-
Multidimensional factors influencing the completion of advance directives among community-dwelling older Koreans
-
Hee-Ju Ji, Soong-Nang Jang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):543-556. Published online November 18, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25098
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
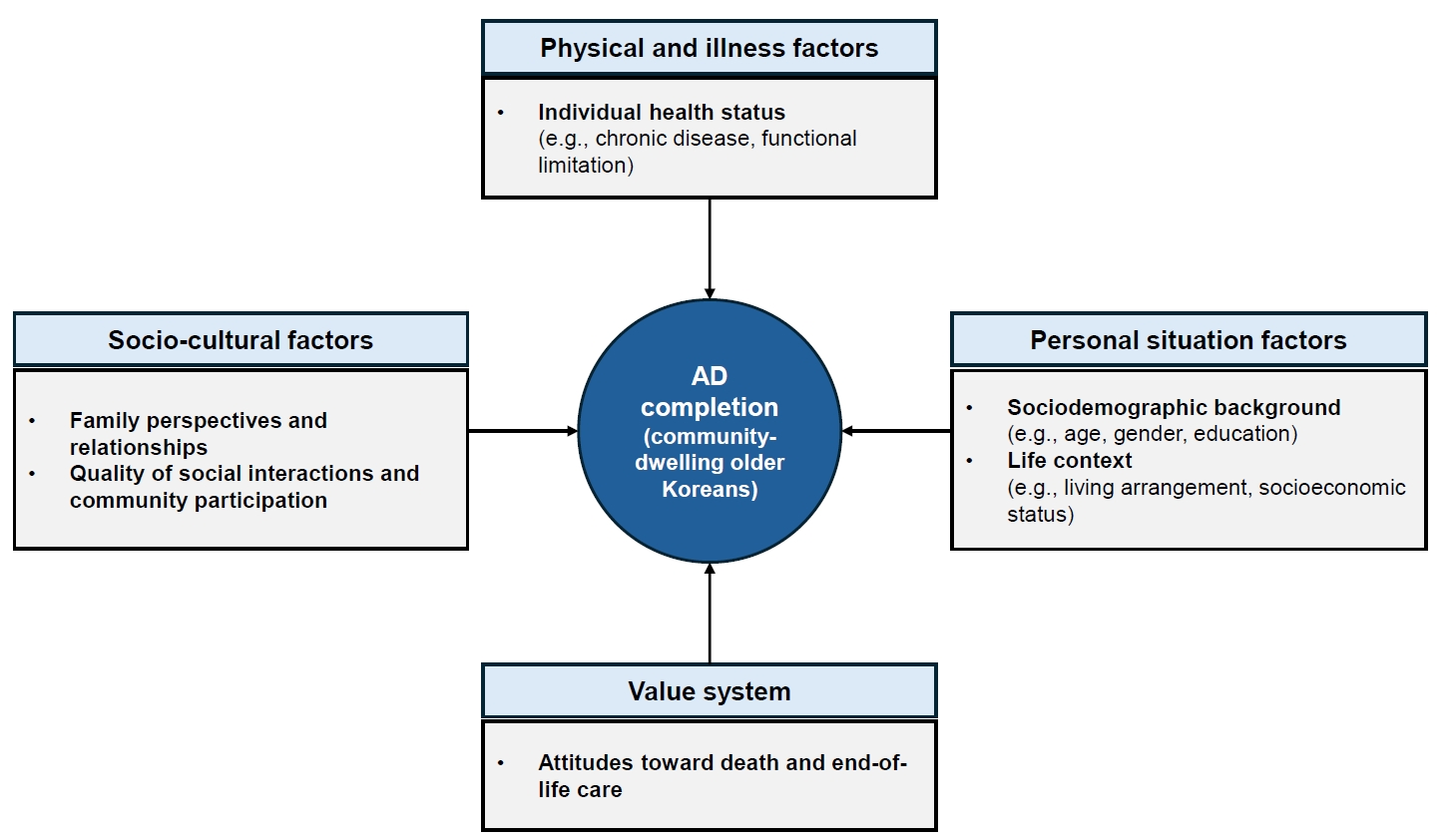
This study aimed to examine the multidimensional factors associated with the completion of advance directives (ADs) among community-dwelling older Koreans, guided by conceptual frameworks developed in Asian contexts.
Methods
Data from the 2023 National Survey of Older Koreans (sixth wave) were analyzed for 9,951 community-dwelling older Koreans aged 65 years or older. Complex sample cross-tabulation and binary logistic regression analyses were conducted.
Results
In total, 11.1% of community-dwelling older Koreans had completed an AD. Significant factors associated with AD completion were identified across four domains—personal situation: age, educational level, religion, and housing preference in the event of poor health; socio-cultural: presence of children, participation in social activities and satisfaction with social relationships; physical and illness: the number of chronic diseases; and value system: awareness of hospice and palliative services, participation in death preparedness education, and documentation of organ donation.
Conclusion
Among older Koreans, AD completion represents more than a documentation process; it reflects a complex decision-making process shaped by their values and life circumstances, underscoring the need for supportive interventions. As the highest AD completion rates are found among older adults, related policies should be aligned with older adult-centered policy frameworks.
-
Willingness to Use and Appropriate Payable Cost for Visiting Nurse Service for the Elderly in the Community
-
Soyoung Seo, Soong-nang Jang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(1):105-119. Published online February 28, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.21193
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to measure willingness to use (WTU) and appropriate payable cost of visiting nurse service for the elderly and explore their impact factors.
Methods
The study included 752 participants selected from data that were completed in 2017 for the elderly aged over 60 nationwide. Logit and Tobit regression analysis were performed to confirm the influencing factors.
Results
The study found that 39.1% of the elderly in the community were WTU the visiting nurse service, and they reported that the cost per visit was 12,650 Korean Won. The factors influencing WTU were having less than moderate subjective health status (OR = 1.63, p = .011), being part of a social participating groups (OR = 1.50, p = .046), or participation in senior health promotion programs (SHPPs) (OR = 1.96, p = .003). The cost was also influenced by less than moderate subjective health status (β = 4.37, p = .021), being part of a social participating groups (β = 4.41, p = .028), or participation in SHPPs (β = 4.87, p = .023). Additionally, elderly people living alone who were used as covariates were highly WTU (OR = 2.20, p = .029).
Conclusion
This study provides evidence to predict demand for visiting nurse service and reflects consumer value in setting the service cost. This is the first study to derive cost from consumers' perspective regarding the service for the elderly. As it is the result of an open-ended survey, follow-up studies are needed to estimate more reliable and reasonable results.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Health and Environmental Monitoring Services for Smart Healthy Cities : Current Practices and Challenges in Local Government Plans
Dong-ah Choi, Yun-jeong Song, Andy Hong
Journal of Korea Planning Association.2024; 59(5): 147. CrossRef
-
2,725
View
-
52
Download
-
1
Crossref
|