diabetes in the logistic regression best gut model were age, relative body weight, systolic blood pressure, triglyceride in men, and systolic blood pressure in women. In conclusion, as age, weight, systolic blood pressure and triglyceride get higher, Diabetes Mellitus and impaired fasting glucose prevalence also increases, porportionally.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
Soo-Hee Jin
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2019; 44(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of Obesity and Family History of Diabetes on the Association ofCETPrs6499861 with HDL-C Level in Korean Populations
Jae Woong Sull, Soriul Kim, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2019; 8(2): 252. CrossRef - Current Status and Effects of Nutrition Education Programs for Diabetic Patients in Korea
Hae Jin Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 106. CrossRef - Effect of smoking on the association of HHEX (rs5015480) with diabetes among Korean women and heavy smoking men
Jae Woong Sull, Tae Yong Lee, Sun Ha Jee
BMC Medical Genetics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Spatial Distribution of Diabetes Prevalence Rates and Its Relationship with the Regional Characteristics
Eun-Kyung Jo, Eun-Won Seo, Kwang-Soo Lee
Health Policy and Management.2016; 26(1): 30. CrossRef - The Relationship between Factors of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adult Males and the Parents' Family History of Diabetes
Hyung-Su Park, Jin-Gyu Jeong, Jin-Ho Yu
The Journal of the Korea institute of electronic communication sciences.2013; 8(5): 779. CrossRef - Thigh Circumference and Diabetes: Obesity as a Potential Effect Modifier
Keum Ji Jung, Heejin Kimm, Ji Eun Yun, Sun Ha Jee
Journal of Epidemiology.2013; 23(5): 329. CrossRef
- The Relation of Impaired Fasting Glucose and HDL-Cholesterol by Gender and Body Mass Index
- 834 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Comparison of blood glucose concentrations from capillaries and veins in SMBG
- Jin Hak Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 1998;28(1):143-147. Published online March 29, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.1998.28.1.143
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF No abstract available.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comparison of the Rates of Hemolysis and Repeated Blood Sampling using Syringe needles versus Vacuum tube needles in the Emergency Department
Young Hee Sung, Moon Sook Hwang, Jee Hyang Lee, Hyung Doo Park, Kwang Hyun Ryu, Myung Sook Cho, Young Hee Yi, S Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2012; 42(3): 443. CrossRef
- A Comparison of the Rates of Hemolysis and Repeated Blood Sampling using Syringe needles versus Vacuum tube needles in the Emergency Department
- 628 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Effect of Oral Glucose on Pain Relief in Newborns
- Hye Young Ahn, Me Young Jang, Myung Haeng Hur
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(6):992-1001. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.6.992
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was done to provide data for a nursing intervention to alleviate newborn pain clinically by investigating the effect of oral glucose.
Purpose Subjects were newborns hospitalized in the nursery. Informed consent was obtained from parents of 60 newborns. A heel stick was carried out for a test on 3 groups; the experimental, placebo, and control group. The Neonatal infant pain scale(NIPS), respiration rate, heart rate, peripheral oxygen partial pressure(SpO2), and crying duration were measured to assess pain reaction. All neonatal behaviors were recorded on videotape.
Purpose There were significant differences in pain behavior during stimulus(F=4.195, p=.020), pain behavior immediately after blood-sampling (F=4.114, p=.021), and pain behavior 3 minutes after that (F=3.630, p=.033). However, there were no significant differences in heart rate, respiration rate, peripheral oxygen partial pressure or crying duration after the heel stick among the groups.
Conclusions Oral administration of glucose before a heel stick caused the reduction of neonatal pain behavior, which means that it has an effect of pain relief.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Bayesian network meta-analysis of non-pharmacological interventions for neonatal pain management: a clinical effectiveness comparison
Lingxue Xu, Lali Xiang, Lihui Pan, Peipei Xue, Juan Li, Yurong He, Hongyan Liu, Yuwei Hu, Bo Zheng
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Arnica D30 – an alternative for managing procedural pain in full-term neonates
Penka Petleshkova, Maya Krasteva, Iliyana Pacheva, Snezhana Dragusheva, Margarita Ruseva, Valentina Petkova, Kristina Kilova
Pharmacia.2024; 71: 1. CrossRef - The effect of oral breast milk on pain response of the neonates during heel lancing
Kyunghwa Kim, Youngim Park, Taeim Kim
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2016; 27(1): 203. CrossRef - Effect of vapocoolant spray and EMLA cream upon DPT vaccination pain in infants
Gunja Jang, Eunyoung Jeon, Eunsil Lee
Journal of the Korean Data and Information Science Society.2014; 25(4): 705. CrossRef - Effects of Local Anesthetic Cream on Pain Relief in Newborns During Venipuncture
Hae-Won Kim, Hye-Young Ahn
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(4): 215. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Neonate Pain Management Performed by Nurses
In-Suk Noh, Jin-A Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2011; 17(3): 190. CrossRef - Pain Response to Procedural Pain in Premature Infants
Jung Sook Kim, Eun Jung Lee, Eun Ha Ham, Ji Hyun Kim, Young Hee Yi
Journal of Korean Academy of Child Health Nursing.2010; 16(4): 352. CrossRef
- A Bayesian network meta-analysis of non-pharmacological interventions for neonatal pain management: a clinical effectiveness comparison
- 909 View
- 8 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Clinical Implications of the Glucose Test Strip Method for Early Detection of Pulmonary Aspiration in Nasogastric Tube- Fed Patients
- Hwa Soon Kim
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(7):1215-1223. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.7.1215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to test the clinical usefulness of the glucose test strip method for early detection of pulmonary aspiration in tube fed patients.
Method The subjects for the study were 36 patients who were receiving enteral feedings and 39 patients who were not given enteral feedings. For the analysis, the tube fed patients were divided into two groups (clinically significant aspiration and no aspiration) according to criteria.
Result The mean glucose concentration of tracheal secretions from non enteral fed patients was 26.35mg/dl and were lower than those concentrations found in tube fed patients (32.75mg/dl). The mean glucose concentration of the aspiration group was 45.60mg/dl and the glucose concentration of the non aspiration group was 19.93mg/dl. The difference was statistically significant (t=2.163, p=. 038). More subjects in the no aspiration group (73%) than the aspiration group (56%) had glucose concentrations below 20mg/dl. After deleting the cases that had samples containing blood, glucose concentrations of tracheal aspirates were lower in both groups.
Conclusion The glucose level of the aspiration group was significantly lower than the no aspiration group and more subjects in the aspiration group had a glucose level higher than 101mg/dl. Therefore, the glucose test of tracheal secretions in tube fed patients could be a desirable test for screening for tracheal aspiration. Especially the patient who is showing repeatedly high glucose levels should not be given feedings until reassessment is completed.
- 554 View
- 2 Download

- The Effects of a Diabetic Educational Program for Coping with Problem Situation on Self-efficacy, Self care behaviors, Coping and Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Choun Hee Ko, Mee Ock Gu
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2004;34(7):1205-1214. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2004.34.7.1205
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was conducted to develop and to test the effects of an educational program for coping with problem situations as a nursing intervention in the diabetic patient.
Method A non-equivalent control group pretest-posttest design was used in this study. Data were collected from January to March, 2002. The subjects of the study consisted of 31 diabetic patients(experimental group : 17 patients, control group : 14 patients). The intervention of an educational program for coping with problem situations was applied to the experimental group for 4weeks(total 8 hours). Data were collected before the educational program, immediately after and 1 months later and were analyzed with repeated measures ANOVA, t-test, and paired t-test.
Result 1. There was a significant difference in self efficacy between the experimental and control groups (F=13.793, p=0.001). 2. There was a significant difference in self care behavior between the experimental and control groups (F=4.583, p=0.041). 3. There was a significant difference in coping behavior of the problem situation between the experimental and control groups (F=62.018, p=0.000). There was a significant difference according to experimental stages(F=4.546, p=0.015) and interaction between education and experimental stages(F=12.039, p=0.000). 4. There was a significant difference in glycemic control between the experimental and control groups (t=-3.112, p=0.004).
Conclusion These results support that a diabetic educational program for coping with problem situations is effective in promoting and maintaining self efficacy, self care behavior, problem coping behaviors and in improving glycemic control. Thus this program can be recommended as an effective nursing intervention of in-depth education for diabetic patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expanding the purview of wellness indicators: validating a new measure that includes attitudes, behaviors, and perspectives
Carolyn E. Schwartz, Brian D. Stucky, Roland B. Stark
Health Psychology and Behavioral Medicine.2021; 9(1): 1031. CrossRef - Development and Effects of a Motivational Interviewing Self-management Program for Elderly Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Hye-Yeon Kang, Mee Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(4): 533. CrossRef - Analysis of Reported Study on Intervention Programs for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Gab-Sun Song, Ho-Jin Kim, Jum-Yi Jun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 541. CrossRef - Development of a Comprehensive Self-Management Program Promoting Self Efficacy for Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Ju-Young Park, Il-Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 74. CrossRef - A Predictive Model on Self Care Behavior for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Based on Self-Determination Theory
Yeong Mi Seo, Won Hee Choi
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2011; 41(4): 491. CrossRef - The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 720. CrossRef
- Expanding the purview of wellness indicators: validating a new measure that includes attitudes, behaviors, and perspectives
- 816 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Crossref

- A Comparison on the Degree of Pain according to Methods of Blood Sugar Test between DM Patients and Healthy Group
- Ja Yun Choi
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2003;33(7):928-935. Published online March 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2003.33.7.928
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study attempts to compare the degree of pain when different methods of blood sugar test are used between a DM patient group and a healthy group.
Method A sample is composed of 56 DM patients and 57 their family who are admitted in a ward of C university hospital in Gwangju. Data were collected from July, 2001 to December, 2001. The blood sugar tests are administered four different ways. The degree of pain is measured twice with a visual analog scale in a week interval.
Result The differences in the degree of pain according to methods of blood sugar test were not found between the DM patient group and the healthy group in both measures. The only use of a 27G needle method was shown to cause highest level of pain in comparison with the rest of methods in the first measure of the DM patient group and in both the measures of the healthy group.
Conclusion The study results indicate that the method using lanceter is more recommendable than method of using a 27G needle. Furthermore, the ice therapy and EMLA cream is likely to be more effective on the pain relief in the healthy group than the DM patient group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Influence of Application Time of Lidocaine Patch on Pain Intensity after Venipuncture
In Sun No, Se Young Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2018; 25(4): 250. CrossRef - Effects of Lidocaine Patch Application to Decrease Pain and Fear during Blood Sugar Test in Elderly Patients with DM*
Se Young Kim, Jin Kim, In Sun No
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2016; 23(1): 12. CrossRef - Comparison of Blood Glucose Levels from the Fingertips of Both Patients with and without Diabetes Who are Receiving Dextrose Fluid Therapy
Suk Hyun Park, Chang Kwan Lee, Yeon Woo Kim, Chi Hye Kwon
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2016; 28(2): 127. CrossRef - The Effect of topical EMLA Cream for venipuncture on Patients' Pain and Anxiety
Jung-Kyoung Kim, Moon-Sook Shim, Kwang-Hwan Kim
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(9): 4065. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of blood glucose test results on the forearm, finger, and vein
Kyung-Ah Kim, In-Kwang Lee, Eun-Young Shin, Yang-Mi Kim, Kyoung-Oak Kim, Eun-Jong Cha, Kyung-Soon Park
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(4): 1751. CrossRef - Accuracy Evaluation of the Alternative Site Blood Glucose Test Using Error Grid
Kyung-Soon Park, Eun-Jong Cha
Journal of Biomedical Engineering Research.2011; 32(1): 25. CrossRef - Comparison of Blood Glucose Measurements Using Samples Obtained from the Forearm, Finger Skin Puncture, and Venous Serum
Kyung-Soon Park, Mi-Sook Park, Young-Joo Cha, Wun-Jae Kim, Seong-Su Choi, Kyoung-Ok Kim, Eun-Jong Cha, Kyung-Ah Kim
Annals of Laboratory Medicine.2010; 30(3): 264. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Influence of Application Time of Lidocaine Patch on Pain Intensity after Venipuncture
- 785 View
- 1 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Effects of a Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Jung Mi Ko, Jong Kyung Lee
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(6):672-681. Published online December 31, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.6.672
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of using a Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification with pregnant women who have gestational diabetes.
Methods The research design for this study was a non-equivalent control group quasi-experimental study. Pregnant women with gestational diabetes were recruited from D women's hospital located in Gyeonggi Province from April to October, 2013. Participants in this study were 34 for the control group and 34 for the experimental group. The experimental group participated in the Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification. The program consisted of education, small group coaching and telephone coaching over 4weeks. Statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS 21.0 program.
Results There were significant improvements in self-care behavior, and decreases in depression, fasting blood sugar and HbA1C in the experimental group compared to the control group. However, no significant differences were found between the two groups for knowledge of gestational diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion The Coaching Program on Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification used in this study was found to be effective in improving self-care behavior and reducing depression, fasting blood sugar and HbA1C, and is recommended for use in clinical practice as an effective nursing intervention for pregnant women with gestational diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lifestyle Interventions for Treatment and Remission of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Lifestyle Medicine
Richard M. Rosenfeld, Meagan L. Grega, Micaela C. Karlsen, Abd Moain Abu Dabrh, R. Nisha Aurora, Jonathan P. Bonnet, Lori Donnell, Stephanie L. Fitzpatrick, Beth Frates, Elizabeth A. Joy, Jane F. Kapustin, Dawn R. Noe, Gunadhar Panigrahi, Arun Ram, Lianna
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a health coaching program based on Cox’s interaction model in older adults with diabetes mellitus in Korea: a quasi-experimental study
Hye Seung Kang
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2025; 27(4): 607. CrossRef - Development and Adaptability of Smartphone-based Dietary Coaching Program for Patients Undergoing Diabetes and Prediabetes with Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
Myoung Soo Kim, Jung Mi Ryu, Minkyeong Kang, Jiwon Park, Yeh Chan Ahn, Yang Seok Kim
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(1): 36. CrossRef - Prepregnancy Glucose Levels Within Normal Range and Its Impact on Obstetric Complications in Subsequent Pregnancy: A Population Cohort Study
Ho Yeon Kim, Ki Hoon Ahn, Geum Joon Cho, Soon-Cheol Hong, Min-Jeong Oh, Hai-Joong Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Self-Care Behavior
Sahar Mansour Lamadah, Heba Abdel-Fatah Ibrahim, Wafaa Taha Elgzar, Hanan Abdelwahab El-Sayed, Samiha Hamdi Sayed, Amira El-Houfey
Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.2022; 27(6): 538. CrossRef - The effect of health-promoting lifestyle education program provided to women with gestational diabetes mellitus on maternal and neonatal health: a randomized controlled trial
Asli Ural, Nezihe Kizilkaya Beji
Psychology, Health & Medicine.2021; 26(6): 657. CrossRef - Comparing the effect of individual counseling with counseling on social application on self-care and quality of life of women with gestational diabetes
Fatemeh Ghasemi, Katayon Vakilian, Zohre Khalajinia
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(5): 842. CrossRef - Effects of nonpharmacological interventions on the psychological health of high-risk pregnant women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Hyeji Yoo, Sukhee Ahn
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(3): 180. CrossRef - Breastfeeding experiences of women with gestational diabetes
Seungmi Park, Soo-Young Yu
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2021; 27(3): 274. CrossRef - The Effects of Snack Control Education and Telephone Coaching on Self-Management, Social Support, Self-Efficacy, and Blood Glucose in Diabetes Patients
Hye Eun Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 274. CrossRef - Psychosocial support interventions for women with gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review
Seulgi Jung, Yoojin Kim, Jeongok Park, Miyoung Choi, Sue Kim
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2021; 27(2): 75. CrossRef - The effects of health care programs for gestational diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a systematic review
Seo Jin Park, Jina Lee
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2020; 26(4): 274. CrossRef - The effectiveness of group hope therapy on the mental health of type II diabetic patients referred to the diabetes clinic in South East Iran
Batool Pouraboli, Tayebeh Ilaghi, Abazari Faroukh, Majid Kazemi
International Journal of Adolescent Medicine and Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of self care counseling on health practices of 35 years or more aged pregnant women referring to Hamadan health care centers, in 2018
Soodabeh Aghababaei, Fereshteh Omidifard, Ghodratollah Roshanaei, Parisa Parsa
Avicenna Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Care.2020; 28(1): 67. CrossRef - Effects of a Web-Based Self-Management Program on the Behavior and Blood Glucose Levels of Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yun-Su Kim, Hee-Seung Kim, Yoo-Lee Kim
Telemedicine and e-Health.2019; 25(5): 407. CrossRef - Effects of a Postnatal Care Program on Self-efficacy, Self-management, and Glycemic Control in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yeong Kyung Jeon, Hyo Jin Kim, Mi Yeon Yang, Da Yeong Jung, Kum Young Yoon, Gie Ok Noh
Korean Journal of Women Health Nursing.2018; 24(4): 367. CrossRef - Knowledge and health beliefs about gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy's breastfeeding intention
Seungmi Park, Jung Lim Lee, Jang In Sun, Youngji Kim
Journal of Clinical Nursing.2018; 27(21-22): 4058. CrossRef - Needs for Development of IT-based Nutritional Management Program for Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Chan-Jung Han, Sun-Young Lim, Eunsuk Oh, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jin-Hee Lee
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2017; 22(3): 207. CrossRef - Effects of a Group Coaching Program on Depression, Anxiety and Hope in Women with Breast Cancer Undergoing Chemotherapy
So Ryoung Seong, Moon-kyung Cho, Jeeyoon Kim, Yeo Ok Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 188. CrossRef - A Review on the Use of Effect Size in Nursing Research
Hyuncheol Kang, Kyupil Yeon, Sang-Tae Han
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2015; 45(5): 641. CrossRef
- Lifestyle Interventions for Treatment and Remission of Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes in Adults: A Clinical Practice Guideline From the American College of Lifestyle Medicine
- 2,504 View
- 28 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Effects of Web-based Health Education on Blood Glucose and Blood Pressure Improvement in Postmenopausal Women with Impaired Fasting Blood Glucose
- Jeong-Ah Oh, Hee-Seung Kim, Min-Jeong Park, Hye-Sun Shim
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(5):724-731. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.5.724
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of an educational intervention that used both cellular phones and the Internet to provide a short messaging service (SMS) relating to blood glucose, blood pressure, and serum lipid levels in postmenopausal women with impaired fasting glucose (IFG).
Methods Twenty-eight postmenopausal women were assigned to an intervention group and twenty-one postmenopausal women to a control group. The intervention was provided for 12 weeks. Patients in the intervention group were asked to access a web site by using a cellular phone or to use the Internet directly and input their blood glucose and blood pressure levels weekly. Participants were sent the optimal recommendations weekly by both cellular phone and Internet.
Results The intervention group had a mean decrease in systolic blood pressure (SBP) level of 8.1 mmHg but changes for the control group were not significant. There was a significant mean change in diastolic blood pressure (DBP) level for the intervention group (-7.7 mmHg). The mean change in the control group was not significant.
Conclusion This educational intervention using the Internet and a SMS by cellular phone improved levels of SBP and DBP in postmenopausal women with IFG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Social Support Interventions on Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review
Reza Faryabi, Nooshin Yoshany, Moradali Zareipour, Salman Daneshi, Fahad Hanna, Ehsan Movahed
Current Women s Health Reviews.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Pre-discharge Group Education Program for Liver Transplant Patients
Ji Seon Yun, Kyung Choon Lim, Jae Sim Jeong, Hea Seon Ha, Jung Ja Hong, Soon Haeng Lee, Lee Young Kim, Yeon Hee Kim, Shin Hwang
Korean Journal of Transplantation.2017; 31(1): 34. CrossRef - Autonomy‐supportive, Web‐based lifestyle modification for cardiometabolic risk in postmenopausal women: Randomized trial
Hye‐Ryoung Kim, Hee‐Seung Kim
Nursing & Health Sciences.2017; 19(4): 509. CrossRef - Web-based interventions for menopause: A systematic integrated literature review
Eun-Ok Im, Yaelim Lee, Eunice Chee, Wonshik Chee
Maturitas.2017; 95: 24. CrossRef - Does nutritional counseling in telemedicine improve treatment outcomes for diabetes? A systematic review and meta-analysis of results from 92 studies
Dejun Su, Chelsea McBride, Junmin Zhou, Megan S Kelley
Journal of Telemedicine and Telecare.2016; 22(6): 333. CrossRef - The influence of intensive lifestyle intervention on patients with isolated impaired fasting glucose: a meta‐analysis
Xiu‐Juan Yang, Shu‐Fang Zou, Yong Xu, Yi Li, Shan‐Shan Yang
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2016; 72(11): 2587. CrossRef - The development of a mobile u-Health program and evaluation for self-diet management for diabetic patients
Yun Ahn, Jeahurn Bae, Hee-Seon Kim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2016; 10(3): 342. CrossRef - Factors Affecting Nurses' Web-based Learning Achievement in Schoolwork
Young Im Kim, Tae Yoon Kim
Korean Journal of Occupational Health Nursing.2013; 22(1): 57. CrossRef - Evaluation of mobile phone and Internet intervention on waist circumference and blood pressure in post-menopausal women with abdominal obesity
Min-Jeong Park, Hee-Seung Kim
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2012; 81(6): 388. CrossRef
- The Impact of Social Support Interventions on Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review
- 1,048 View
- 13 Download
- 9 Crossref

- Influence of Pre-operative Fasting Time on Blood Glucose in Older Patients
- Misuk Hong, Haesang Yoon
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(2):157-164. Published online April 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.2.157
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was performed to identify changes in blood glucose at preoperative fasting time in surgical patients over 60 yr.
Methods Data collection was performed from July, 2008 through July, 2009. Participants consisted of 80 nondiabetic surgical patients. Blood glucose was checked from 3 to 5 times. The 5 times were 2-hr fasting on the pre-operative day (T1, n=80), 8 hr (T2, n=80), 10 hr (T3, n=17), 12 hr (T4, n=34) and 14 hr fasting on the day of the operation (T5, n=29).
Results Of the patients, 27.5% had a blood glucose level of less than 79 mg/dL at T2; 17.6% at T3; 32.4% at T4; and 17.2% at T5. Mean blood glucose levels were 93.8 mg/dL at T1; 88.4 mg/dL at T2; 91.7 mg/dL at T3; 87.4 mg/dL at T4: and 94.1 mg/dL at T5. Blood glucose was the lowest at T2 (
p <.001).Conclusion As 17.6-32.4% of the patients showed the blood glucose level of less than 79 mg/dL at 8-14 hr pre-operative fasting, the authors recommend that surgical patients >60 yr-of-age be observed for hypoglycemia during pre-operative fasting of more than 10 hr and that surgical patients >60 yr-of-age with risks for hypoglycemia be scheduled for operation within 10 hr preoperative fasting.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Postinduction Blood Glucose on Intraoperative Hypothermia
Zhangtian Shen, Kosuke Kuroda, Hiroshi Morimatsu
Medicina.2023; 59(2): 395. CrossRef - Comparison of fasting and non‐fasting patients receiving intravenous (IV) sedation
E. Besi, C. Besi, R. Lees, A. Morrison, N. O'Connor
Oral Surgery.2018; 11(2): 98. CrossRef - A Cross-sectional Observational Analysis of Preoperative Blood Glucose Levels in Nondiabetic Patients presenting for Surgery
Aparna A Nerurkar, Swagat Pattajoshi, Bharati A Tendolkar
Journal of Research & Innovation in Anesthesia.2017; 2(2): 29. CrossRef
- The Effect of Postinduction Blood Glucose on Intraoperative Hypothermia
- 1,396 View
- 9 Download
- 3 Crossref

- The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
- Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(5):720-730. Published online October 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.5.720
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The purpose of this study was to test the effects of tailored diabetic education on blood glucose control and self-care for patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin therapy.
Methods The participants were 60 patients (experimental group: 30, control group: 30) with type 2 diabetes on insulin therapy. The patients were being seen at a university hospital in Seoul, Korea. Group diabetic education and tailored diabetic education were given to the experiment group while group diabetic education only was given to the control group. Data were collected before and three months after the education. χ2 test, t-test, and ANCOVA were used to analyze the data.
Results No significant differences in postprandial (PP2hrs) glucose and HbA1c levels were found between the two groups. Participants in the experiment group showed statistically significant differences in the area of self-glucose test, management of insulin injection, and life style change compared to those in the control group.
Conclusion The results indicate that tailored education for patients with diabetes on insulin therapy improve self-glucose test, management of insulin injection, and life style. Therefore it is suggested that tailored education can be applied in diabetic education to improve self-care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Designing a Self-Care Integrated Protocol and Evaluating its Validity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients; the Case of a Single Subject
Susan Salary, Rasul Roshan, Hamid Pour Sharifi, Hojjatollah Farahani
Health Research Journal.2021; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Self-Management Nursing Intervention for Controlling Glucose among Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Mi-Kyoung Cho, Mi Young Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(23): 12750. CrossRef - Assessment of type 2 diabetes patients’ self-care status learned based on the national diabetes control and prevention program in health centers of a selected city, Iran
Roghayeh Ershad Sarabi, Zahra Mokhtari, Ahmad Naghibzadeh Tahami, Vahid Reza Borhaninejad, Ali Valinejadi
Koomesh journal.2021; 23(4): 465. CrossRef - The Effects of a Self-care Management Program for Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Jung Yoon Kim, Eui-Young Cheon
Journal of Korean Biological Nursing Science.2016; 18(2): 78. CrossRef - Group based diabetes self-management education compared to routine treatment, waiting list control or no intervention for people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Aslak Steinsbekk, Lisbeth Ø. Rygg, Monde Lisulo, Marit By Rise, Atle Fretheim
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Individual and Group Education Programs on Coping and Self-care Behaviors in Cancer Patients
Young Mi Kim, Won Ock Kim, Sang Sook Han
Journal of East-West Nursing Research.2014; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Development of a Comprehensive Self-Management Program Promoting Self Efficacy for Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Ju-Young Park, Il-Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 74. CrossRef - Investigation of Effect on Glycosylated Hemoglobin, Blood Pressure, and Body Mass Index of Diabetes Intensive Education Program in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Emel Beyazıt, Mukadder Mollaoğlu
American Journal of Men's Health.2011; 5(4): 351. CrossRef
- Designing a Self-Care Integrated Protocol and Evaluating its Validity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients; the Case of a Single Subject
- 1,065 View
- 7 Download
- 8 Crossref

- The Effects of a Comprehensive Life Style Modification Program on Glycemic Control and Stress Response in Type 2 Diabetes
- Ji Soo Yoo, Eun Jung Kim, Suk Jeong Lee
- Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2006;36(5):751-760. Published online August 31, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2006.36.5.751
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose This study was to evaluate the effects of a comprehensive life style modification program on glycemic control and stress response in type 2 diabetes.
Method The participants(n=34) with type 2 diabetes were divided into either a usual care(control) or treatment(experimental) group. The experimental group(n=21) received a program that was based on a comprehensive life style modification protocol at a weekly meeting for 16 weeks. They also participated in individually prescribed exercise and diet along with stress management and self monitoring. The participants were followed for 6 months, during which postprandial glucose, HbA1C, and stress response inventory were measured.
Result The experimental group showed a significant lower postprandial glucose and stress response compared to those of the control group. However, there was no significant change in the HbA1C value in either group.
Conclusions These results suggest that a type 2 diabetes comprehensive lifestyle modification program may lead to clinical improvement in glycemic control and reduce the stress response.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Literature Review on Lifestyle Intervention Program for Adults in Korea
Keun-Young Yang
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2023; 24(8): 1815. CrossRef - Gender-dependent Association Between the Risk of Diabetes and the Concentration of Ambient Particulate Matter
Dong-Wook Sohn
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2016; 51(4): 211. CrossRef - Analysis of Reported Study on Intervention Programs for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Gab-Sun Song, Ho-Jin Kim, Jum-Yi Jun
Journal of Digital Convergence.2015; 13(9): 541. CrossRef - The Effect of the Experience of Diabetes Education on Knowledge, Self-Care Behavior and Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Seung Hei Moon, Young Whee Lee, Ok-Kyung Ham, Soo-Hyun Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2014; 20(1): 81. CrossRef - Comparative Study on Self-Care Behavior, Diabetes-related Stress, and Stress Coping among Good, Inadequate, and Poor Glycemic Control Groups
Hye-Yeon Kang, Mee-Ock Gu
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(2): 168. CrossRef - Development of a Comprehensive Self-Management Program Promoting Self Efficacy for Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Ju-Young Park, Il-Sun Ko
Journal of Korean Academy of Fundamentals of Nursing.2012; 19(1): 74. CrossRef - Effect of an abdominal obesity management program on dietary intake, stress index, and waist to hip ratio in abdominally obese women - Focus on comparison of the WHR decrease and WHR increase groups -
Ji Won Lee, Sook Young Yoo, So Young Yang, Hyesook Kim, Seong Kyung Cho
Korean Journal of Nutrition.2012; 45(2): 127. CrossRef - The Effects of Tailored Diabetes Education on Blood Glucose Control and Self-Care
Kyung Sun Hyun, Kwang Mi Kim, Sook Hee Jang
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2009; 39(5): 720. CrossRef - The Effect of a Comprehensive Lifestyle Modification Program on Glycemic Control and Body Composition in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ji-Soo Yoo, Suk-Jeong Lee, Hyun-Chul Lee, Mi-Ja Kim
Asian Nursing Research.2007; 1(2): 106. CrossRef
- Literature Review on Lifestyle Intervention Program for Adults in Korea
- 836 View
- 2 Download
- 9 Crossref

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION

 First
First Prev
Prev