-
Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
-
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):454-467. Published online August 4, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25018
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
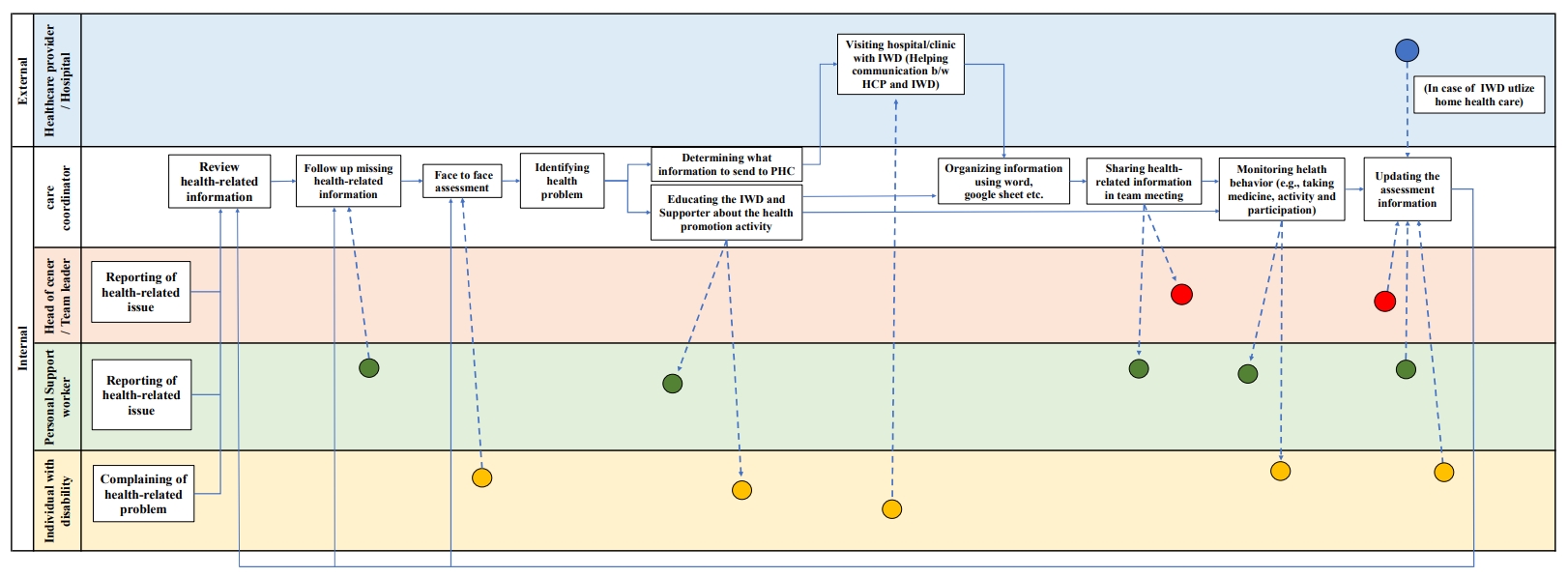
This study conducted a work-system analysis using the Systems Engineering Initiative for Patient Safety (SEIPS) framework to assess the flow of health-related information, and the current status of health management tasks for individuals with disabilities (IWD) in supportive housing.
Methods
This qualitative study utilized focus groups. Participants included a head of supportive housing, a team leader, a care coordinator and three personal support workers for IWD. Semi-structured interviews were guided by the SEIPS framework to explore the components of persons, tasks, tools and technology, organization, and environments.
Results
This study identified five key themes within the five SEIPS components: (1) disparities in role identity and health literacy among staff, (2) challenges in health care support reflecting a person-centered approach, (3) barriers in health-related information exchange and communication tools, (4) needs for organizational strategies or information communication, and (5) needs for integrating health-related information across external healthcare institutions. Additionally, 10 sub-themes were identified.
Conclusions
These findings provide a comprehensive system-wide perspective and offer insights into the systematic approaches needed to improve healthcare processes and structures within disability supportive housing. Specifically, healthcare providers and effective tools for integrating health-related information are identified as critical components.
-
Support Needs for Health Promotion of Community-Dwelling People with Disabilities: Perspectives of Operators Managing Disability Supportive Housing
-
Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Han Nah Park, Sujin Lee, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2024;54(2):211-223. Published online May 31, 2024
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23143
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
Recent studies have focused on policies aimed at supporting the independence of individuals with disabilities in communities. As part of this initiative, supportive housing, integrated care, and residential spaces offer tailored services based on individual needs and autonomy. The attitudes and knowledge of the administrators supporting supportive housing residents regarding health management can influence the well-being of individuals with disabilities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the challenges faced by supporting housing workers in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities.
Methods
In this qualitative study, focus group interviews were conducted in August 2023 with nine administrators working to support housing in Seoul. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the interview data.
Results
The needs and challenges in enhancing the self-management skills of individuals with disabilities were as follows: (1) the complexity of health management challenges, (2) bidirectional strategies for strengthening health management capabilities, and (3) support for systematic health management. Additionally, eight subthemes were derived.
Conclusion
By investigating the difficulties experienced and identifying the necessary support requirements for supportive housing workers, this study seeks to uncover insights and identifies areas for improvement and strategies for health management. This study acknowledges the educational and institutional support necessary to improve the health and quality of life of individuals with disabilities residing in supportive housing.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Work system analysis of health management for individuals with disabilities in supportive housing: a focus group study using the SEIPS framework
Haesun Lee, Hye Jin Nam, Bohye Kim, Ju Young Yoon
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(3): 454. CrossRef - Intention to use a health information platform in supportive housing for people with disabilities: An application of the UTAUT model
Bohye Kim, Hye Jin Nam, Haesun Lee, Hannah Park, Ju Young Yoon, Nicola Diviani
PLOS One.2025; 20(10): e0332072. CrossRef - A preliminary study on the development of a chronic disease self-management curriculum for disability support workers: educational needs analysis
Han Nah PARK, Hye Jin NAM, Haesun LEE MSN, Sujin LEE, Bohye KIM, Ju Young YOON
BMC Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
-
2,260
View
-
100
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Exploring Spatial Variations and Factors associated with Walking Practice in Korea: An Empirical Study based on Geographically Weighted Regression
-
Eunjoo Kim, Yeongseo Lee, Ju Young Yoon
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(4):426-438. Published online August 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23045
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
Walking practice is a representative indicator of the level of physical activity of local residents. Although the world health organization addressed reduction in prevalence of insufficient physical activity as a global target, the rate of walking practice in Korea has not improved and there are large regional disparities. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the spatial variations of walking practice and its associated factors in Korea.
Methods
A secondary analysis was conducted using Community Health Outcome and Health Determinants Database 1.3 from Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A total of 229 districts was included in the analysis. We compared the ordinary least squares (OLS) and the geographically weighted regression (GWR) to explore the associated factors of walking practice. MGWR 2.2.1 software was used to explore the spatial distribution of walking practice and modeling the GWR.
Results
Walking practice had spatial variations across the country. The results showed that the GWR model had better accommodation of spatial autocorrelation than the OLS model. The GWR results indicated that different predictors of walking practice across regions of Korea.
Conclusion
The findings of this study may provide insight to nursing researchers, health professionals, and policy makers in planning health programs to promote walking practices in their respective communities.
-
Development of Outcome Indicators of Urinary Incontinence for Quality Evaluation in Long Term Care Hospitals
-
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2010;40(1):110-118. Published online February 28, 2010
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.1.110
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
To develop outcome indicators of urinary incontinence to measure quality of care in long term care hospitals in Korea.
Methods
The draft indicators of urinary incontinence were developed from a literature review and clinical expert panel. A survey of medical records of 280 patients in 20 hospitals was conducted to test inter-rater reliability. Statistical analysis was done to test risk adjustment criteria, variation between hospitals, and stability of indicators, using assessment data from 77,918 patients in 623 hospitals.
Results
The inter-rater reliability of items was high (Kappa range: 0.66-0.92). Severe cognitive impairment (odds ratio [OR]: 3.15, confidence interval [CI]: 3.03-3.26) and total mobility activities of daily living (ADLs) dependency (OR: 4.85, CI: 4.72-4.98) increased the prevalence of urinary incontinence, thus they proved to be significant criteria to stratify high and low risk groups. The prevalence for low risk showed more substantial variation than the high risk group. The indicators were stable over one month.
Conclusion
This study demonstrated the feasibility of outcome indicators of urinary incontinence. Improving the reliability of the patient assessment tool and refining the indicators through validation study is a must for future study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Development of Health Assessment Tool for Middle-aged Adults in Long-term Care Settings
Yoon-Jin Park, Nam Cho Kim
The Korean Journal of Rehabilitation Nursing.2017; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Factors Associated with the Changes in Activities of Daily Living in Older Adults with Stroke: A Comparison of Home Care and Institutional Care
Woon-Sook Jung, Eun-Shil Yim
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2016; 27(4): 388. CrossRef - Mobility is the key! Trends and associations of common care problems in German long-term care facilities from 2008 to 2012
Nils A. Lahmann, Antje Tannen, Simone Kuntz, Kathrin Raeder, Gabriela Schmitz, Theo Dassen, Jan Kottner
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2015; 52(1): 167. CrossRef - Comparison of Hospital Standardized Mortality Ratio Using National Hospital Discharge Injury Data
Jong-Ho Park, Yoo-Mi Kim, Sung-Soo Kim, Won-Joong Kim, Sung-Hong Kang
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2012; 13(4): 1739. CrossRef - The impact of organizational factors on the urinary incontinence care quality in long-term care hospitals: A longitudinal correlational study
Ju Young Yoon, Ji Yun Lee, Barbara J. Bowers, David R. Zimmerman
International Journal of Nursing Studies.2012; 49(12): 1544. CrossRef
-
951
View
-
1
Download
-
5
Crossref
|