-
Research trends in generative artificial intelligence in nursing: a scoping review
-
Myung Jin Choi, Myoung Hee Seo, Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):468-487. Published online August 5, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25006
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
Generative artificial intelligence (AI) has yet to be comprehensively analyzed in the nursing literature. This study aimed to identify research trends in generative AI within the nursing field through a scoping review and propose strategies for its effective utilization in nursing.
Methods
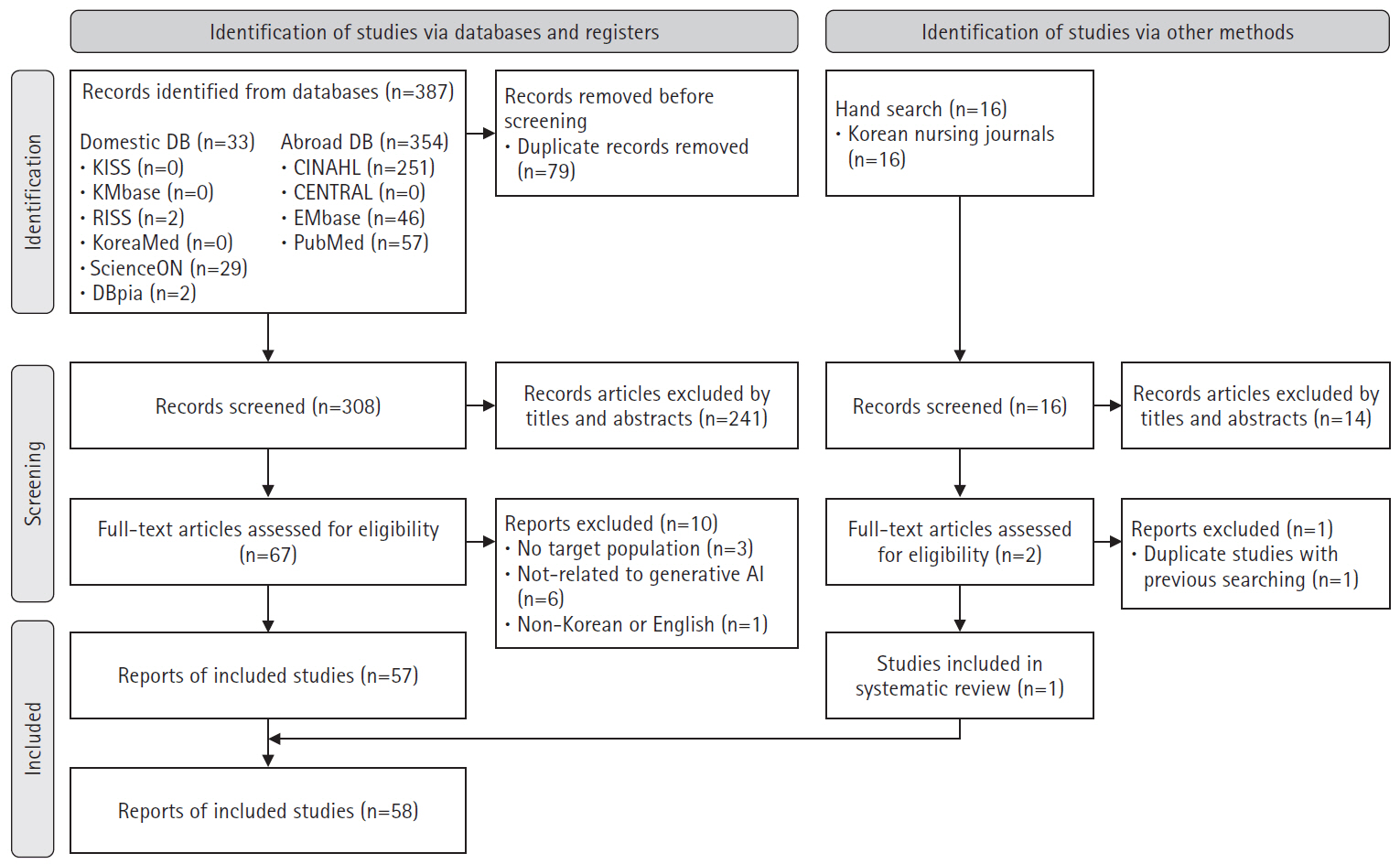
A scoping review was conducted following Arksey and O’Malley’s six-stage framework. The inclusion criteria included: (1) studies conducted in nursing; (2) research related to generative AI; and (3) original research articles, theses, communications, editorials, letters, or commentaries published in academic journals. Database used PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL, CINAHL, KMbase, KoreaMed, KISS, ScienceON, RISS, DBpia, and 27 nursing-specific journals.
Results
In total, 403 studies were initially identified, and 58 were included in the final analysis. In the care domain, strengths included rapid information retrieval and improved nurse-patient communication, while limitations included the irreplaceable human element and low reliability. The administration domain had no relevant studies. In the research domain, generative AI exhibited strengths such as enhanced efficiency in the paper writing process and improved dissemination speed, but its weaknesses included lack of ethical and legal accountability and a risk of inaccurate or biased information. In the education domain, generative AI was effective in saving time in educational design and implementation, as well as supporting content creation, but challenges included algorithmic bias and risks of plagiarism.
Conclusion
This study identified potential benefits and limitations of generative AI across nursing domains. For effective application, it is essential to develop comprehensive guidelines and policies, provide user education and support, and create opportunities for nurses, educators, and students to learn about strengths and risks of generative AI.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nursing Students' Perspectives on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Psychiatric Nursing Education: A Qualitative Meta-Synthesis
Sukyung Son, Eunyoung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2025; 34(Special Is): 9. CrossRef
-
6,007
View
-
427
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
-
Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
Methods
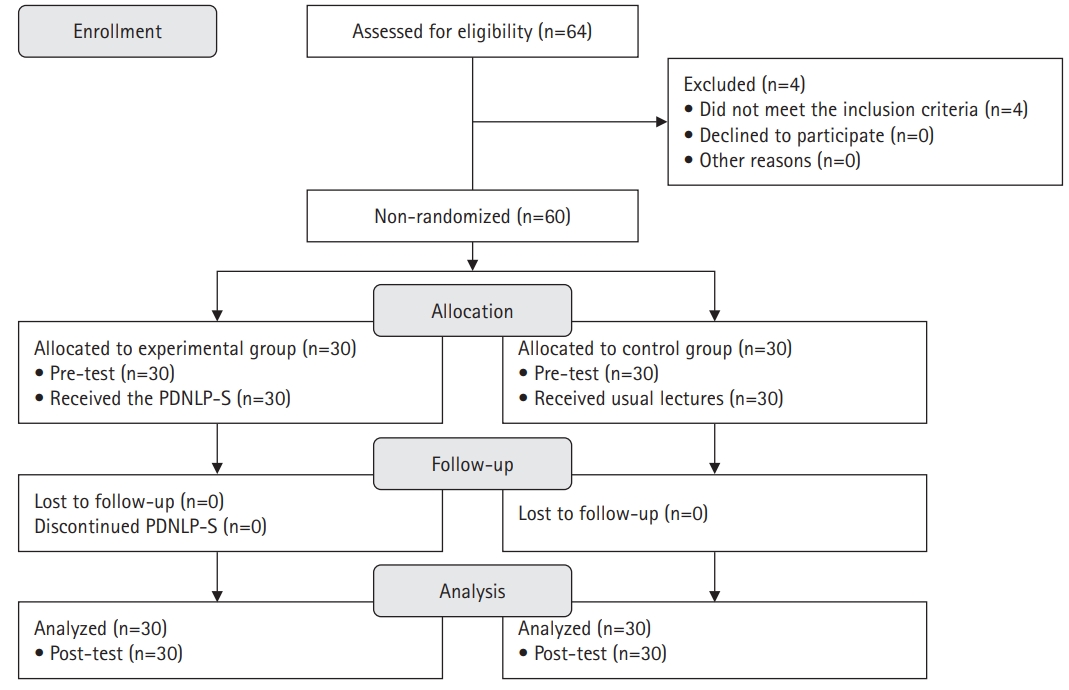
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
-
6,749
View
-
269
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis on the Outcome Variables of Nursing Unit Managers’ Transformational Leadership: Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2020;50(6):757-777. Published online December 31, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.20205
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify the outcome variables of nursing unit managers’ transformational leadership and to test a hypothetical model using meta-analytic path analysis.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines. Data analysis, conducted using R version 3.6.2 software, included 49 studies for the meta-analysis and 119 studies for meta-analytic path analysis.
Results
In the meta-analysis, four out of 32 outcome variables were selected. These four variables were empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment, which showed larger effect sizes than the median and more than five k. The hypothetical model for the meta-analytic path analysis was established by using these four variables and transformational leadership. A total of 22 hypothetical paths including nine direct effects and 13 indirect effects were set and tested. The meta-analytic path analysis showed that transformational leadership had direct effects on the four variables. Finally, eight direct effects, 12 indirect effects, and six mediating effects were statistically significant, and the hypothetical model was verified.
Conclusion
Nursing unit managers can use the transformational leadership to improve empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment of nurses. This study empirically showed the importance of transformational leadership of nursing managers. This finding will be used as evidence to develop strategies for enhancing transformational leadership, empowerment, nursing performance, job satisfaction, and organizational commitment in nursing science and practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Strategies Employed by Nursing Managers Within a Transformational Approach: A Qualitative Study
Gholamhossein Mahmoudirad, Ayob Akbari, Suja P. Davis
Nursing Research and Practice.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Using Behaviour Diagnostics to Identify Enablers and Barriers to Optimise Nurse and Midwife Manager Leadership Time
Julie Considine, Philippa Blencowe, Naida Lumsden, Jordana Schlieff, Judy Currey, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Leadership Development in Undergraduate Nursing Students: A Scoping Review
Patrícia Costa, Joana Pereira Sousa, Tiago Nascimento, Paulo Cruchinho, Elisabete Nunes, Filomena Gaspar, Pedro Lucas
Nursing Reports.2025; 15(5): 160. CrossRef - Effect of Nursing Managers’ Ethical Leadership on Clinical Nurse Empowerment, Performance, and Organizational Commitment
Jihun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Myung Ha Lee
Journal of Nursing Research.2025; 33(4): e400. CrossRef - Transformational Leadership, Psychological Empowerment, and Organizational Citizenship Behaviors among Nursing Workforce: A Single Mediation Analysis
Ibrahim Abdullatif Ibrahim, Ahmed Hashem El-Monshed, Marwan Altheeb, Mohamed Gamal El-Sehrawy, Abdulqadir J. Nashwan
Journal of Nursing Management.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Personal and organisational attributes that support transformational leadership in acute healthcare: scoping review
Julie Considine, Jenny Dempster, Nga Man Wendy Wong, Noelleen Kiprillis, Leanne Boyd
Australian Health Review.2024; 48(3): 274 . CrossRef - Leadership styles and transformational leadership skills among nurse leaders in Qatar, a cross‐sectional study
Amer Al‐Thawabiya, Kalpana Singh, Badriya Abdulla Al‐Lenjawi, Albara Alomari
Nursing Open.2023; 10(6): 3440. CrossRef - Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(5): 479. CrossRef - Patient Safety Management Activities of Korean Nurses: A Meta-Analytic Path Analysis
Seohee Jeong, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2022; 52(4): 363. CrossRef - Nurses' ethical leadership and related outcome variables: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sunmi Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Myoung Hee Seo
Journal of Nursing Management.2022; 30(7): 2308. CrossRef
-
2,557
View
-
116
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
|