Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Development of a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission after kidney transplantation: a retrospective study
- Hye Jin Chong, Ji-hyun Yeom
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):528-542. Published online November 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25030
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study aimed to develop and validate a machine learning-based prediction model for early hospital readmission (EHR) post-kidney transplantation.
Methods
The study was conducted at the organ transplantation center of a university hospital, utilizing data from 470 kidney transplant recipients. We built and trained four machine learning models and tested them to identify the strongest EHR predictors. Predictive performance was evaluated using confusion matrices and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC AUC).
Results
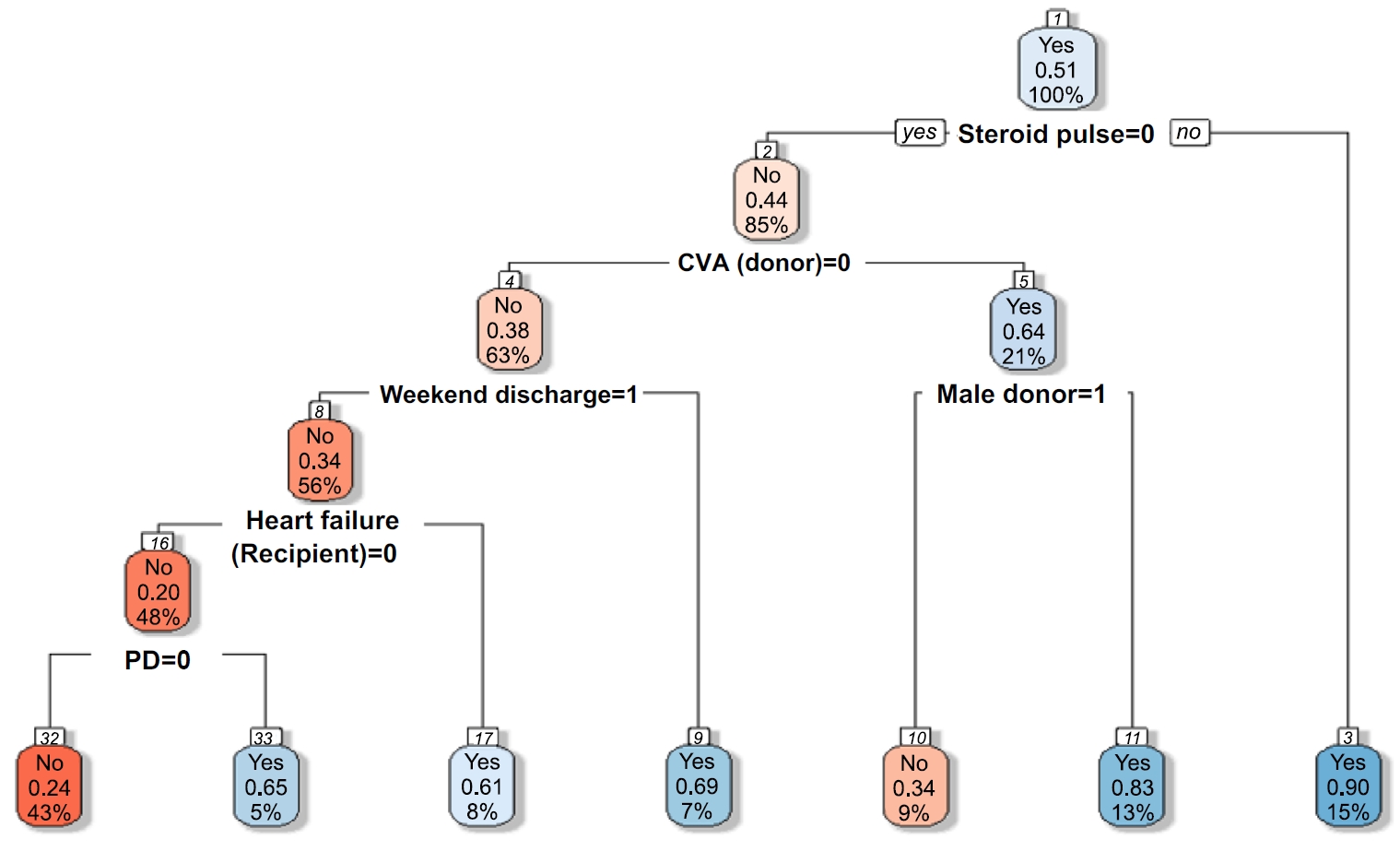
Among the 470 kidney transplant recipients with a mean age of 46.1 ± 12.02 years, 322 (68.5%) were males, and 74 (15.7%) were readmitted within 30 days after kidney transplantation. In total, 241 (51.2%) recipients were found to have experienced EHR after applying the random over-sampling examples method. The random forest model achieved the best performance, with an ROC AUC of .87 (validation set) and .82 (test set). The 15 most important features were steroid pulse therapy (recipient), cerebrovascular accident (recipient), heart failure (recipient), male sex (donor), cardiovascular disease (recipient), weekend discharge (recipient), peritoneal dialysis (recipient) cerebrovascular accident as the cause of brain death (donor), current smoker (recipient), cardiac arrest (donor), previous kidney transplantation (recipient), age (donor), hypertension (donor), male sex (recipient), and dialysis duration (recipient).
Conclusion
Our framework demonstrated strong predictive interpretability. It can support appropriate and effective clinical decision-making by assisting transplant professionals in stratifying recipients based on their risk of EHR. prioritizing post-discharge care and follow-up for high-risk individuals, and allocating targeted interventions such as closer monitoring or education.
- 974 View
- 125 Download

- Implementation of Ontology-based Clinical Decision Support System for Management of Interactions Between Antihypertensive Drugs and Diet
- Jeong-Eun Park, Hwa-Sun Kim, Min-Jung Chang, Hae-Sook Hong
- J Korean Acad Nurs 2014;44(3):294-304. Published online June 30, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2014.44.3.294
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Purpose The influence of dietary composition on blood pressure is an important subject in healthcare. Interactions between antihypertensive drugs and diet (IBADD) is the most important factor in the management of hypertension. It is therefore essential to support healthcare providers' decision making role in active and continuous interaction control in hypertension management. The aim of this study was to implement an ontology-based clinical decision support system (CDSS) for IBADD management (IBADDM). We considered the concepts of antihypertensive drugs and foods, and focused on the interchangeability between the database and the CDSS when providing tailored information.
Methods An ontology-based CDSS for IBADDM was implemented in eight phases: (1) determining the domain and scope of ontology, (2) reviewing existing ontology, (3) extracting and defining the concepts, (4) assigning relationships between concepts, (5) creating a conceptual map with CmapTools, (6) selecting upper ontology, (7) formally representing the ontology with Protégé (ver.4.3), (8) implementing an ontology-based CDSS as a JAVA prototype application.
Results We extracted 5,926 concepts, 15 properties, and formally represented them using Protégé. An ontology-based CDSS for IBADDM was implemented and the evaluation score was 4.60 out of 5.
Conclusion We endeavored to map functions of a CDSS and implement an ontology-based CDSS for IBADDM.
- 739 View
- 4 Download

 KSNS
KSNS
 E-SUBMISSION
E-SUBMISSION
 First
First Prev
Prev