-
Impact of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on parental anxiety and depression in severe hypospadias patients in China: a randomized controlled trial
-
Ruijuan Wu, Lucai Jia, Biyu Ding, Ying Li, Yaqing Cao, Zhaojun Shi, Yanfang Yang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):327-341. Published online August 12, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24147
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to explore the effects of an integrated disease-specific nursing care model on alleviating perioperative and post-surgical anxiety and depression in parents of children with severe hypospadias.
Methods
Parents of children with severe hypospadias were recruited and randomly allocated into a control group (n=87), which received standard nursing care, and an intervention group (n=93), which was given an integrated disease-specific nursing intervention in addition to standard care. Parental anxiety and depression were measured using the Self-Rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-Rating Depression Scale (SDS) at admission, discharge, and 6-month follow-up post-surgery.
Results
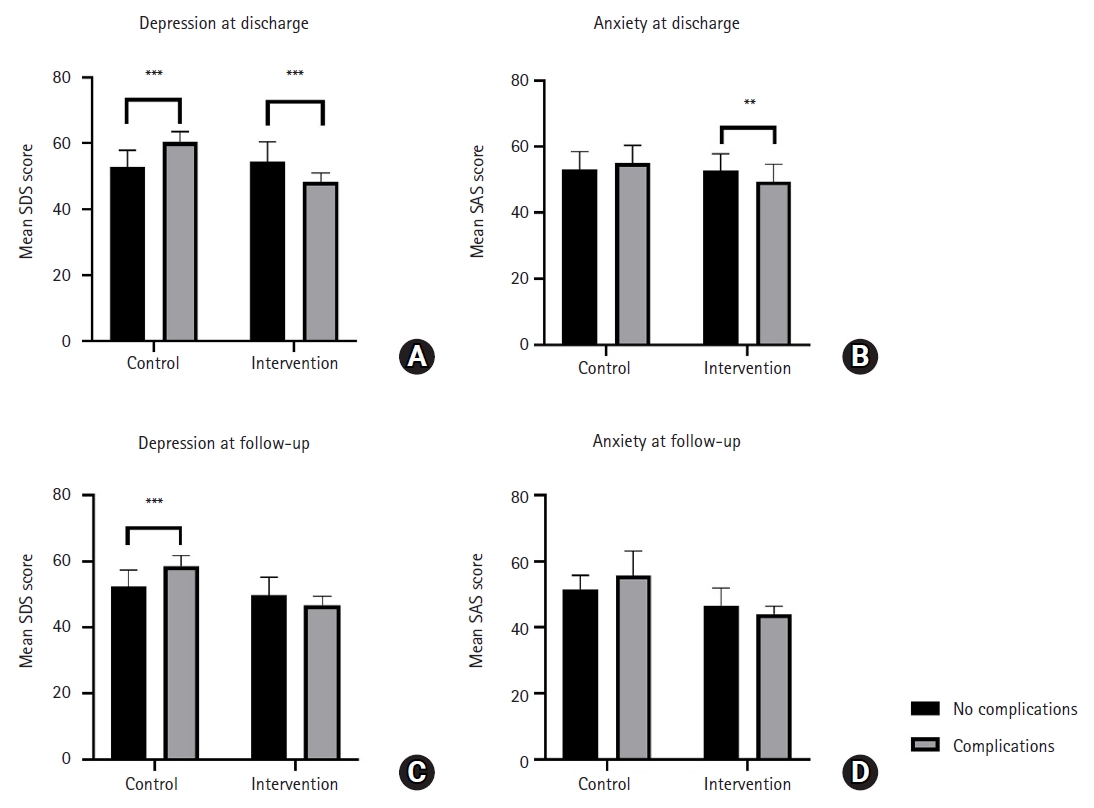
A linear mixed-effects model showed that SAS and SDS scores in the intervention group decreased to a significantly greater extent over time, from admission to follow-up, compared to the control group. Post-hoc analysis showed a trend for increased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up for the control group. Meanwhile, the intervention group exhibited a trend for decreased parental anxiety and depression among patients with complications at discharge and follow-up.
Conclusion
The integrated disease-specific nursing model significantly alleviated parental anxiety and depression over time compared to standard care, highlighting its effectiveness in supporting families of children with severe hypospadias. Notably, the intervention appeared to mitigate the negative emotional impact of postoperative and follow-up complications, suggesting its potential as a targeted approach to improve both emotional well-being and overall care outcomes.
|