-
Development of a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults: a psychometric validation study
-
Dayeon Lee, Sunghee H Tak
-
J Korean Acad Nurs 2025;55(3):413-424. Published online August 21, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.25036
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF ePub ePub
- Purpose
This study aimed to develop a scale to measure fear of falling in older adults and to validate its reliability and validity.
Methods
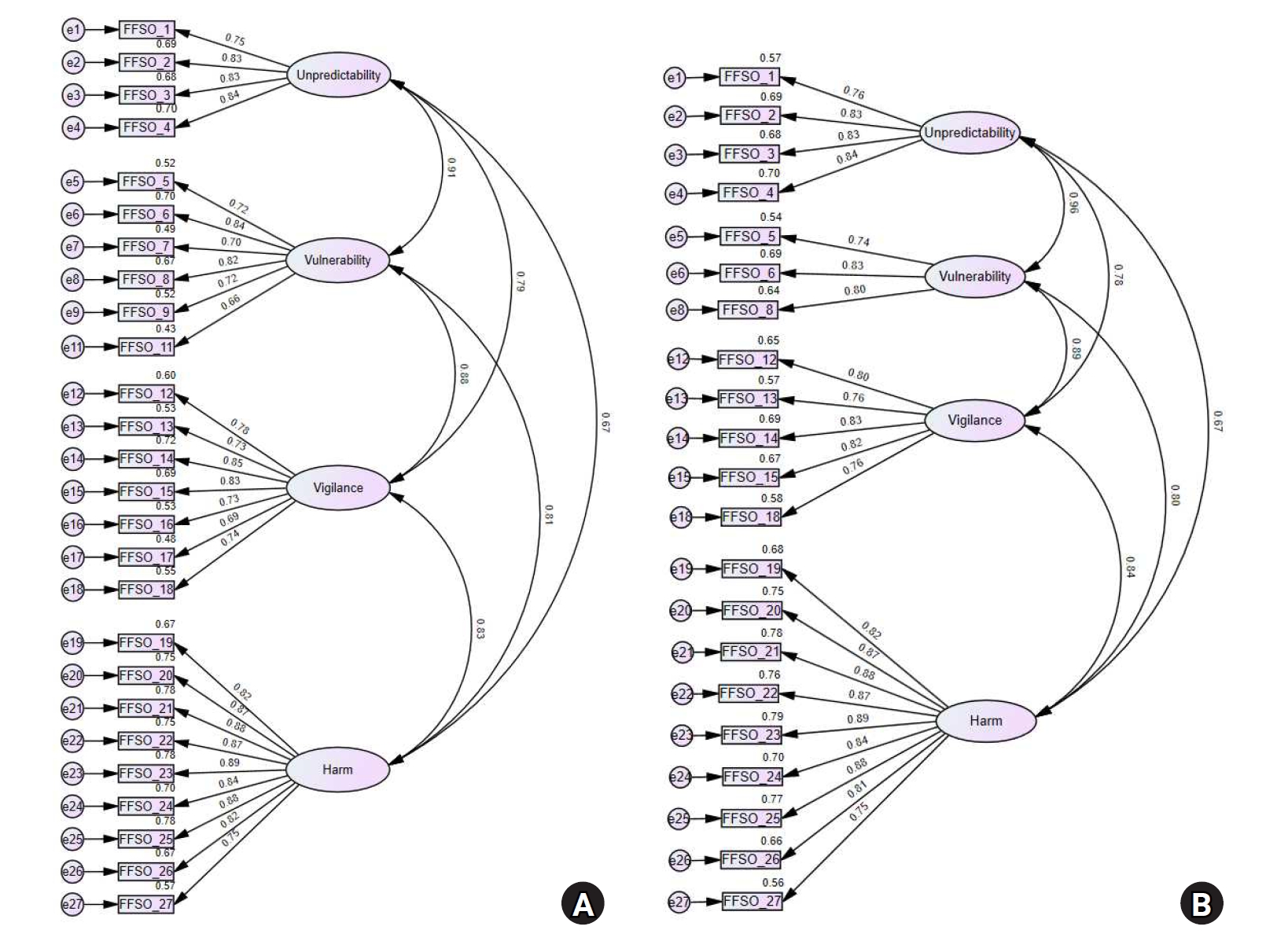
In total, 31 initial items were developed by referring to expressions from previous studies and items from existing instruments. After verifying content validity through expert evaluation, the remaining 27 items were used to construct a survey. Data from 252 participants recruited at three senior welfare centers in the metropolitan area were analyzed to examine item analysis, construct validity, convergent validity, discriminant validity, and reliability. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was conducted to test construct validity. The correlation with the Korean version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International (KFES-I) was used to assess convergent validity. Cronbach’s alpha was calculated to determine reliability.
Results
The final instrument consisted of 21 items. CFA confirmed acceptable model fit. Convergent validity was also acceptable and discriminant validity was partially supported. Correlations with the KFES-I ranged from .54 to .63. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficients for the total score and all factors ranged from .84 to .97.
Conclusion
The Fear of Falling Scale for Older Adults developed in this study is a validated tool capable of measuring various dimensions of fear of falling. It provides a foundation for accurately assessing fear of falling in older adults and addressing its specific aspects.
|