-
Effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea: a quasi-experimental study
-
Sunmi Kim, Young Ju Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(1):137-151. Published online February 25, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.24110
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
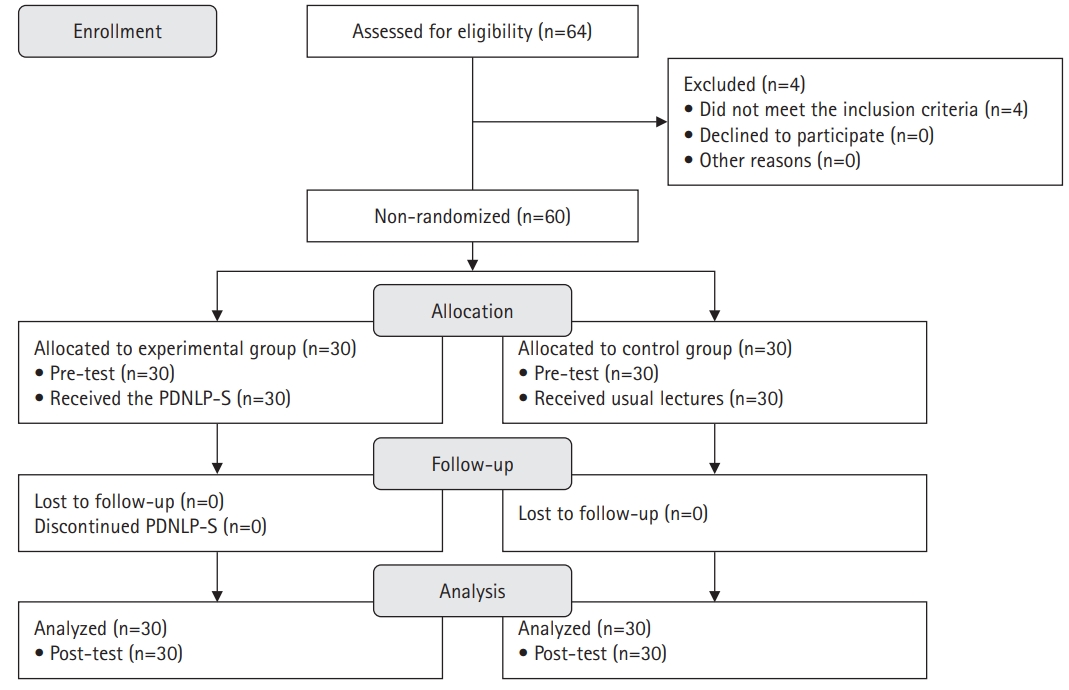
This study investigated the effects of a nursing leadership program on self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, problem-solving abilities, and nursing professionalism among nursing students in South Korea.
Methods
A quasi-experimental study was conducted. The Practice-Driven Nursing Leadership Program for Students (PDNLP-S) was developed based on the ADDIE model (analysis, design, development, implementation, and evaluation). This quasi-experimental study design included 60 nursing students. The experimental group (n=30) participated in the PDNLP-S for 120-minute sessions over 5 weeks, while the control group (n=30) received usual lectures. The PDNLP-S included lectures, discussions, and individual and group activities to cultivate core nursing leadership competencies such as individual growth, collaboration, nursing excellence, creative problem-solving, and influence. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, the Mann-Whitney U-test, and the independent t-test with IBM SPSS Windows ver. 26.0.
Results
The experimental group demonstrated significant improvements in self-leadership (t=3.28, p=.001), interpersonal relationships (t=3.07, p=.002), clinical performance (U=268.50, p=.004), and problem-solving abilities (t=2.20, p=.017) compared to the control group. No significant difference was observed in nursing professionalism (t=0.50, p=.311).
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that the PDNLP-S improved nursing students’ self-leadership, interpersonal relationships, clinical performance, and problem-solving abilities. The PDNLP-S can play a significant role in cultivating future nurse leaders by enhancing these nursing leadership competencies among nursing students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Self-Determination Theory in Return to Work Interventions: A Scoping Review
Kexin Chen, Ling Yang, Jiajia Tu
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2025; Volume 18: 7539. CrossRef
-
6,749
View
-
269
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
-
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(6):635-651. Published online December 31, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.23052
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to identify the main keyword, network structure, and main topics of the national petition related to “nursing” in South Korea.
Methods
Data were gathered from petitions related to the national petition in Korea Blue House related to the topic “nursing” or “nurse” from August 17, 2017, to May 9, 2022. A total of 5,154 petitions were searched, and 995 were selected for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were analyzed using the Netminer 4.5.0 program.
Results
Regarding network characteristics, a density of 0.03, an average degree of 144.483, and an average distance of 1.943 were found. Compared to results of degree centrality and betweenness centrality, keywords such as “work environment,” “nursing university,” “license,” and “education” appeared typically in the eigenvector centrality analysis. Topic modeling derived four topics: (1) “Improving the working environment and dealing with nursing professionals,” (2) “requesting investigation and punishment related to medical accidents,” (3) “requiring clear role regulation and legislation of medical and nonmedical professions,” and (4) “demanding improvement of healthcare-related systems and services.” Conclusion: This is the first study to analyze Korea's national petitions in the field of nursing. This study's results confirmed both the internal needs and external demands for nurses in South Korea. Policies and laws that reflect these results should be developed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - A Study on Internet News for Patient Safety Campaigns: Focusing on Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Sun-Hwa Shin, On-Jeon Baek
Healthcare.2024; 12(19): 1914. CrossRef
-
2,592
View
-
39
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Factors Affecting Radiation Protective Behaviors in Perioperative Nurses Applying the Theory of Planned Behavior: Path Analysis
-
Se Young Jang, Hee Sun Kim, Seok Hee Jeong, Young Man Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2023;53(2):222-235. Published online April 30, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22099
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The aim of this study was to identify the factors explaining protective behaviors against radiation exposure in perioperative nurses based on the theory of planned behavior.
Methods
This was a cross-sectional study. A total of 229 perioperative nurses participated between October 3 and October 20, 2021. Data were analyzed using SPSS/WIN 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 software. The three exogenous variables (attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control) and two endogenous variables (radiation protective intention and radiation protective behaviors) were surveyed.
Results
The hypothetical model fit the data (χ2/df = 1.18, SRMR = .02, TLI = .98, CFI = .99, RMSEA = .03). Radiation protective intention (β = .24, p = .001) and attitude toward radiation protective behaviors (β = .32, p = .002) had direct effects on radiation protective behaviors. Subjective norm (β = .43, p = .002) and perceived behavior control (β = .24, p = .003) had direct effects on radiation protective intention, which explained 38.0% of the variance. Subjective norm (β = .10, p = .001) and perceived behavior control (β = .06, p = .002) had indirect effects via radiation protective intention on radiation protective behaviors. Attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control were the significant factors explaining 49.0% of the variance in radiation protective behaviors.
Conclusion
This study shows that the theory of planned behavior can be used to effectively predict radiation protective behaviors in perioperative nurses. Radiation safety guidelines or education programs to enhance perioperative nurses’ protective behaviors should focus on radiation protective intention, attitude toward radiation protective behaviors, subjective norm, and perceived behavioral control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Health Protective Behavior in Occupational Health Practice: A Concept Analysis
Fenggang Liu, Juanjuan Wang, Weeraporn Suthakorn, Li Liao
Health Science Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors related to preventive measures towards PM2.5 exposure: A systematic review
Jeevan Bhatta, Orapin Laosee, Cheerawit Rattanapan
Global Transitions.2024; 6: 212. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Radiation Protection Behavior of Nurses in Intensive Care Units
Seo Jeong Kim, Yun Hee Kim
Journal of Korean Critical Care Nursing.2024; 17(3): 1. CrossRef - A Review of the Relationship between Health Behaviors and Career Adaptability among University Students
Dongming Jia, Xia Yuan
Journal of Medicine and Health Science.2024; 2(4): 43. CrossRef
-
2,437
View
-
94
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
-
Effects of Leadership Styles of Nursing Managers on Turnover Intention of Hospital Nurses: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
-
Yunjeong Cho, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Young Man Kim
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(5):479-498. Published online October 31, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22039
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
This study aimed to examine effect sizes of leadership styles of nursing managers on turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Methods
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted in accordance with the PRISMA and MOOSE guidelines. Participants were nurses working in hospitals. The intervention involved nursing managers’ leadership styles; the outcome assessed was nurses’ turnover intention. This was an observational study design. Eleven databases were searched to obtain articles published in Korean or English. Of the 14,428 articles reviewed, 21 were included in systematic review and meta-analysis. Comprehensive Meta-Analysis and R software programs were used.
Results
The total effect size r (ESr) was - 0.25 (95% confidence interval: - 0.29 to - 0.20). Effect sizes of each leadership style on turnover intention were as follows: ethical leadership (ESr = - 0.34), transformational leadership (ESr = - 0.28), authentic leadership (ESr = - 0.23), transactional leadership (ESr = - 0.21), and passive avoidant leadership (ESr = 0.13). Ethical leadership was the most effective style in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses.
Conclusion
Positive leadership styles of nurse managers effectively decrease turnover intention of hospital nurses, and negative leadership styles of nurse managers effectively increase turnover intention of hospital nurses. The ethical leadership style is the most effective in decreasing turnover intention of hospital nurses; however, it requires careful interpretation as its effects are reported by only two studies. This study contributes to addressing the high turnover rate of hospital nurses and developing positive leadership styles of nurse managers in hospital settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of organizational communication and grit on turnover intention of rehabilitation hospital nurses: A cross-sectional correlation study
Inji Ha, Heeok Park, Ji Hun Joung
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2025; 27(1): 35. CrossRef - Influence of Leadership Styles on Turnover Intentions in Technology Startups
Sheeza Fayyaz, Saima Majeed
Journal of Professional & Applied Psychology .2025; 6(1): 36. CrossRef - Protecting Workers From Rude Customers to Enhance Organizational Identification in Emotional Labor Environments: A Study With Call Center Agents
Hyojeong Kim, Nagesh N Murthy, Anurag Agarwal, Kwangtae Park
Production and Operations Management.2025; 34(10): 3250. CrossRef - Humanistic nursing care management strategies: from formulation to implementation
Jing Lv, Yajie Su, Hongmei Tang, Xiaolin Jiang, Xiaojuan Chen
Frontiers in Public Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - When Leadership Drives Nurses Away: Empirical Research Qualitative on High Turnover Rates Reasons
Saleem Al‐Rjoub
Nursing Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between different leadership styles of nursing managers and nurses’ turnover intention in hospitals: an integrative review
Alicia Jimenez-Caceres, Anna Agusti-Boada, Conxi Caro-Benito, Olga Monistrol
BMC Nursing.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Structured Subjective Readiness in Situational Leadership: Validating the 4D Model as an Associative Predictor
Dino Giergia, Nikola Drašković, Mario Fraculj
Administrative Sciences.2025; 15(12): 488. CrossRef - Mediating Effect of Leader-Member Exchange on the Ethical Leadership of Nursing Unit Managers and Turnover Intention of Clinical Nurses: A Nationwide Survey using Proportional Quota Sampling
Jihun Kim, Sunmi Kim, Nara Han, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(1): 42. CrossRef - Effects of Resilience, Nursing Managers’ Empowering Leadership on Turnover Intention among New Nurses: Mediating role of Transition Shock
Hyun Jin Jung, Hyun Kyung Kim, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(3): 212. CrossRef - Investigation of the relationship between nurses' perception of toxic leadership and their organizational trust levels and turnover intentions
Sultan Türkmen Keskin, Meltem Özduyan Kiliç
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2024; 80(5): 1859. CrossRef - The structural relationship of job stress, job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and turnover intention among youth sports education leaders in Korea
Myung Kyu Jung, Tae Gyeom Jung, Min Woo Jeon, Ji Hae Lee
Frontiers in Psychology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Patient Safety Management System, Leadership, and Communication Types on Nurse’ Patient Safety Management Activities
Eunji Lee, Haejung Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(4): 367. CrossRef - Nursing-sensitive Indicators in East Asian Hospitals: A Scoping Review
Jae Jun Lee, Won Jin Seo, Dong Ah Park, Hwa Yeong Oh, Seung Eun Lee
Quality Improvement in Health Care.2024; 30(2): 88. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Nurses Turnover in Saudi Arabia: A Systematic Review
Abdulmajeed M. Albalawi, Glezzeelyne P. Pascua, Sameer A. Alsaleh, Walaa Sabry, Sitti Nursa Ahajan, Jeseela Abdulla, Amal Abdulalim, Suad S. Salih, Sulaiman Al Sabei
Nursing Forum.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Nursing Unit Managers’ Authentic Leadership, Transformational Leadership, and Transactional Leadership on Turnover Intention in Advanced Beginner Nurses: Mediation Effects of Positive Psychological Capital
Eun Jeong Kim, Eungyung Kim, Son Ja Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 409. CrossRef - Factors related to the organizational silence of Korean nurses: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Kyungja Kang, Jeong-Hee Kim
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2023; 29(3): 302. CrossRef
-
7,458
View
-
461
Download
-
8
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
Images of Nurses Appeared in Media Reports Before and After Outbreak of COVID-19: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
-
Min Young Park, Seok Hee Jeong, Hee Sun Kim, Eun Jee Lee
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2022;52(3):291-307. Published online June 30, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.22002
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose
The aims of study were to identify the main keywords, the network structure, and the main topics of press articles related to nurses that have appeared in media reports.
Methods
Data were media articles related to the topic “nurse” reported in 16 central media within a one-year period spanning July 1, 2019 to June 30, 2020. Data were collected from the Big Kinds database. A total of 7,800 articles were searched, and 1,038 were used for the final analysis. Text network analysis and topic modeling were performed using NetMiner 4.4.
Results
The number of media reports related to nurses increased by 3.86 times after the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak compared to prior. Pre- and post-COVID-19 network characteristics were density 0.002, 0.001; average degree 4.63, 4.92; and average distance 4.25, 4.01, respectively. Four topics were derived before and after the COVID-19 outbreak, respectively. Pre-COVID-19 example topics are “a nurse who committed suicide because she could not withstand the Taewoom at work” andf “a nurse as a perpetrator of a newborn abuse case,” while post-COVID-19 examples are “a nurse as a victim of COVID-19,” “a nurse working with the support of the people,” and “a nurse as a top contributor and a warrior to protect from COVID-19.” Conclusion: Topic modeling shows that topics become more positive after the COVID-19 outbreak. Individual nurses and nursing organizations should continuously monitor and conduct further research on nurses’ image.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Honoring donors: medical students’ reflections on cadaveric dissection
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Chan Woong Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of the relative importance of key factors in nursing workforce management for pandemic response in general hospitals and long-term care hospitals
Jeong Eun Cha, Eun Kyoung Yun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2025; 55(2): 236. CrossRef - Shifting social perceptions of dietitians in Korea after the legislation of nutrition teachers: a keyword network analysis of unstructured data
Yunkyoung Oh, Eunsil Her
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2025; 30(3): 214. CrossRef - Media Portrayals of Nurse Retention: A Decade of News With Topic Modeling and Network Analysis
Taewha Lee, JooHyun Lee
International Nursing Review.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Voice of Customer Analysis of Nursing Care in a Tertiary Hospital: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Hyunjung Ko, Nara Han, Seulki Jeong, Jeong A Jeong, Hye Ryoung Yun, Eun Sil Kim, Young Jun Jang, Eun Ju Choi, Chun Hoe Lim, Min Hee Jung, Jung Hee Kim, Dong Hyu Cho, Seok Hee Jeong
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2024; 30(5): 529. CrossRef - Impact of a game-based interprofessional education program on medical students’ perceptions: a text network analysis using essays
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Sun Jung Myung, Eun Kyung Eo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of issues related to nursing law: Examination of news articles using topic modeling
JooHyun Lee, Hyoung Eun Chang, Jaehyuk Cho, Seohyun Yoo, Joonseo Hyeon, Andrea Cioffi
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(8): e0308065. CrossRef - Medical students’ perceptions of improving physician satisfaction and patient care: a text network analysis approach
Young Gyu Kwon, Myeong Namgung, Song Hee Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Hyo Hyun Yoo, Chan Woong Kim
BMC Medical Education.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Socialisation of children to nurse and nursing images: A Goffman‐inspired thematic analysis of children's picture books in a Swedish context
Stinne Glasdam, Hongxuan Xu, Sigrid Stjernswärd
Nursing Inquiry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Agendas on Nursing in South Korea Media: Natural Language Processing and Network Analysis of News From 2005 to 2022
Daemin Park, Dasom Kim, Ah-hyun Park
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e50518. CrossRef - Research trends over 10 years (2010-2021) in infant and toddler rearing behavior by family caregivers in South Korea: text network and topic modeling
In-Hye Song, Kyung-Ah Kang
Child Health Nursing Research.2023; 29(3): 182. CrossRef - The Analysis of Research Trends and Public Awareness of Smart Farms using Text Mining
Sung-Ho Kil, Hye-Mi Park, Eunseok Lee, Jin-Young Kim, Ji-Woo Kim
Journal of People, Plants, and Environment.2023; 26(1): 9. CrossRef - National Petition Analysis Related to Nursing: Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
HyunJung Ko, Seok Hee Jeong, Eun Jee Lee, Hee Sun Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing.2023; 53(6): 635. CrossRef - An analysis of Research Published in the Journal of Korean Academy of Psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing from 2013 to 2022 using Text Network Analysis and Topic Modeling
Eun Jo Kim, Kuem-Sun Han
Journal of Korean Academy of psychiatric and Mental Health Nursing.2023; 32(2): 188. CrossRef - Chronological Changes in the Portrayal of Korean Nurses in TV Documentaries
Eunjin Kim, Gumhee Baek, Aram Cho, Mijin Byun
Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing Administration.2023; 29(4): 341. CrossRef - A topic modeling analysis for Korean online newspapers: Focusing on the social perceptions of nurses during the COVID-19 epidemic period
Soo Jung Chang, Sunah Park, Yedong Son
The Journal of Korean Academic Society of Nursing Education.2022; 28(4): 444. CrossRef
-
3,260
View
-
49
Download
-
10
Web of Science
-
16
Crossref
-
An Explanatory Model for Sleep Disorders in People with Cancer
-
Hee Sun Kim, Eui Geum Oh
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2011;41(4):460-470. Published online August 31, 2011
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.460
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The aim of this study was to develop and test an explanatory model for sleep disorders in people with cancer. A hypothetical model was constructed on the basis of a review of previous studies, literature, and sleep models, and 10 latent variables were used to construct a hypothetical model.
Methods
Data were collected from April 19 to June 25, 2010, using self-report questionnaires. The sample was 291 outpatients with cancer who visited the oncology cancer center at a university hospital. Collected data were analyzed using SPSS Win 15.0 program for descriptive statistics and correlation analysis and AMOS 7.0 program for covariance structural analysis.
Results
It appeared that overall fit index was good as χ2/df=1.162, GFI=.969, AGFI=.944, SRMR=.052, NFI=.881, NNFI=.969, CFI=.980, RMSEA=.024, CN=337 in the modified model. The explanatory power of this model for sleep disorders in people with cancer was 62%. Further, sleep disorders were influenced directly by cancer symptom experience, dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes about sleep, and past sleep pattern.
Conclusion
Findings suggest that nurses should assess past sleep pattern and consider the development of a comprehensive nursing intervention program to minimize the cancer symptom experience, dysfunctional beliefs and attitudes about sleep, and thus, reduce sleep disorders in people with cancer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Effects of Symptoms and Patient Activation on Sleep Disturbance in Patients with Acute Leukemia Undergoing Chemotherapy
Suna Lee, Eunjung Ryu
Asian Oncology Nursing.2021; 21(3): 173. CrossRef - Sleep Pattern and Factors Causing Sleep Disturbance in Adolescents with Cancer before and after Hospital Admission
Jin Jung, Eun-Hye Lee, You-Jin Yang, Bo-Yoon Jang
Asian Oncology Nursing.2017; 17(3): 143. CrossRef - Symptom Clusters in Korean Patients With Metastatic Cancer Undergoing Palliative Chemotherapy
Hee Sun Kim, Miok Kim, Seon Heui Lee
Journal of Hospice & Palliative Nursing.2016; 18(4): 292. CrossRef - Predictors of symptom experience in Korean patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy
Hee Sun Kim, Eui Geum Oh, Hyangkyu Lee, Soo Hyun Kim, Hyun Kyung Kim
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2015; 19(6): 644. CrossRef - Related Factors to Quality of Life among Hospitalized Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Ji Yeon Jeong, Hyang Sook So, Ji Eun Hong, Myeong Jeong Chae, Geunhye Han
Asian Oncology Nursing.2012; 12(1): 84. CrossRef
-
897
View
-
6
Download
-
5
Crossref
-
Identification and Validation of Symptom Clusters in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Myung Sook Cho, In Gak Kwon, Hee Sun Kim, Kyunghee Kim, Eunjung Ryu
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2009;39(5):683-692. Published online October 31, 2009
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2009.39.5.683
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
-
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to identify cancer-related symptom clusters and to validate the conceptual meanings of the revealed symptom clusters in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Methods
This study was a cross-sectional survey and methodological study. Patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (N=194) were recruited from a medical center in Seoul. The 20-item Symptom Checklist was used to assess patients' symptom severity. Selected symptoms were factored using principal-axis factoring with varimax rotation. To validate the revealed symptom clusters, the statistical differences were analyzed by status of patients' performance status, Child-Pugh classification, and mood state among symptom clusters.
Results
Fatigue was the most prevalent symptom (97.4%), followed by lack of energy and stomach discomfort. Patients' symptom severity ratings fit a four-factor solution that explained 61.04% of the variance. These four factors were named pain-appetite cluster, fatigue cluster, itching-constipation cluster, and gastrointestinal cluster. The revealed symptom clusters were significantly different for patient performance status (ECOG-PSR), Child-Pugh class, anxiety, and depression.
Conclusion
Knowing these symptom clusters may help nurses to understand reasonable mechanisms for the aggregation of symptoms. Efficient symptom management of disease-related and treatment-related symptoms is critical in promoting physical and emotional status in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Symptoms and symptom clusters in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and commonly used instruments: An integrated review
Thitiporn Pathomjaruwat, Yaowarat Matchim, Jane M. Armer
International Journal of Nursing Sciences.2024; 11(1): 66. CrossRef - Symptom clusters and network analysis of patients with intermediate and advanced liver cancer treated with targeted immunotherapy
Mei Chen, Shan Li, Guangzhi Jin, Rui Li, Zhi Qi, Yalun He
Supportive Care in Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anxiety and depression prevalence in digestive cancers: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Mohammad Zamani, Shaghayegh Alizadeh-Tabari
BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care.2023; 13(e2): e235. CrossRef - Symptom Clusters in Patients with Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma Receiving Chemotherapy
YuJeong Kim, In Gak Kwon
Asian Oncology Nursing.2022; 22(2): 93. CrossRef - Symptom clusters of ovarian cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy, and their emotional status and quality of life
Kyung-Hye Hwang, Ok-Hee Cho, Yang-Sook Yoo
European Journal of Oncology Nursing.2016; 21: 215. CrossRef - Effects of Acupressure on Fatigue and Depression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Treated with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization: A Quasi-Experimental Study
Su-Chen Lan, Yueh-E Lin, Shu-Ching Chen, Yu-Fang Lin, Yu-Jen Wang
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Quality of Life in Colorectal Cancer Patients according to the Severity of Symptom Clusters Classification
Gyeonghui Jeong, Kyunghee Kim, Yeunhee Kwak
Asian Oncology Nursing.2014; 14(2): 74. CrossRef - Development and Evaluation of Learning Program for Oncology Unit-based Core Nursing Practice - Outcomes based Cancer Patients Pain Management Learning Program -
Yeon Hee Kim, Young Sun Jung, Soon Haeng Lee, Kyoung Ok Kim, Young Nam Jeong, Hye Ryun Jung, Kyunghee Kim
Asian Oncology Nursing.2013; 13(4): 231. CrossRef - Symptom Clusters and Quality of Life in Korean Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Eunjung Ryu, Kyunghee Kim, Myung Sook Cho, In Gak Kwon, Hee Sun Kim, Mei R. Fu
Cancer Nursing.2010; 33(1): 3. CrossRef
-
1,095
View
-
18
Download
-
9
Crossref
|