-
Risk factors for the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
-
Hyerim Ji, Sun-Kyung Hwang
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(4):634-650. Published online November 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25072
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to identify risk factors associated with the readmission of patients with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) through a systematic review and meta-analysis.
Methods
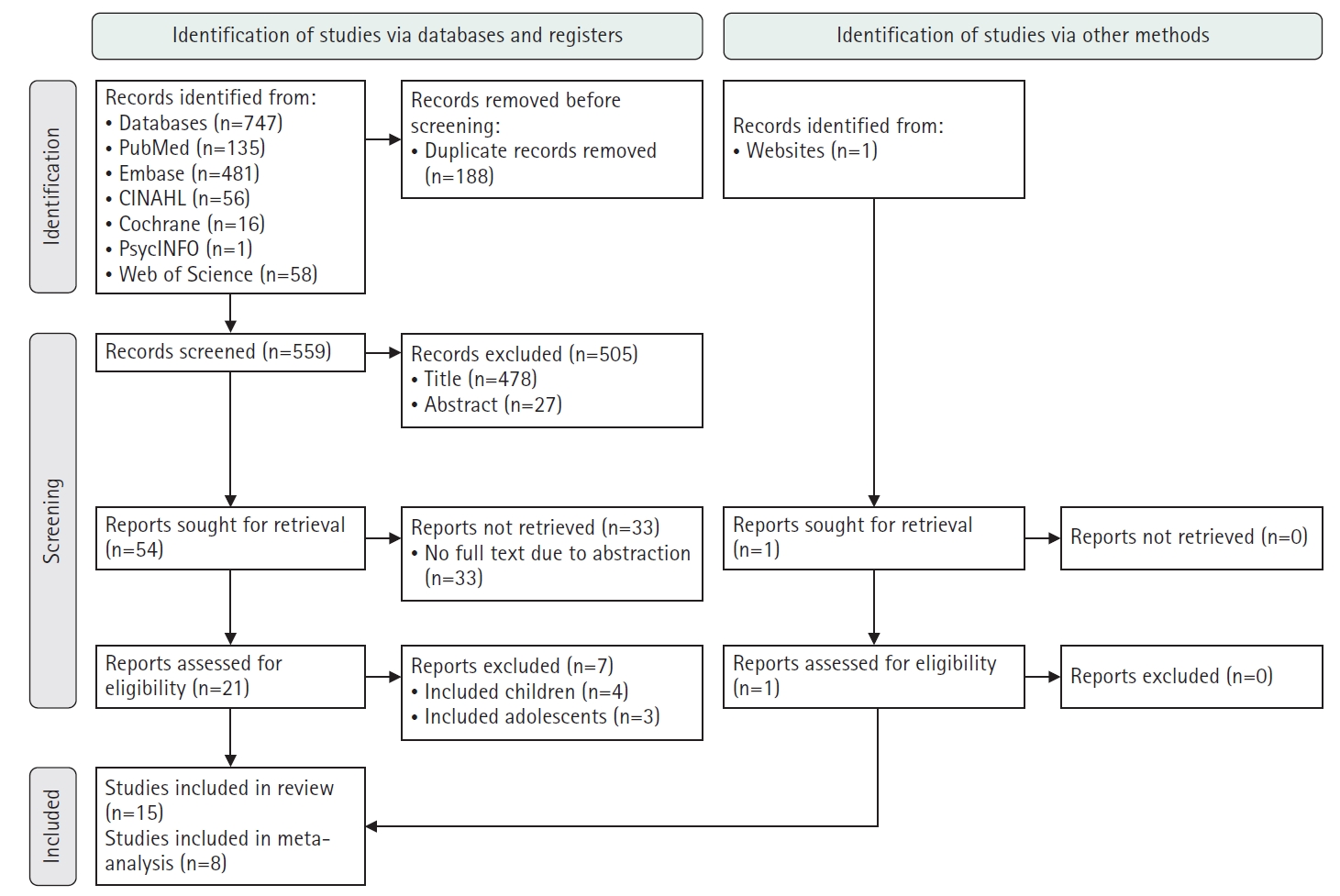
A systematic literature review was conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines. Relevant studies were retrieved from international databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, CINAHL, PsycINFO, and Web of Science) and Korean databases (RISS, KoreaMed, KMbase, KISS, and DBpia). Study quality was evaluated using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model with the Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman adjustment to account for the limited number of studies and heterogeneity.
Results
Fifteen studies were included in the review, and eight were eligible for meta-analysis. From the systematic review, 21 risk factors for DKA readmission were identified and categorized into five domains: demographic, socioeconomic, diabetes-related, comorbidity, and health-behavioral factors. In the meta-analysis, significant risk factors included low income, psychiatric disorders, and discharge against medical advice.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that DKA readmissions result from the complex interplay of multiple clinical and social factors. By identifying these risk factors and suggesting risk-stratification criteria, the findings may support the development of tailored interventions, such as self-management education, integrated mental health care, structured discharge planning, and coordinated post-discharge follow-up.
|